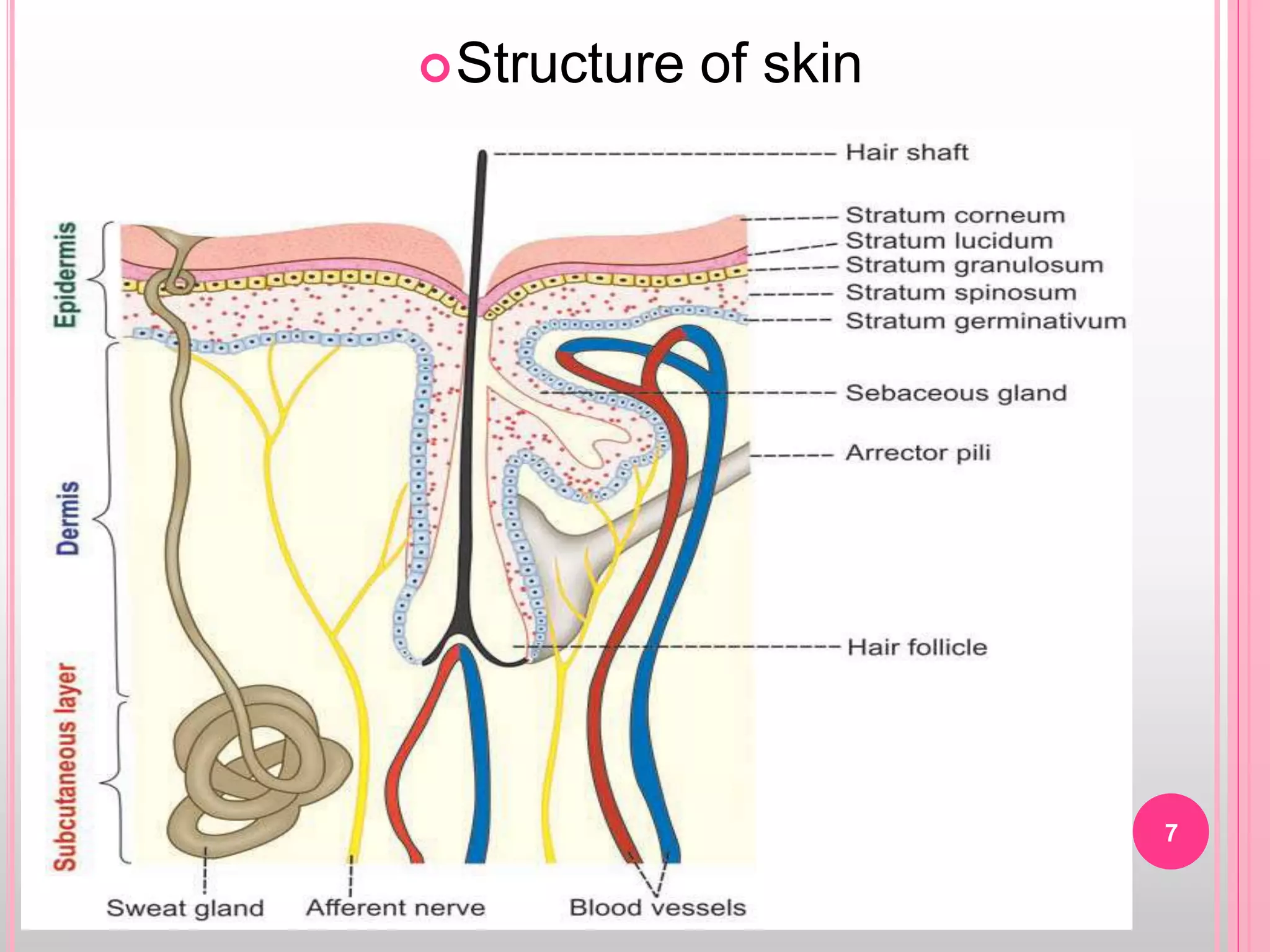
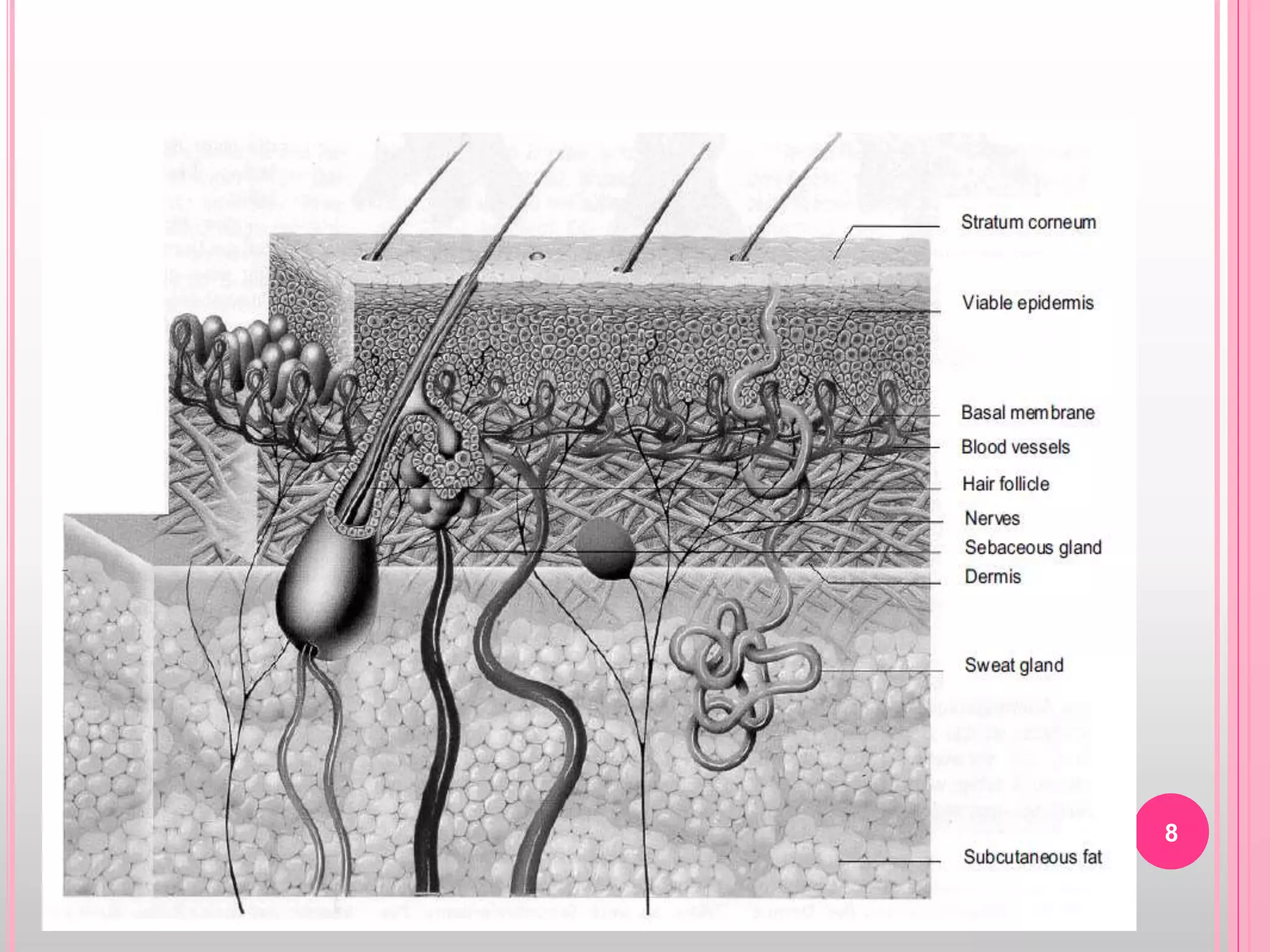
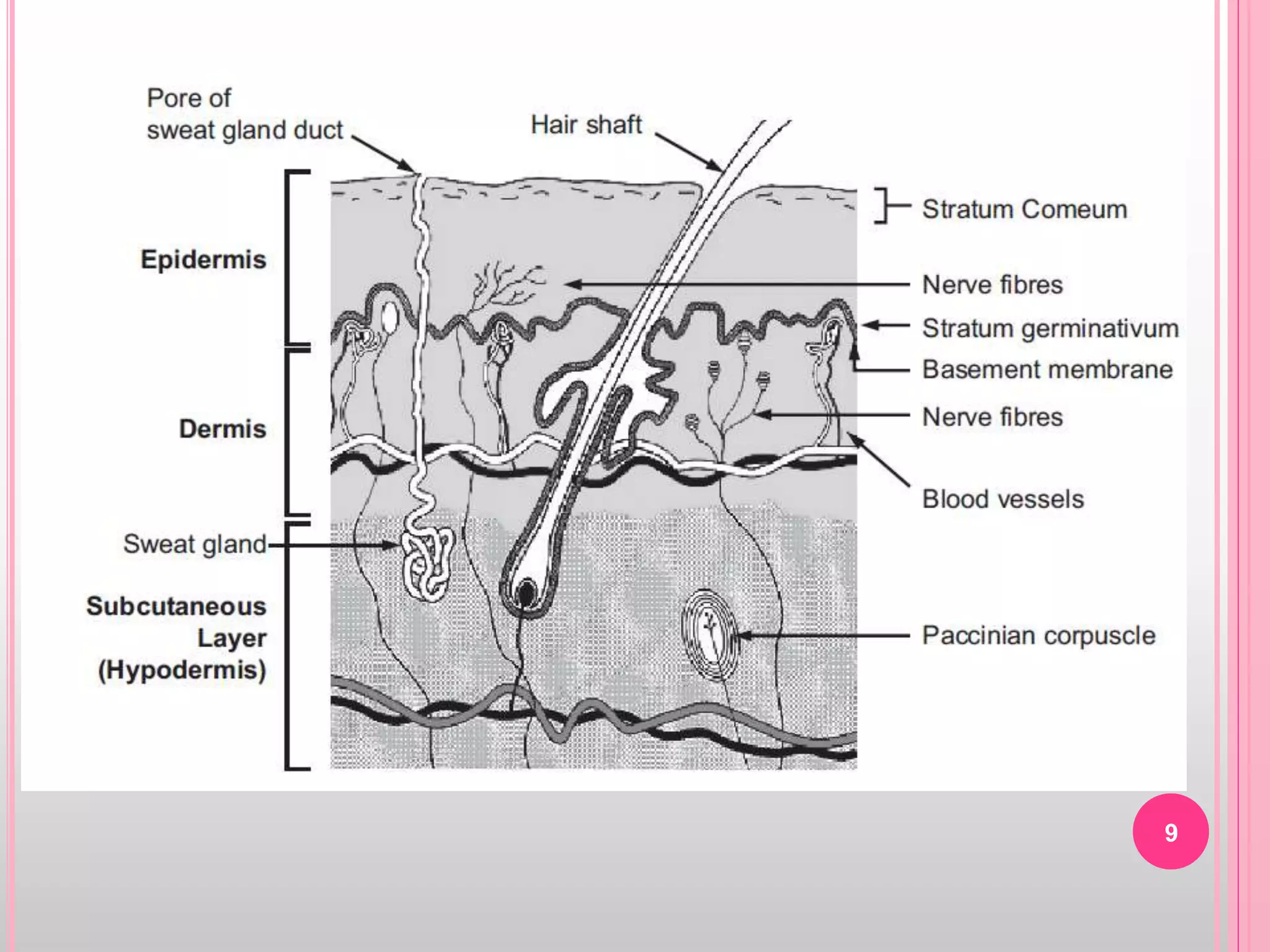
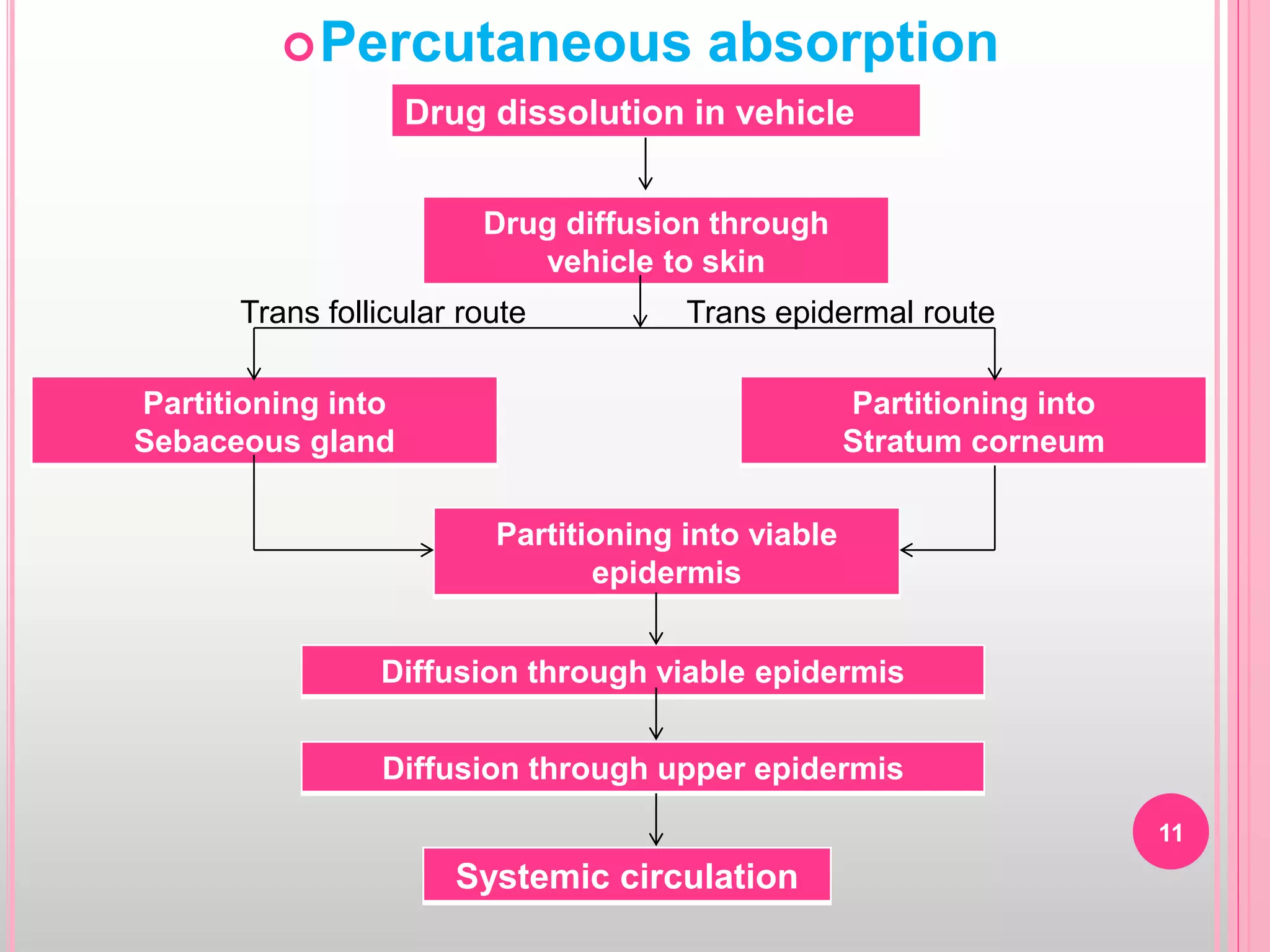
