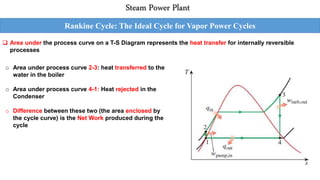
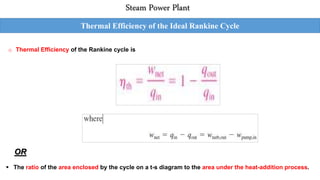
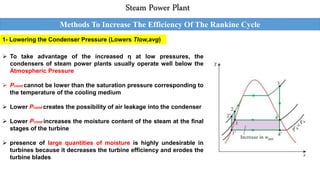
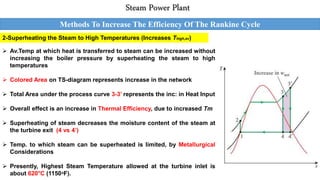
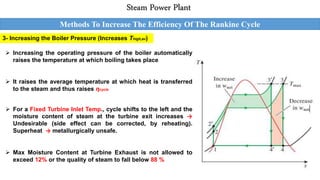
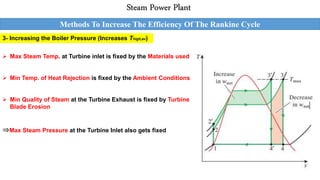
This document outlines the Rankine cycle and methods to increase the efficiency of steam power plants. The ideal Rankine cycle consists of four processes: an isentropic compression in a pump, isobaric heat addition in a boiler, isentropic expansion in a turbine, and isobaric heat rejection in a condenser. The thermal efficiency of the cycle can be increased by lowering the condenser pressure, increasing the boiler pressure, and superheating the steam to raise average temperatures. These modifications aim to increase the average fluid temperature during heat addition and decrease it during heat rejection.