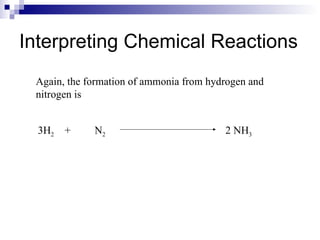
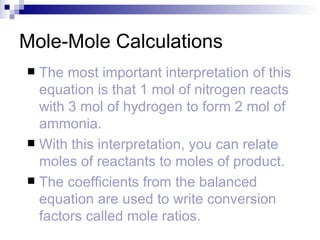
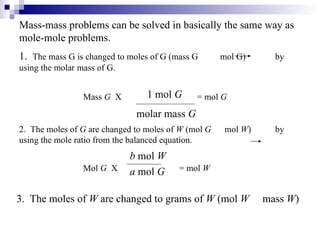
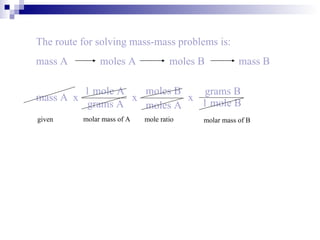
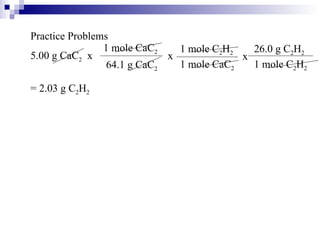
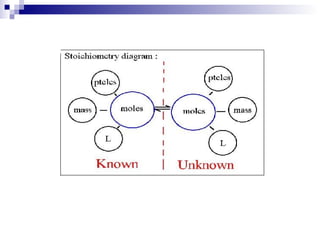
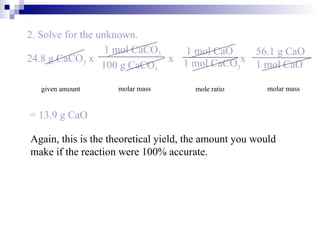
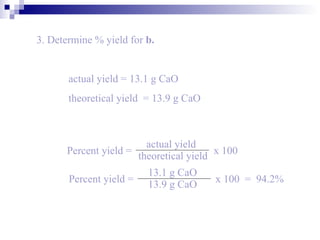
This document discusses stoichiometry, which is the calculation of quantities in chemical reactions. It explains that quantities of reactants and products can be determined from a balanced chemical equation. It also discusses how to perform mole-mole, mass-mole, mass-mass, and other stoichiometric calculations using conversion factors derived from balanced equations. Percent yield is defined as the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield expressed as a percentage.