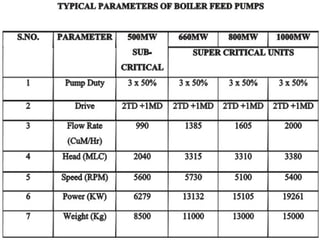
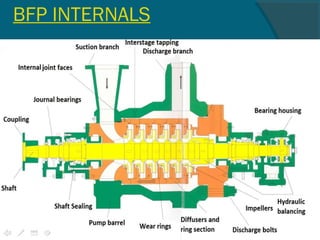
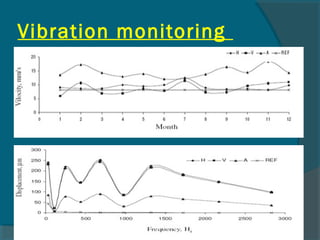
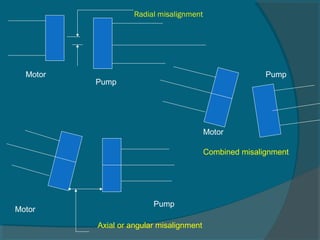
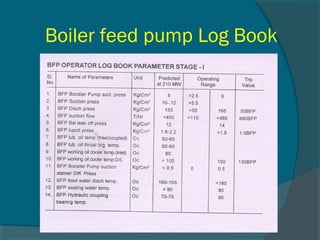
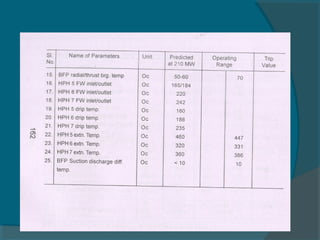
The document outlines best practices for the maintenance and condition monitoring of boiler feed pumps (BFP), emphasizing the importance of preventive and predictive maintenance methods to ensure operational efficiency and longevity. It details various maintenance types including breakdown, preventive, reliability-centered maintenance, and the use of a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) for tracking. Additionally, it covers troubleshooting procedures and technical specifications of the BFP, highlighting key maintenance activities and the importance of shaft alignment.