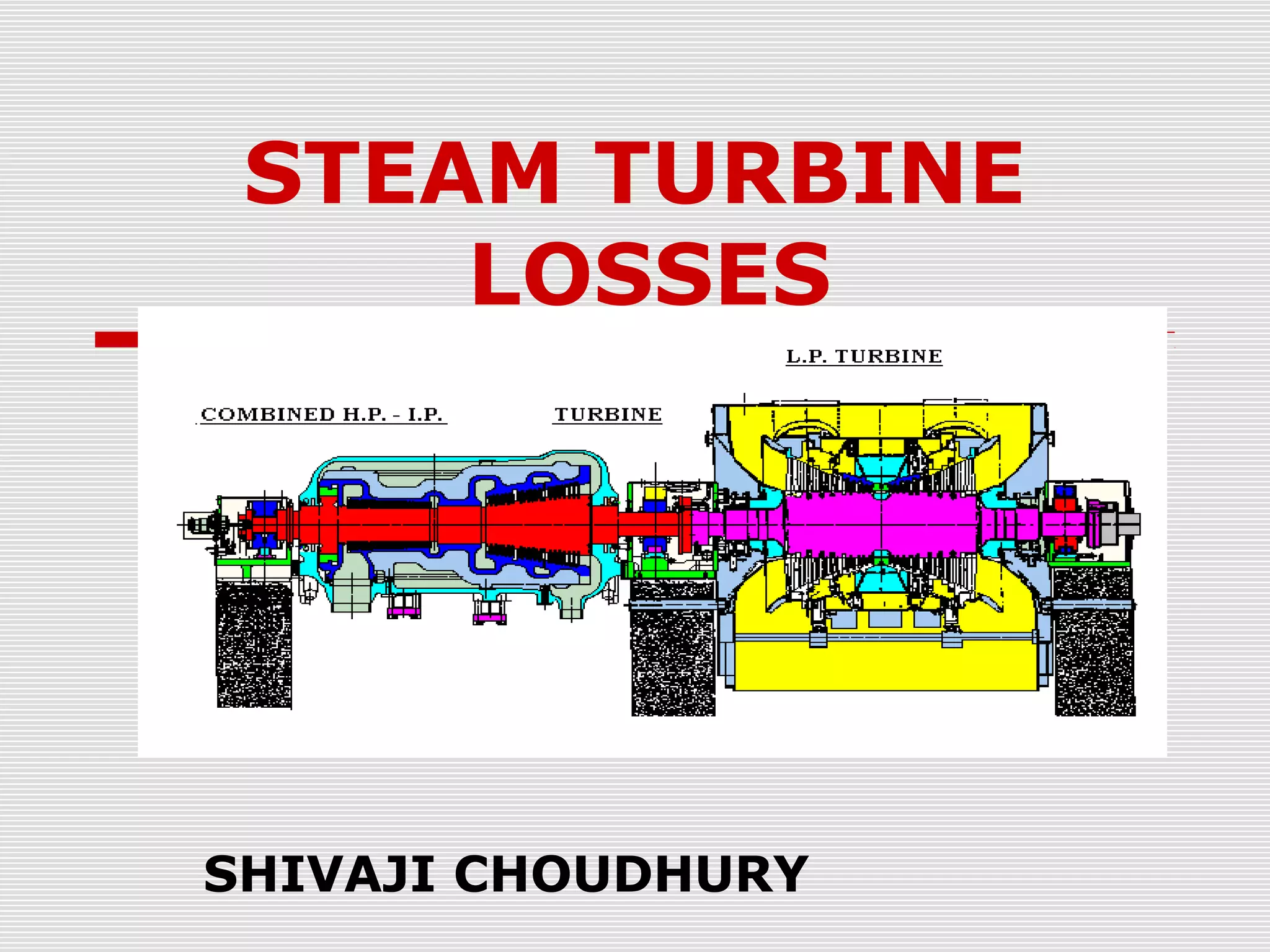
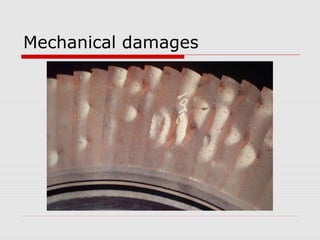
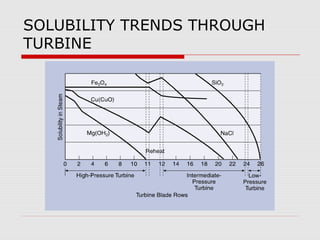
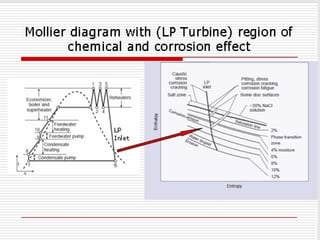
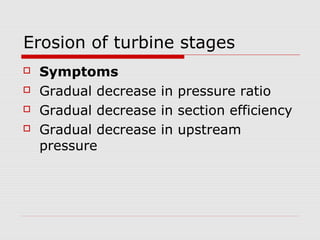
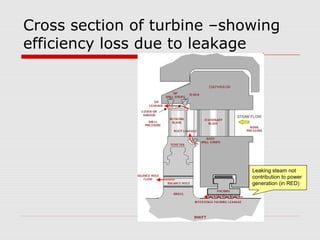
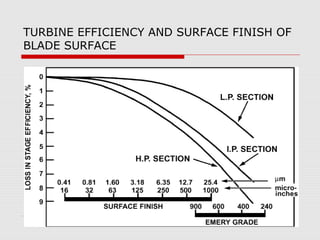
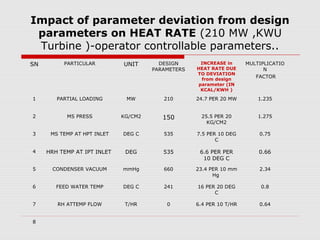
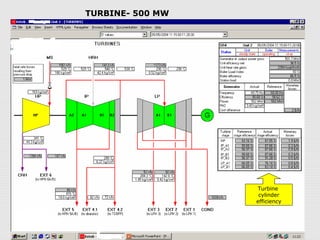
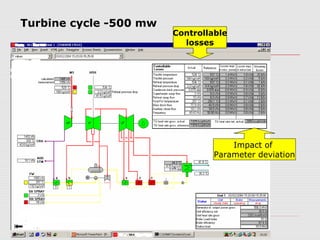
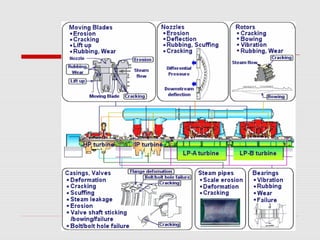
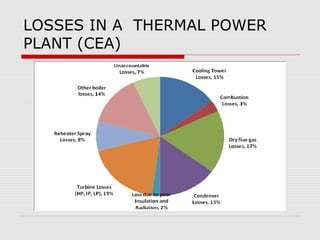
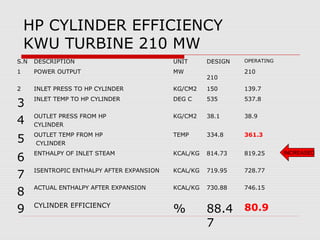
The document discusses steam turbine losses and how to identify them. It outlines several types of losses including mechanical damages, flow area decreases or increases, and flow area bypasses. Specific examples of each type of loss are provided along with their symptoms and causes. These losses can lead to reduced turbine efficiency. The document also discusses the impact of deviations from design parameters on heat rate and gives an example analysis of efficiency losses for a KWU turbine.