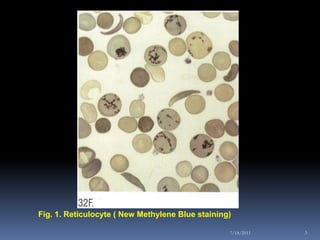
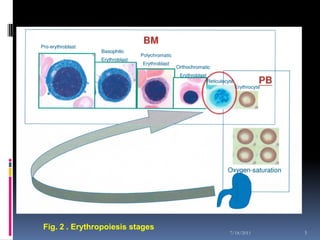
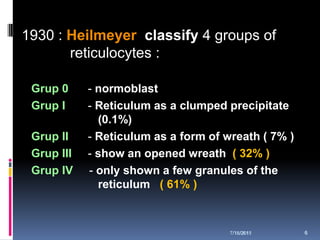
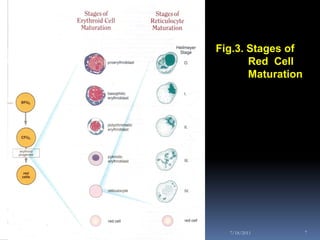
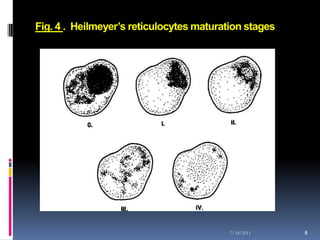
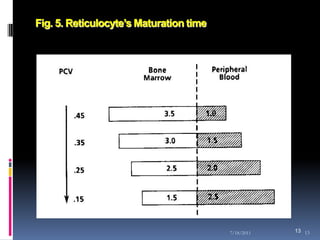
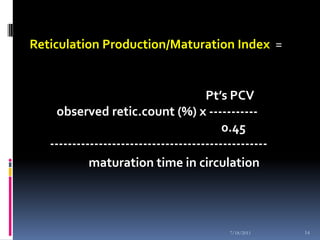
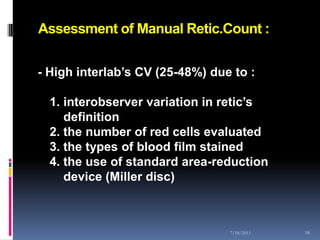
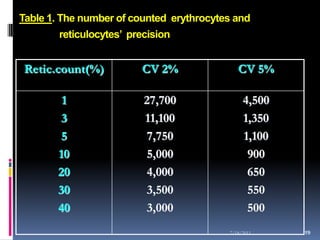
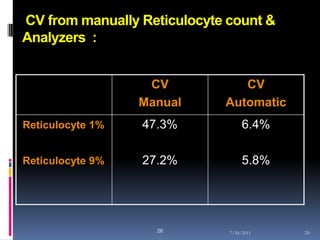
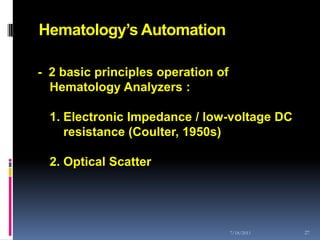
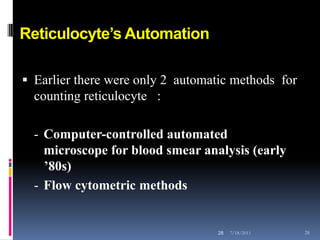
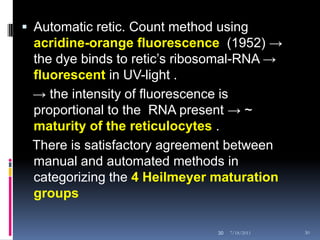
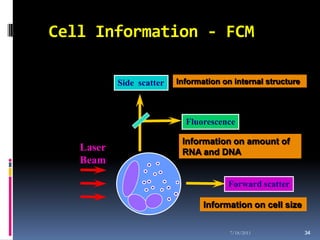
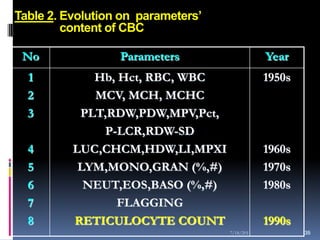
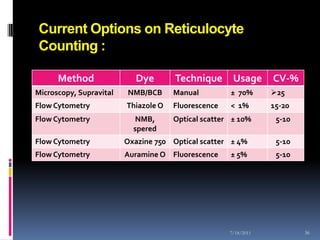
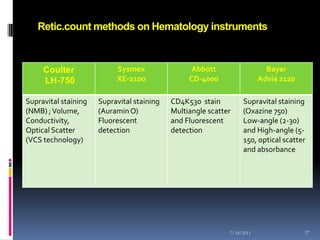
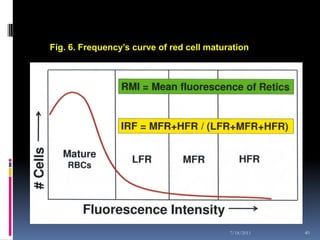
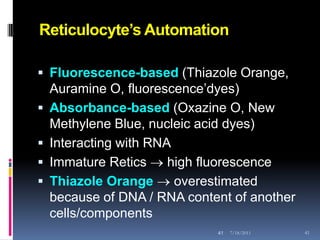
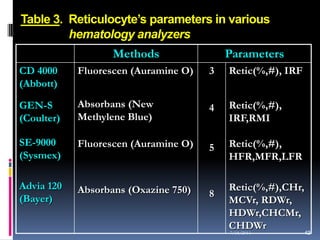
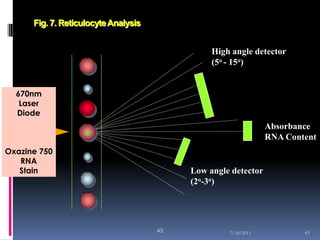
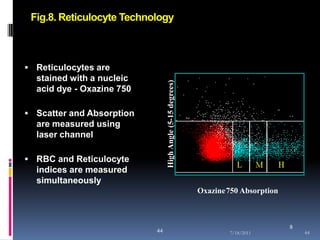
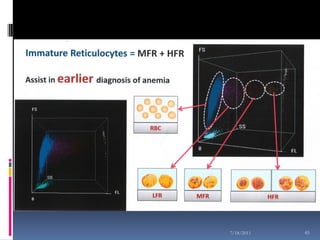
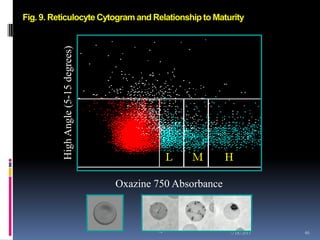
