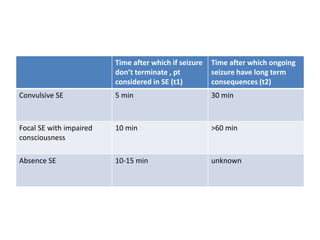
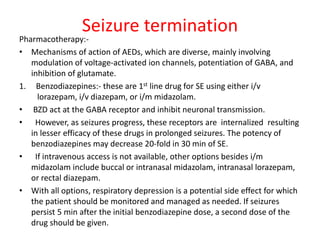
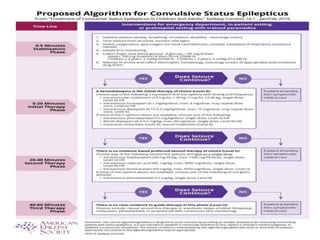
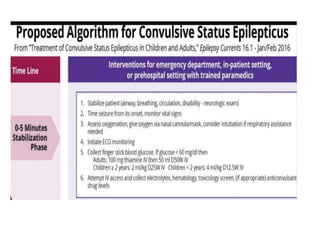
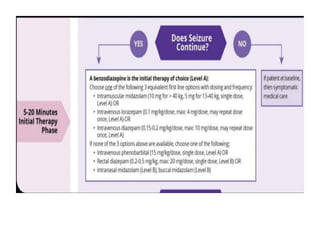
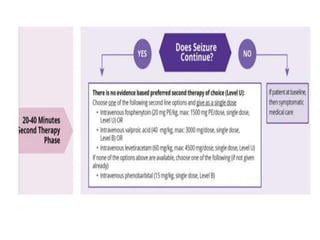
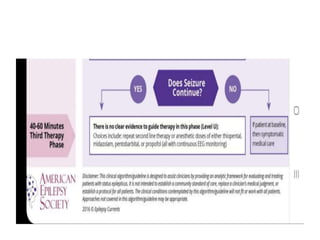
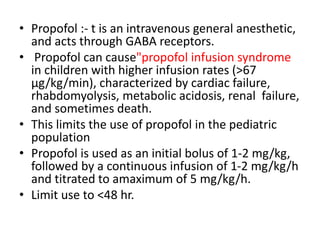
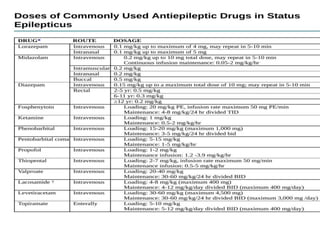
Status epilepticus (SE) is a medical emergency defined by continuous seizure activity lasting more than 5 minutes for generalized seizures or more than 10 minutes for focal seizures. The condition requires rapid treatment to prevent neuronal injury and death from prolonged excitatory activity. Management involves initial airway and hemodynamic stabilization, followed by benzodiazepines as first-line treatment. If seizures continue, second-line drugs like phenytoin are used. Refractory SE fails to respond to first- and second-line drugs, while super-refractory SE continues despite anesthesia with midazolam or barbiturates. Early, aggressive treatment is needed to terminate seizures and prevent neurological complications.