Embed presentation
Downloaded 225 times






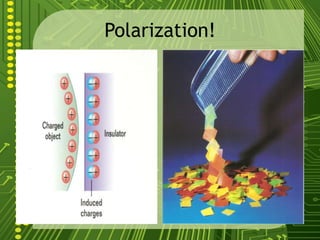



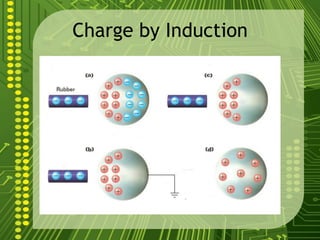
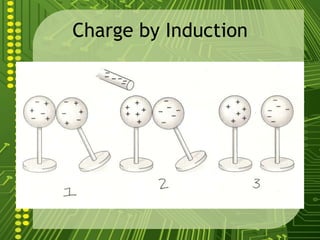

Electrostatics describes the behavior of static electricity and the forces between electrically charged objects. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Normally atoms have an equal number of protons and electrons, giving them no overall charge. Charge results from gaining or losing electrons. Oppositely charged objects attract, while like charges repel based on the electric charge-force law. Objects can be charged through friction, conduction, polarization, or induction by a nearby charged object attracting or repelling their electrons. The magnitude of electric force depends on the charges' magnitudes and their distance.












