This document discusses various topics related to data transmission including:
- Data transmission involves transferring electromagnetic signals over a physical communication channel like copper wires or wireless channels.
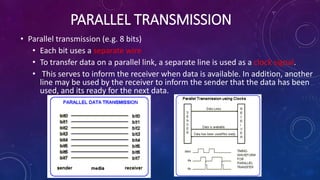
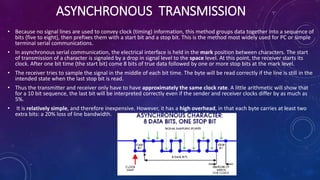
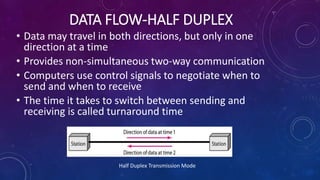
- Transmission modes can be parallel (multiple bits sent at once) or serial (one bit at a time). Serial transmission is further divided into asynchronous and synchronous types.
- Asynchronous transmission groups data into start-stop bit sequences while synchronous transmission uses device-generated clocks for synchronization.