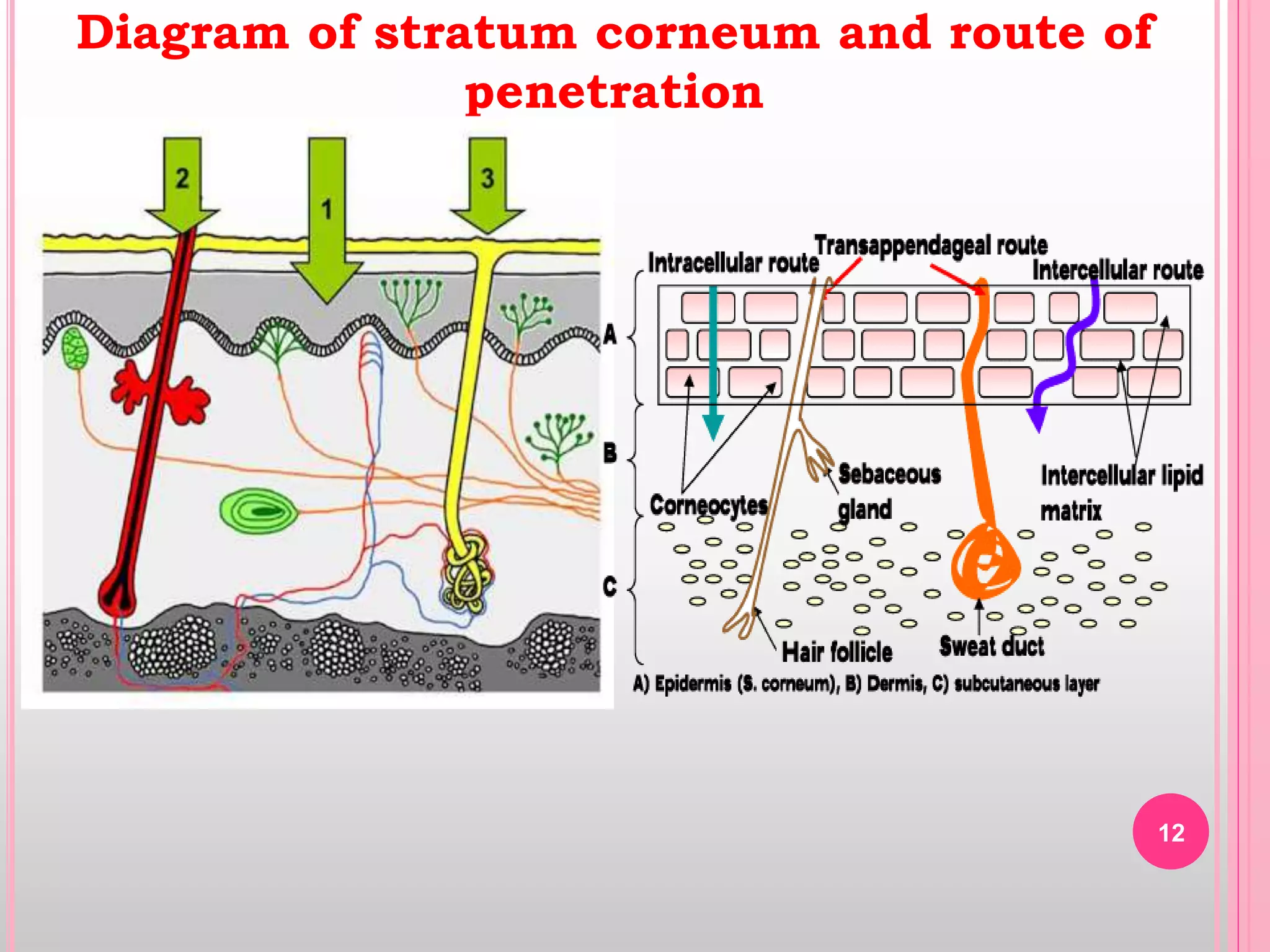
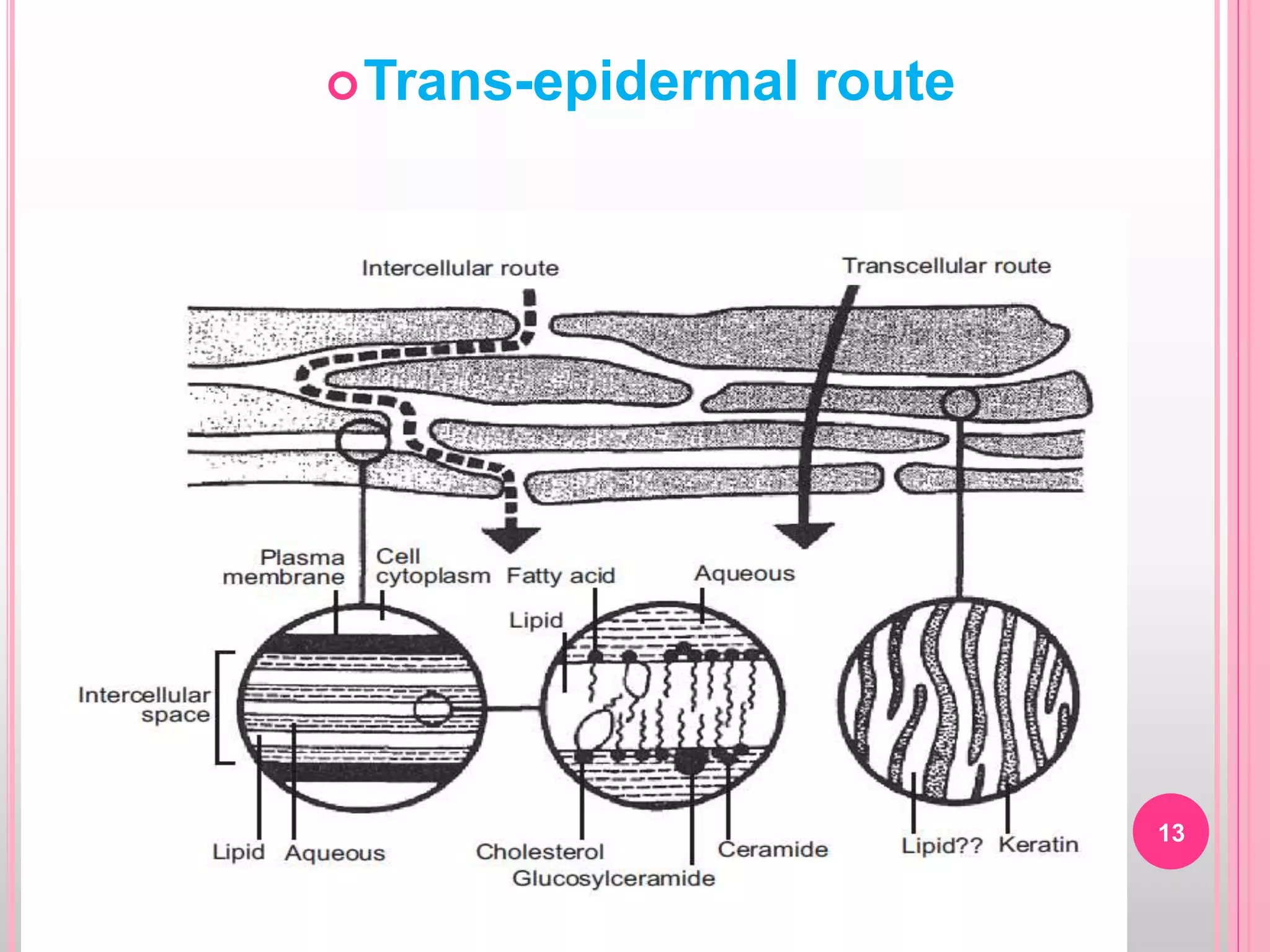
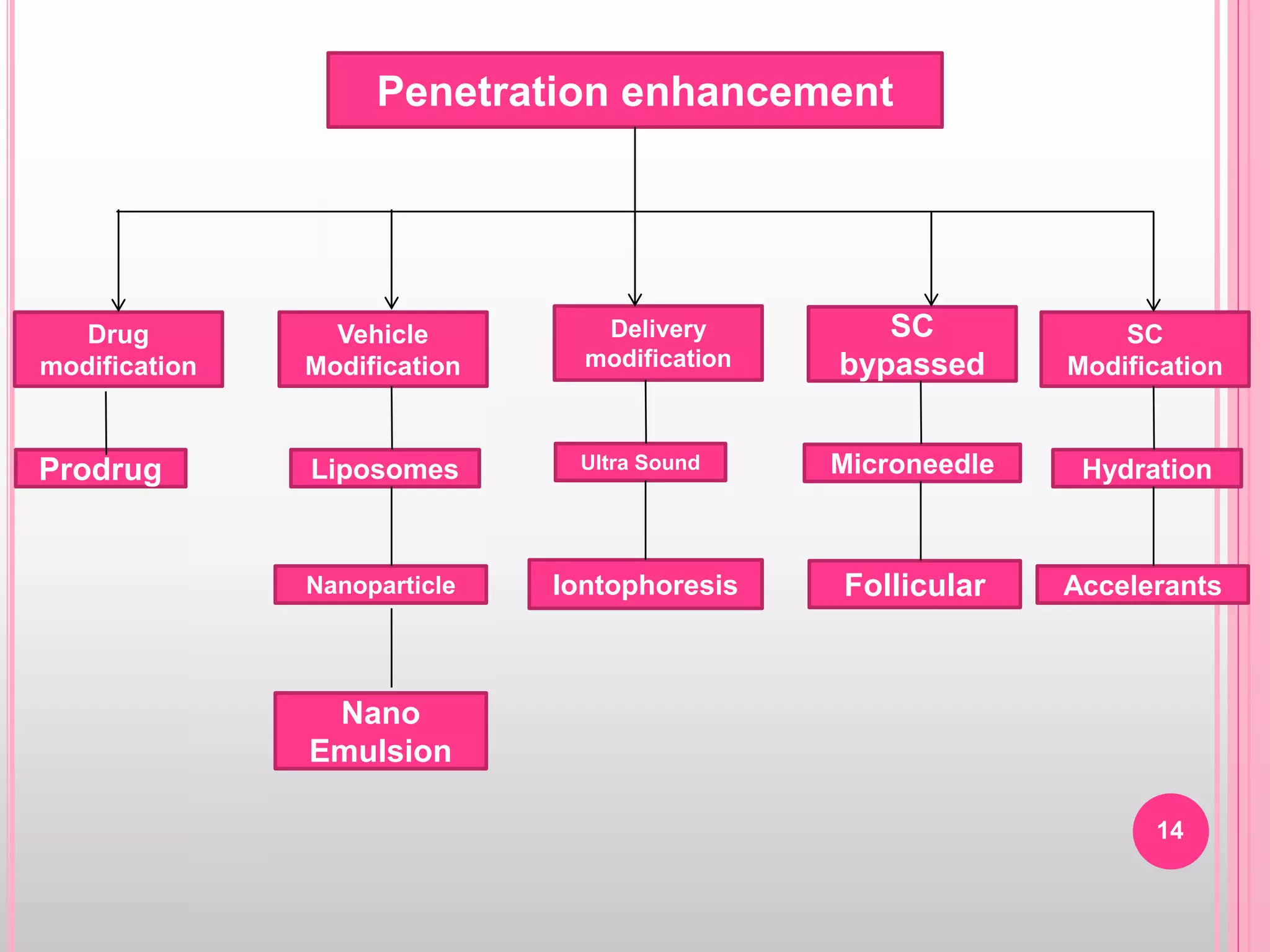
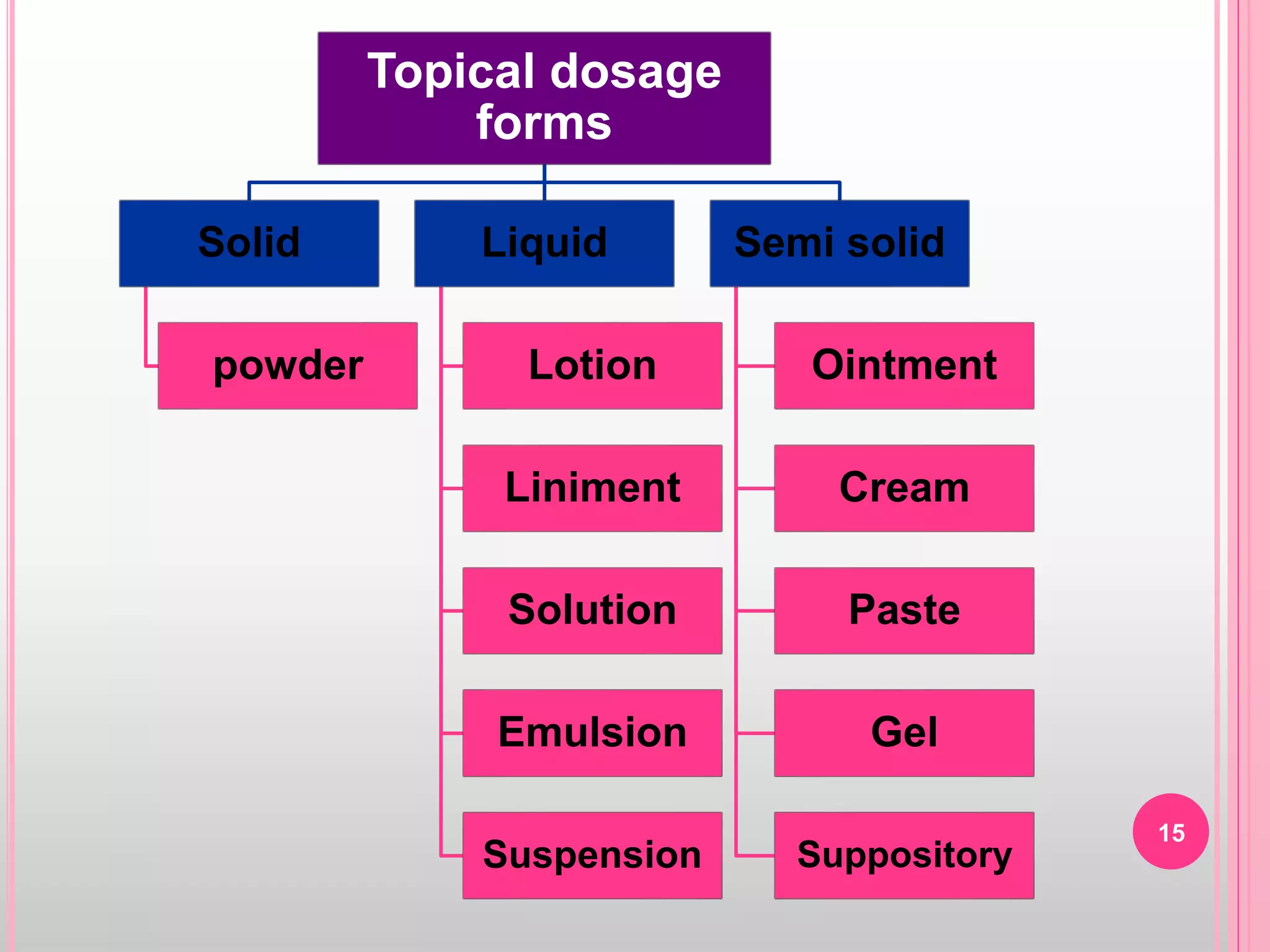
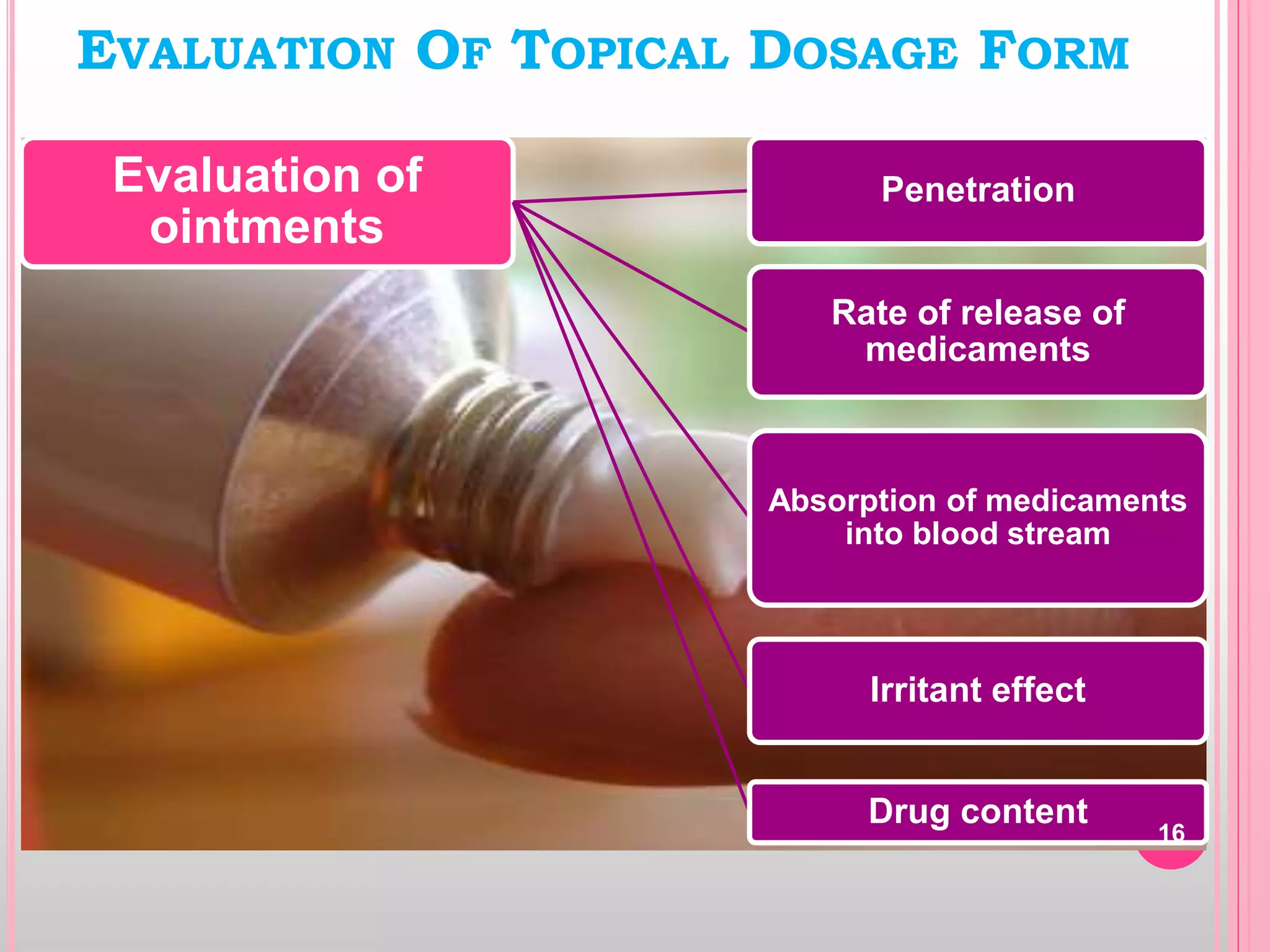
