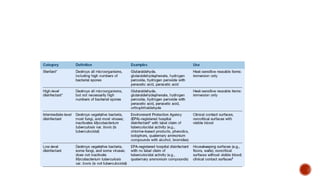
Sterilization is a process that destroys or removes all living microorganisms. There are various sterilization methods including heat sterilization methods like dry heat sterilization using hot air ovens, flame sterilization, and moist heat sterilization using steam under pressure in an autoclave. Chemical methods include the use of ethylene oxide, formaldehyde, and glutaraldehyde. Radiation methods involve the use of ionizing radiation like gamma rays or non-ionizing radiation like infrared rays. Proper sterilization controls and standards must be followed to validate the sterilization process. Biomedical waste is categorized into different colored bins for appropriate treatment and disposal.