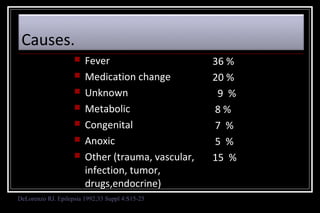
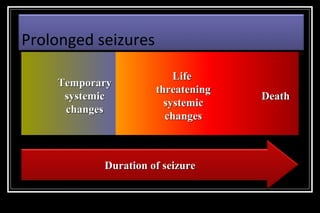
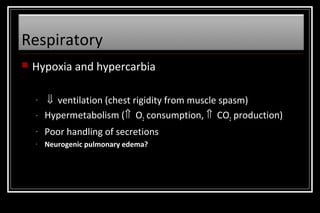
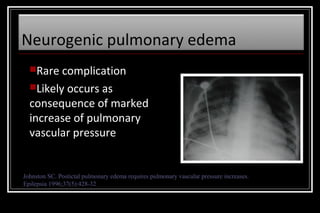
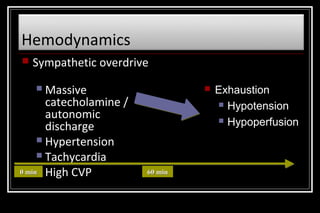
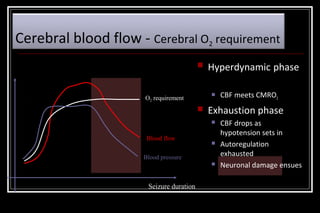
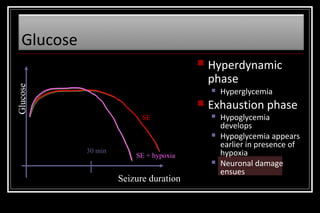
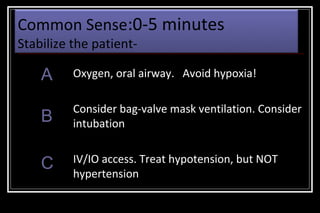
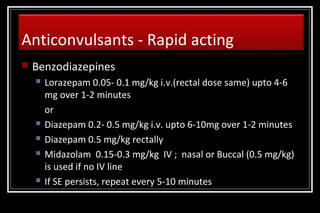
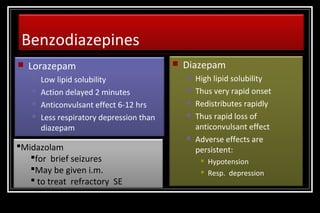
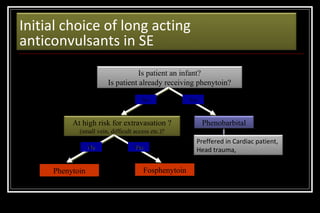
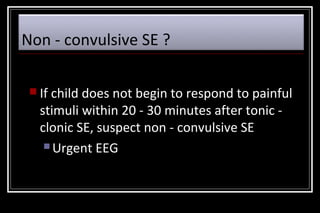
Status epilepticus is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent neurological damage or death. It is defined as continuous seizure activity lasting more than five minutes or two or more discrete seizures between which there is incomplete recovery of consciousness. The document discusses the definition, causes, pathophysiology, treatment approach, and medications used to treat status epilepticus in children. Treatment involves stabilizing the patient, administering rapid-acting anticonvulsants like lorazepam followed by long-acting medications like fosphenytoin if seizures persist, with progression to anesthetic treatments in refractory cases to stop seizures.