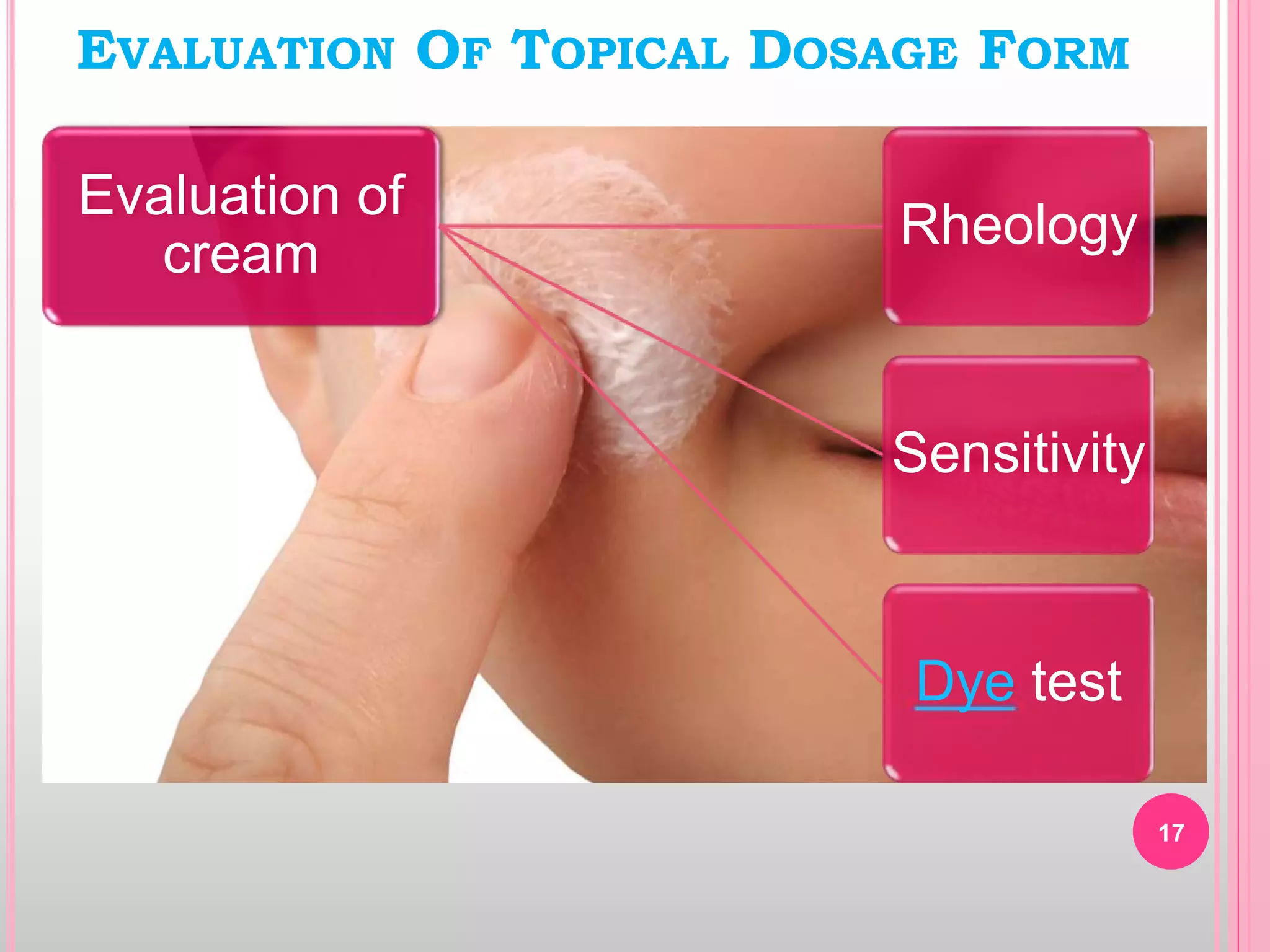
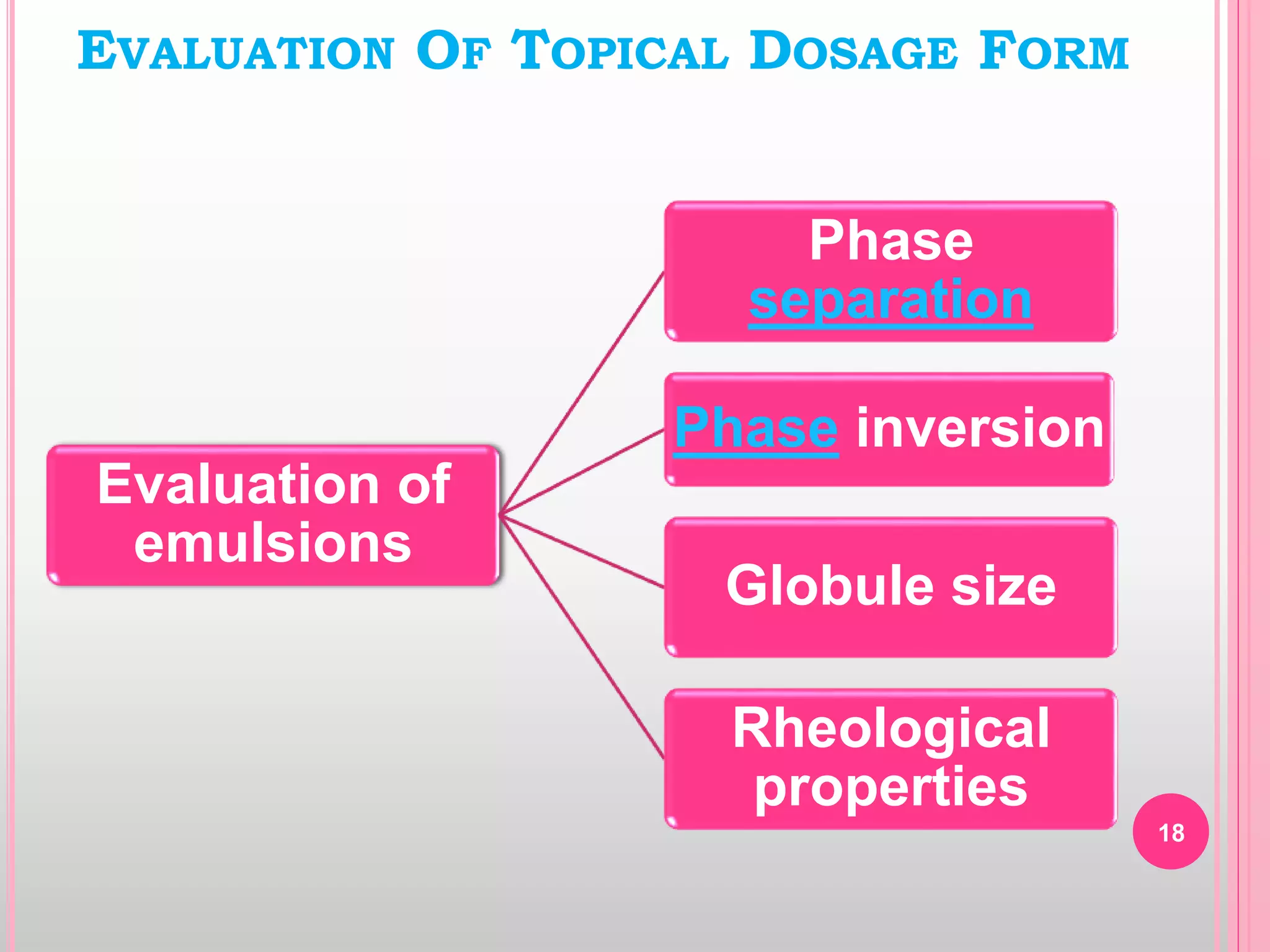
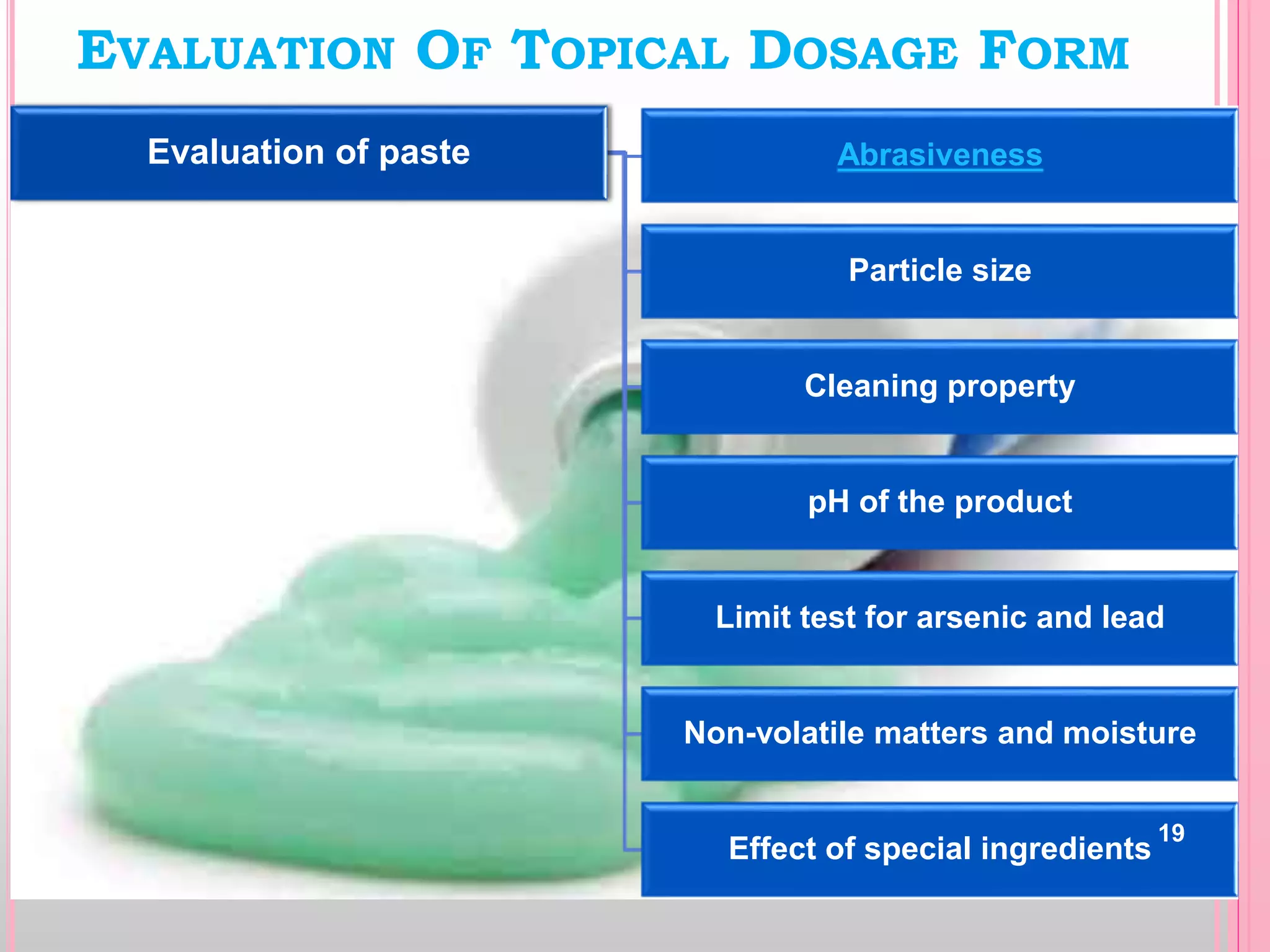
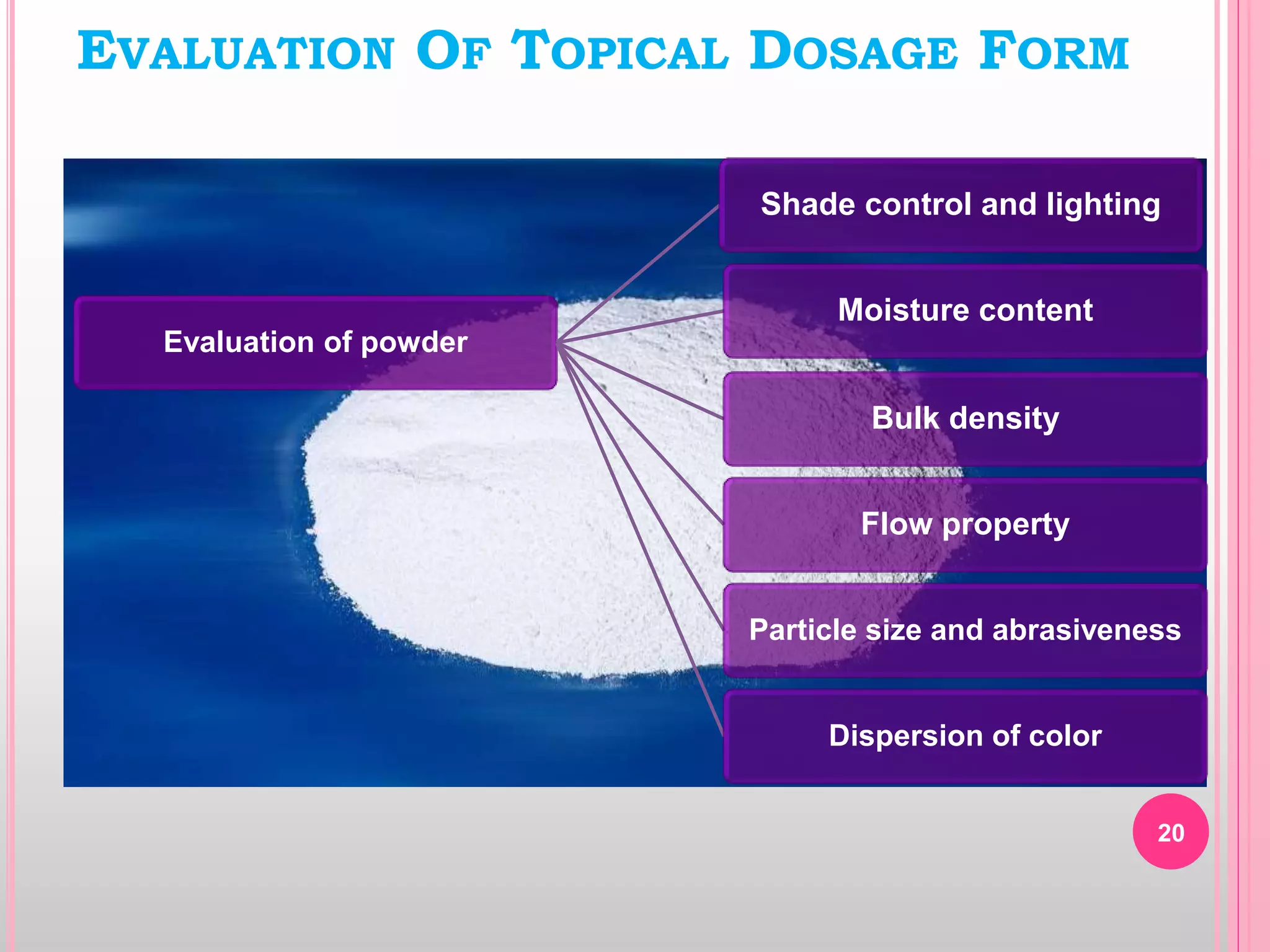
