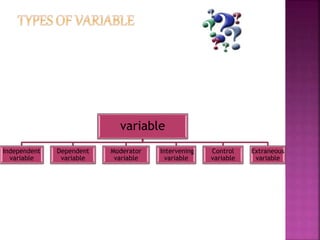
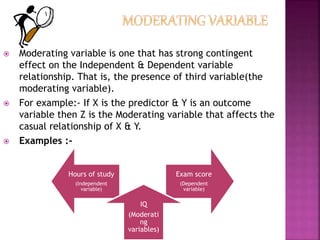
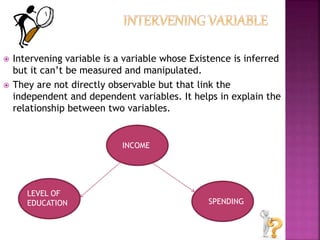
This document defines key terms related to variables in research. It discusses that a variable is anything that can take on different values, such as gender or marital status. There are several types of variables: independent variables which are manipulated by the researcher; dependent variables which depend on the independent variables; moderator variables which influence the relationship between independent and dependent variables; intervening variables which link independent and dependent variables but cannot be directly measured; control variables which are kept constant during an experiment; and extraneous variables which are uncontrolled factors that could influence dependent variables. Research involves identifying these different types of variables to understand relationships and effects.