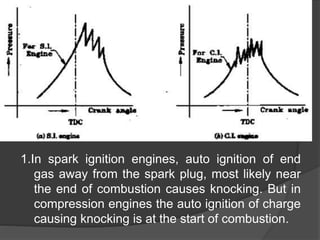
1. Combustion involves the rapid chemical combination of fuel and oxygen, resulting in heat release. It requires a combustible mixture, an ignition source, and flame propagation.
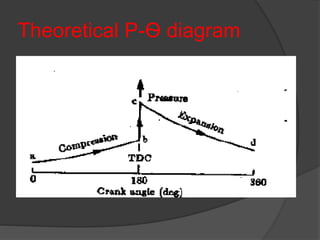
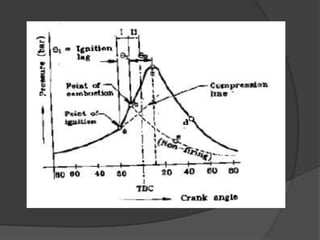
2. In spark ignition (SI) engines, a carburetor supplies an air-fuel mixture and a spark plug ignites it. Combustion in SI engines occurs in three stages: ignition lag, flame propagation, and afterburning.
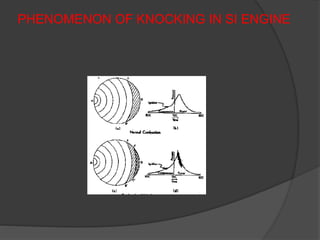
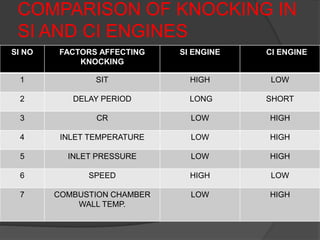
3. Factors like air-fuel ratio, compression ratio, load, turbulence, and engine speed affect the flame propagation rate in SI engines. Higher propagation speeds improve efficiency and fuel economy.