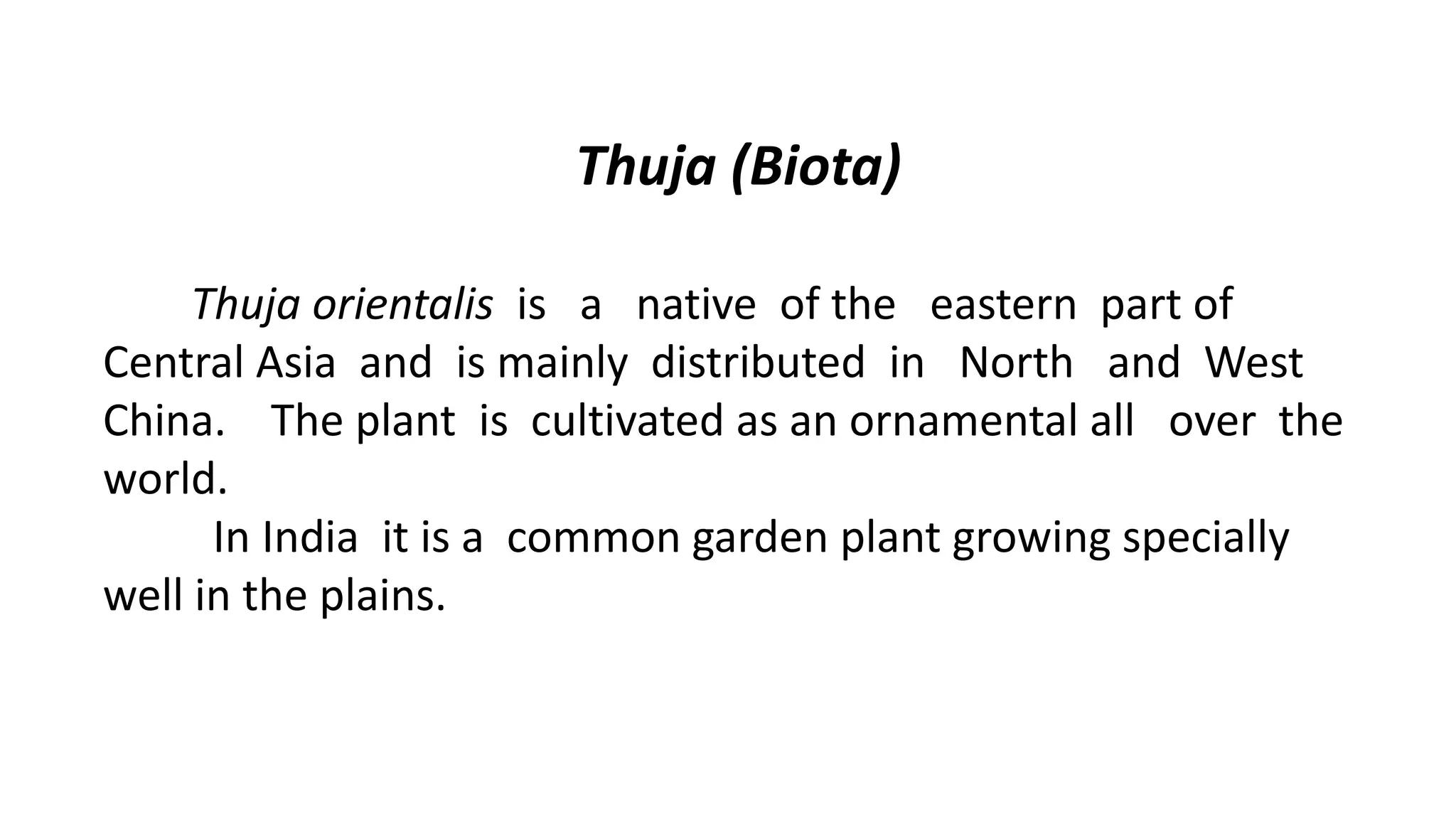
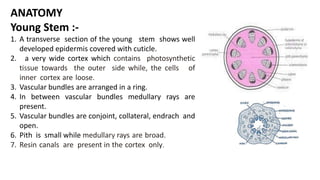
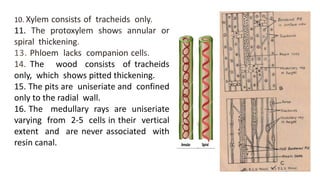
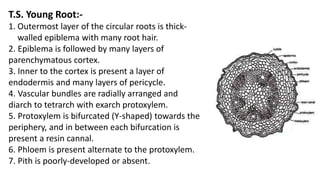
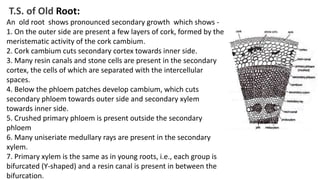
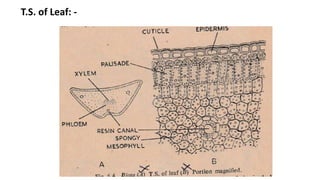
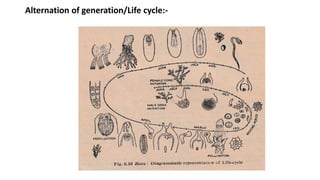
1. Thuja orientalis is an evergreen tree native to Central Asia that is commonly cultivated as an ornamental plant.
2. It can reach heights of 15 meters but is often trimmed in gardens to remain bushy.
3. The plant is dioecious, with male and female cones developing on separate branches. Female cones contain 1-3 wingless ovules that develop into seeds if fertilized by pollen from the male cones.