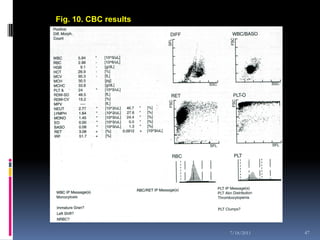
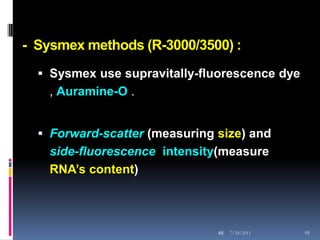
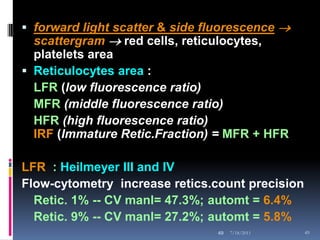
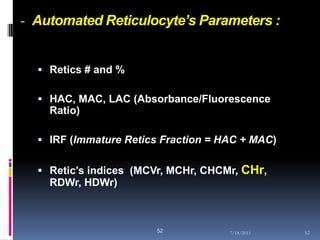
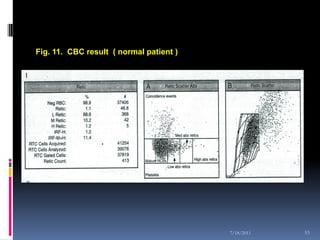
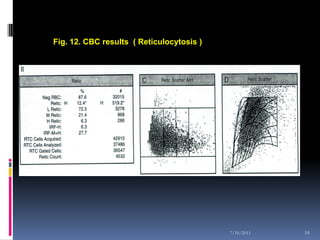
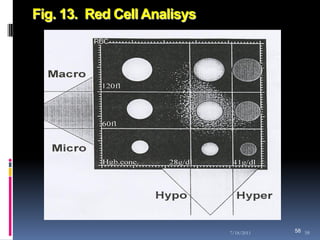
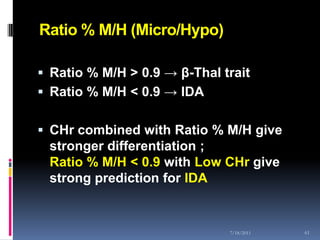
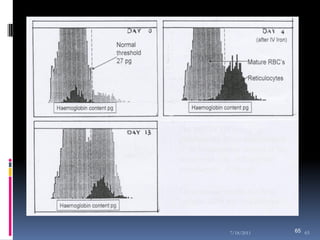
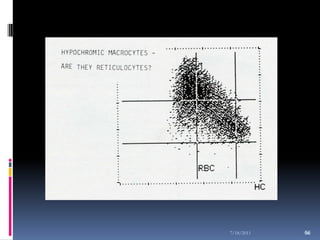
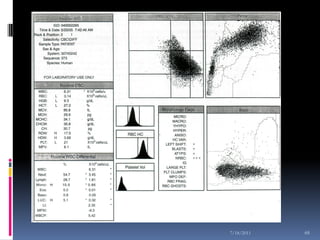
This document discusses automated reticulocyte analysis. It begins by defining reticulocytes as the last immature erythrocyte stage that still contains RNA and organelles. It then reviews the history of reticulocyte classification and counting methods, from early manual methods to modern automated analyses using flow cytometry and fluorescent dyes. The document compares the improved precision of automated methods over manual counts and evaluates different automated analyzers and their approaches to classifying reticulocyte maturity.