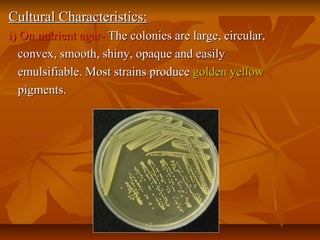
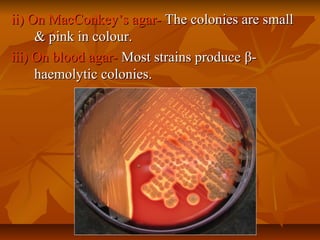
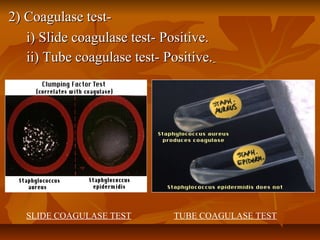
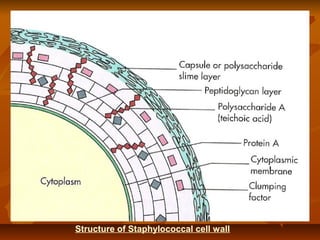
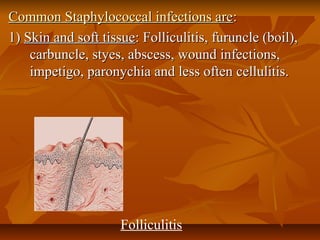
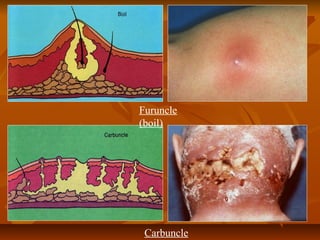
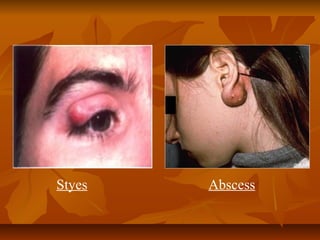
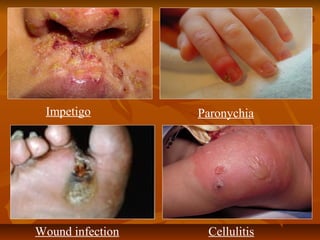
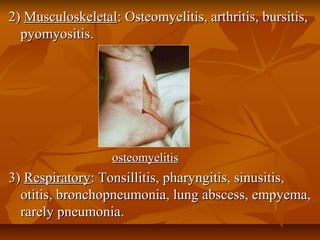
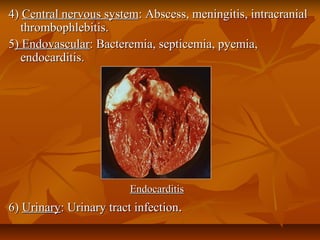
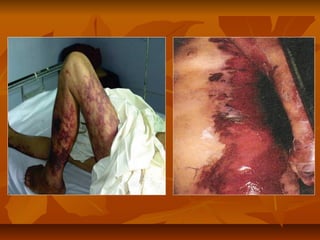
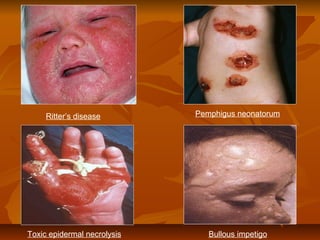
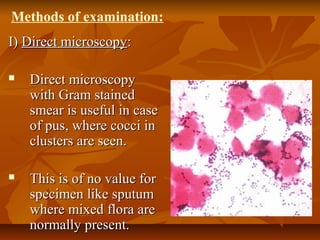
Staphylococci are gram positive cocci that occur in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is classified based on coagulase production and pathogenicity, and is a common human pathogen. S. aureus has spherical cells that are arranged in clusters and produce enzymes and toxins that allow it to cause infections like skin infections, pneumonia, sepsis and food poisoning or toxic shock syndrome through toxin production. Identification involves culture and biochemical testing, and treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin or vancomycin depending on antibiotic resistance.