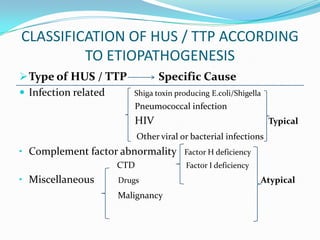
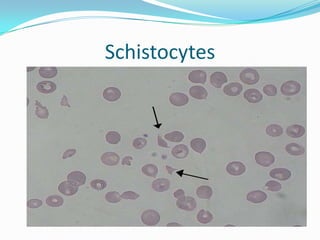
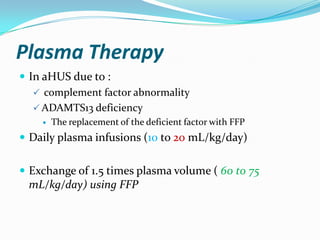
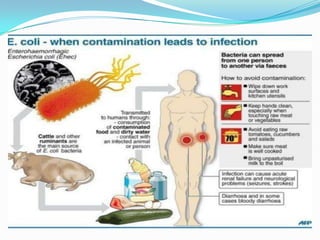
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia, low platelet count, and kidney failure. It predominantly affects children and can be caused by infections from E. coli or pneumococcal bacteria or complement factor abnormalities. The typical pathophysiology involves Shiga toxin or other bacterial toxins damaging endothelial cells and platelets. Treatment involves supportive care, antibiotics for infections, plasma therapy for complement abnormalities, and long-term prognosis depends on severity and treatment.