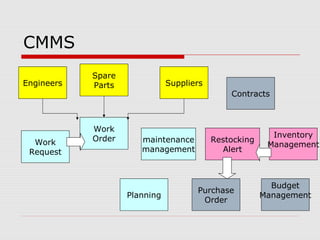
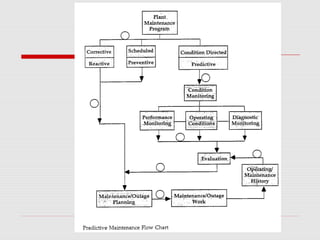
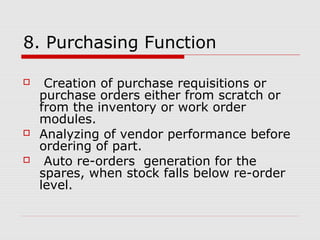
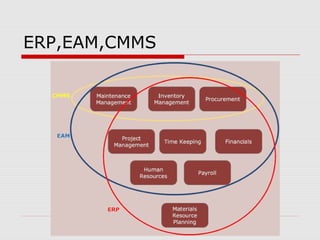
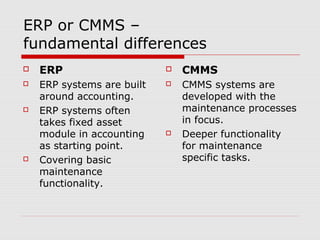
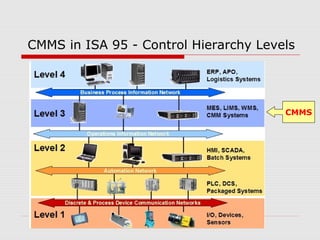
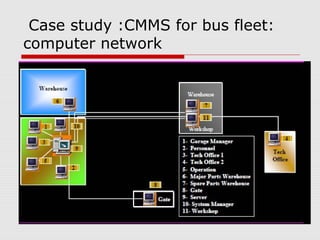
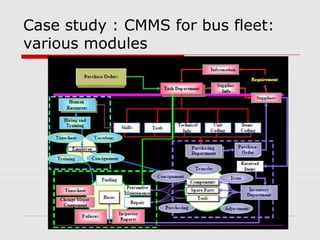
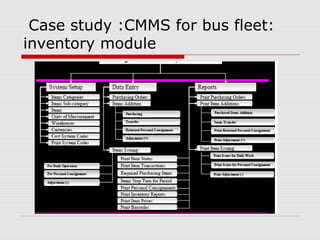
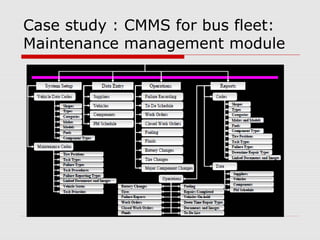
The document describes a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) and its functions. A CMMS maintains a database of information about an organization's maintenance operations to help workers perform their jobs more effectively. It enables management to schedule preventive maintenance, project costs and downtime, and analyze failures and resource usage. The CMMS has several key functional requirements including asset management, inventory management, work orders, job planning, resource planning, and reporting. It helps organizations achieve greater efficiency, minimize costs and downtime, and maximize asset usage.