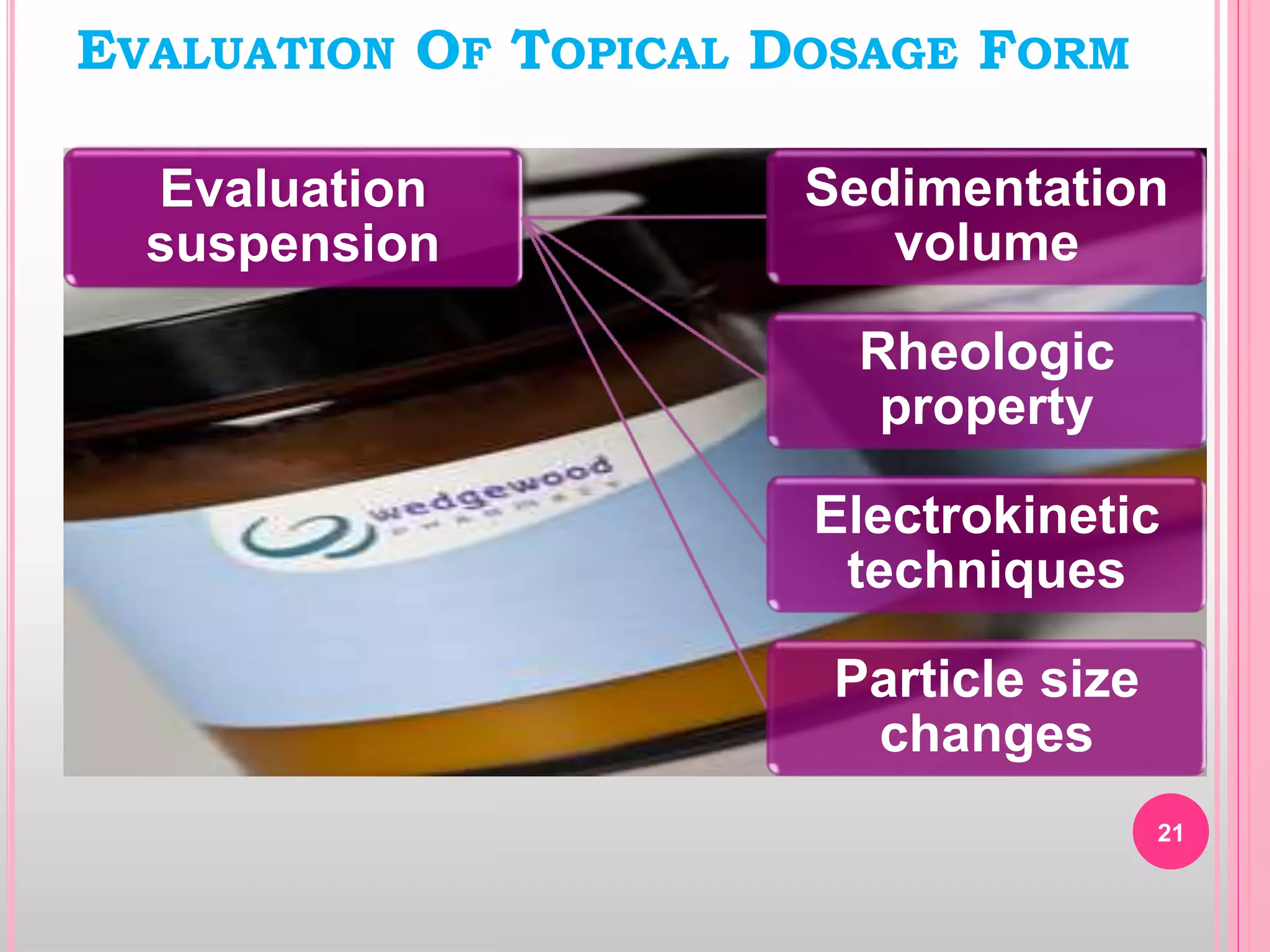
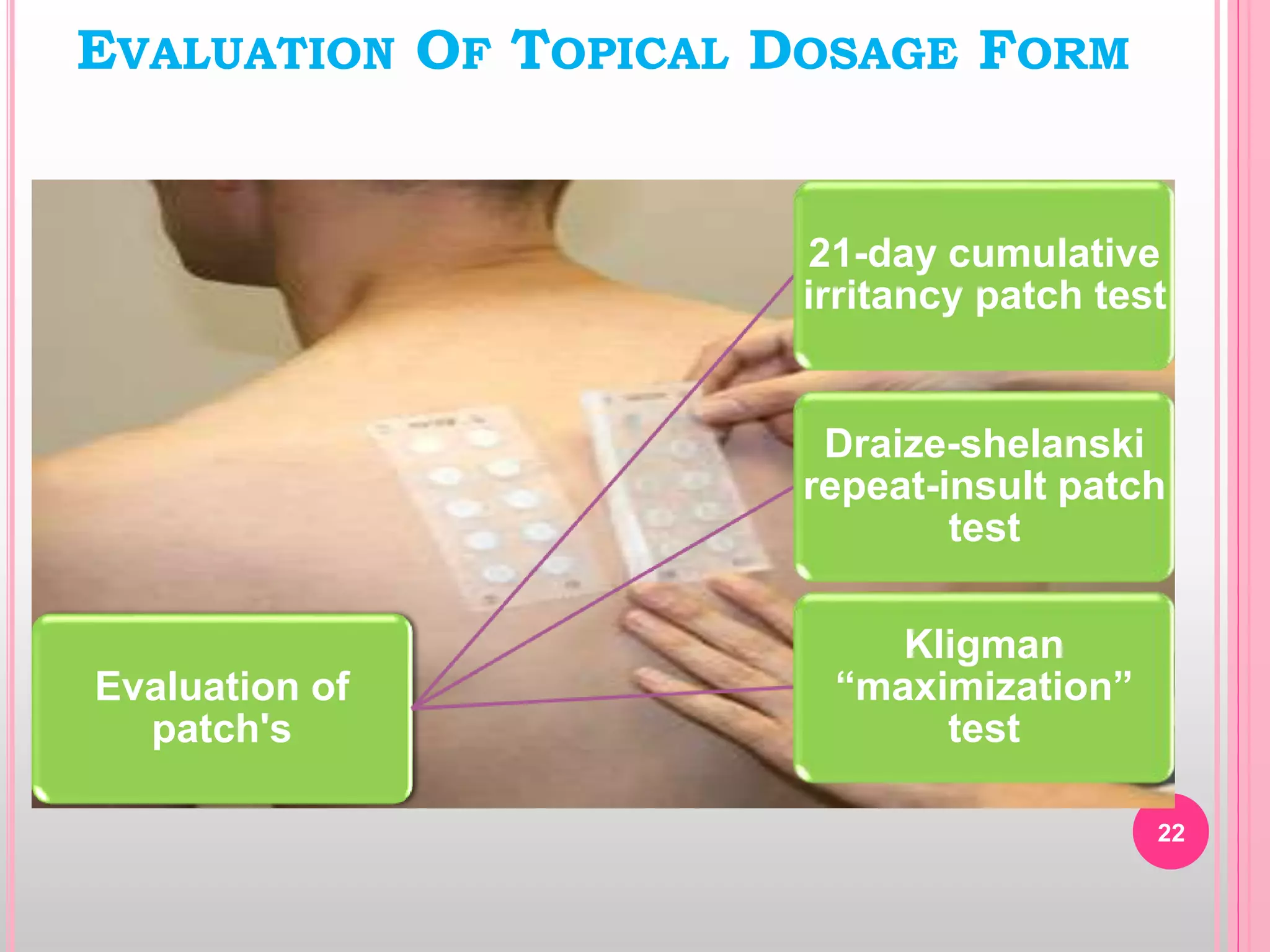
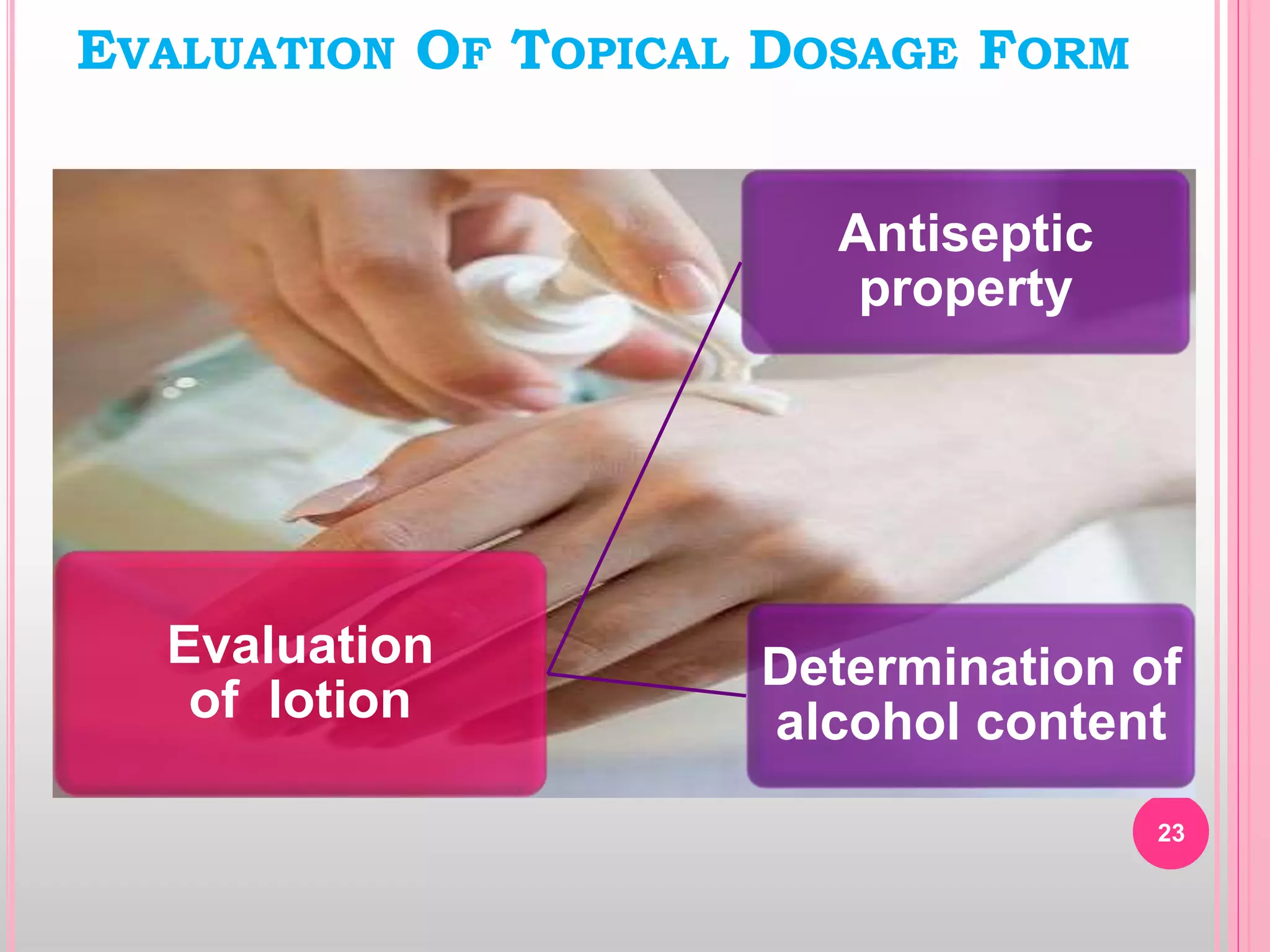
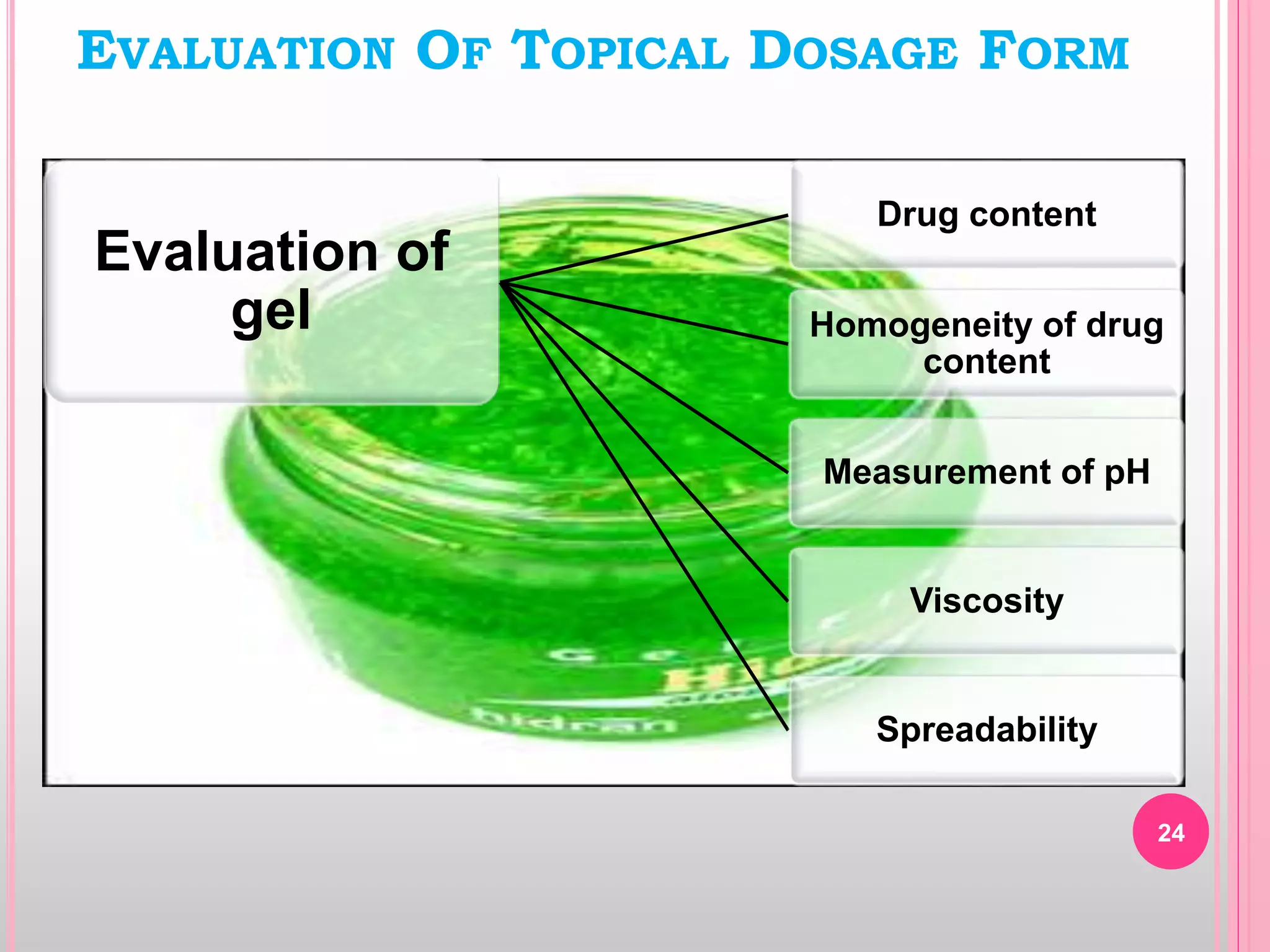
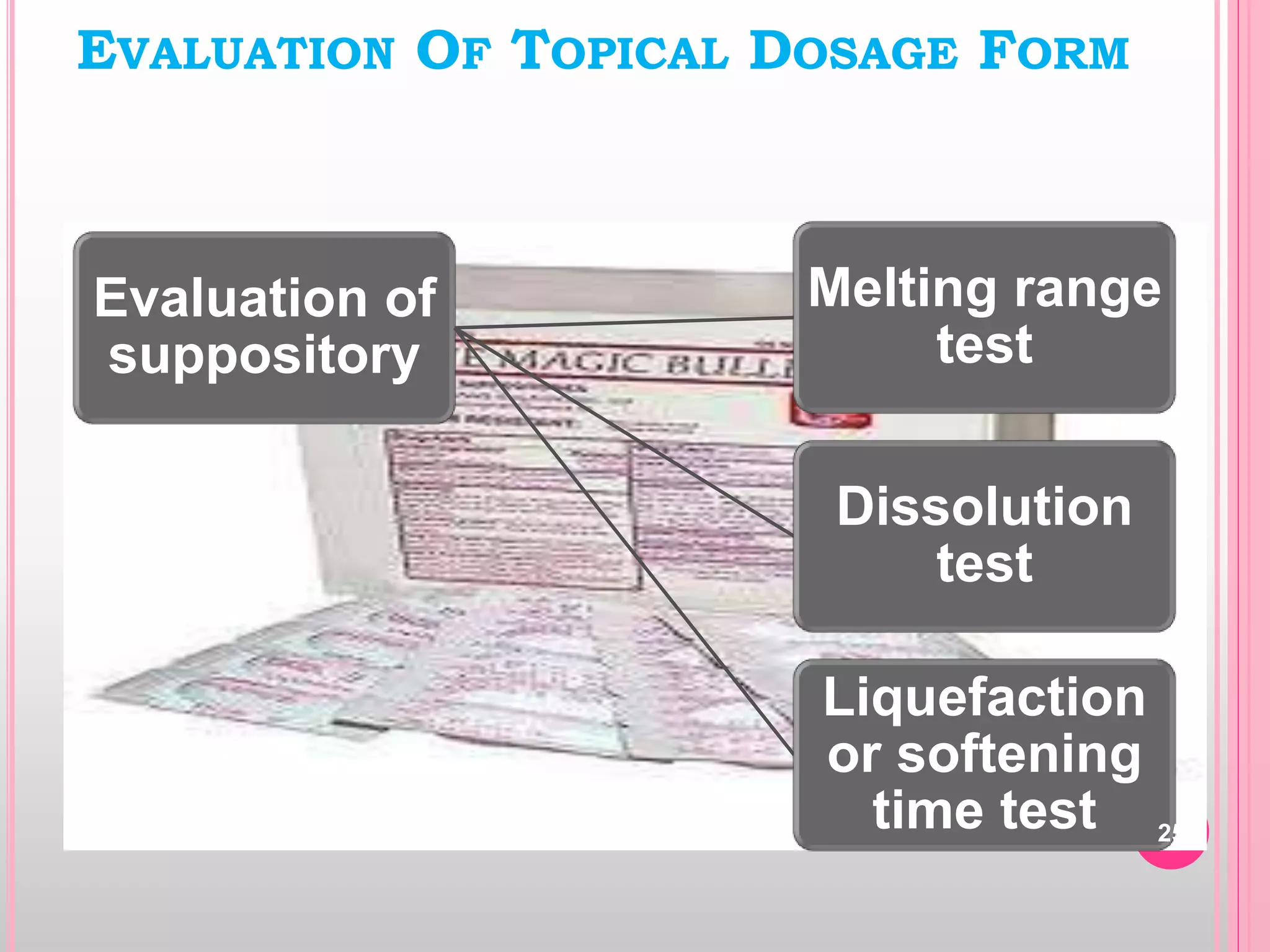
Topical drug delivery involves application of medications to the skin or mucous membranes for local or systemic effects. It has advantages like avoidance of first-pass metabolism and convenient self-administration. The skin is made of three layers - epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. Drugs can penetrate the skin via trans-epidermal or trans-follicular routes. Evaluation of topical dosage forms includes testing for drug content and release, absorption, irritation potential, rheological properties, and stability. Common topical dosage forms are solids, liquids, semi-solids and patches which are evaluated using methods specific to the product type and administration route.