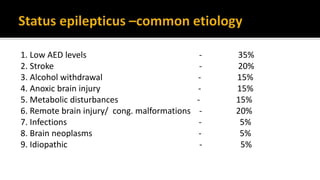
1. Convulsive status epilepticus has a bimodal distribution, peaking in children and the elderly, and has multiple potential causes including infections, strokes, alcohol withdrawal and brain injuries.
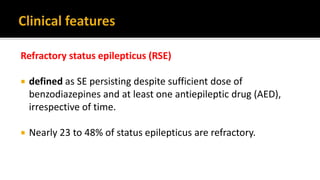
2. Mortality rates range from 10.5-28% and neurological sequelae occur in 11-16% of patients. Refractory status epilepticus is defined as continuing despite benzodiazepines and other anticonvulsants.
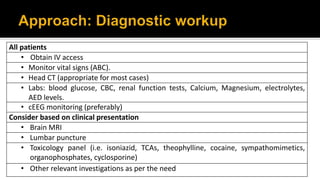
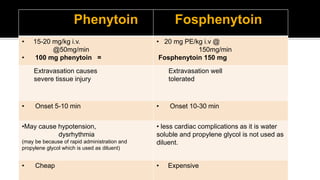
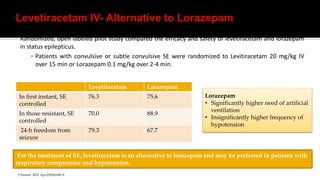
3. Treatment involves terminating seizures acutely with benzodiazepines like lorazepam and diazepam. For refractory cases, second line drugs like phenytoin, fosphenytoin, valproate, levetirac