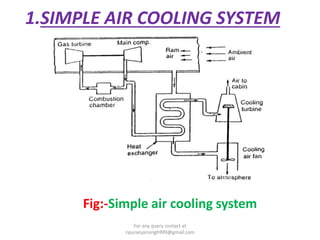
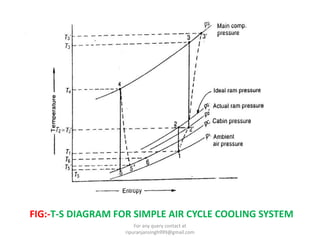
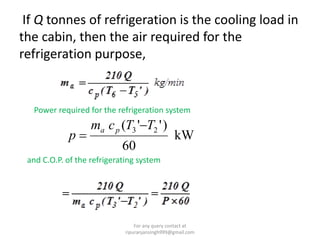
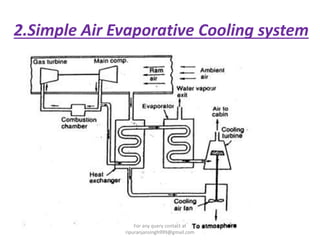
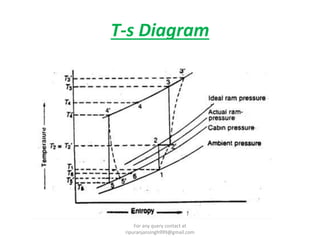
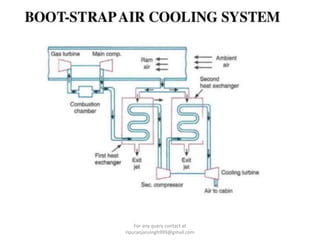
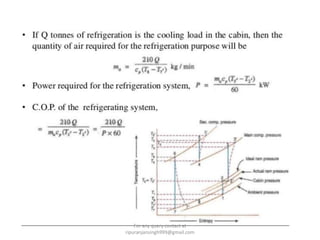
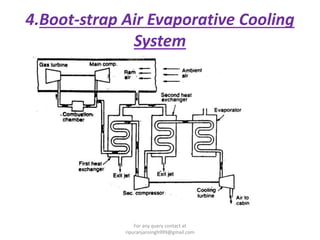
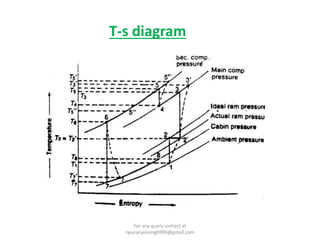
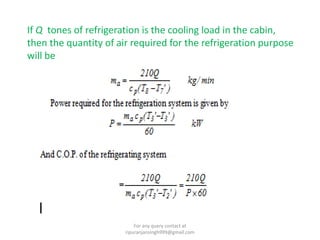
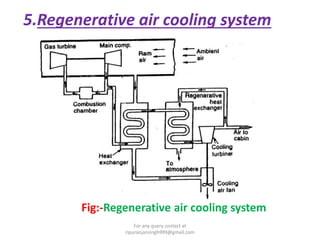
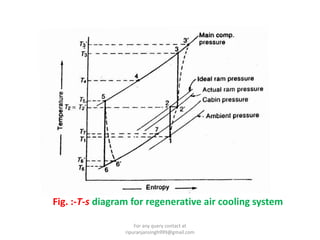
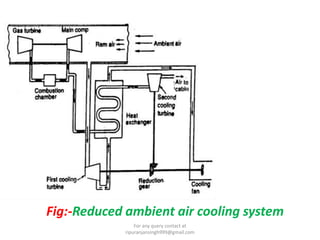
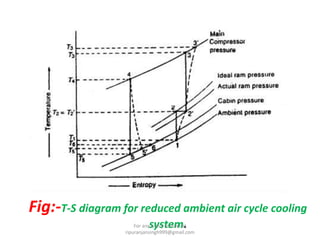
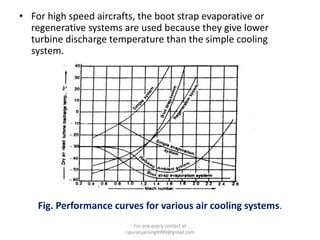
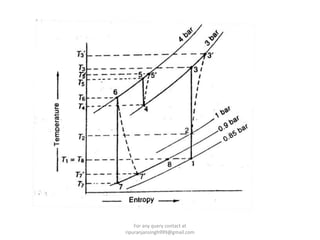
The document discusses various air refrigeration systems used in aircraft, including simple air cooling, boot strap, regenerative, and reduced ambient air cooling systems. It explains the principles behind these systems, their components, efficiency calculations, and the cooling load requirements for specific aircraft scenarios. Additionally, it contains queries regarding calculations for mass air circulation and the coefficient of performance (C.O.P.) of these systems.