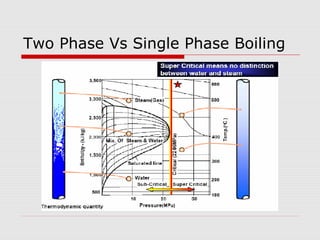
1. Supercritical boilers operate above the critical pressure of water (221 bar), where there is no distinction between water and steam.
2. Operating above the critical pressure provides benefits like higher cycle efficiency, lower fuel consumption and emissions, and improved load change flexibility compared to subcritical boilers.
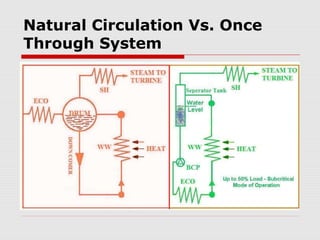
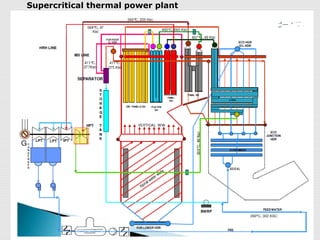
3. The key difference between subcritical and supercritical boilers is that supercritical boilers are drumless, with evaporation occurring in a single pass and flow induced by the feed pump rather than natural circulation.














![Increase of Cycle Efficiency due to
Steam Parameters
300
241
175 538 / 538
538 / 566
566 / 566
580 / 600
600 / 620
6,77
5,79
3,74
5,74
4,81
2,76
4,26
3,44
1,47
3,37
2,64
0,75
2,42
1,78
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
HP / RH outlet temperature [deg. C]Pressure [bar]
Increase of efficiency [%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/supercriticalboiler-140821064600-phpapp02/85/Super-critical-boiler-18-320.jpg)














