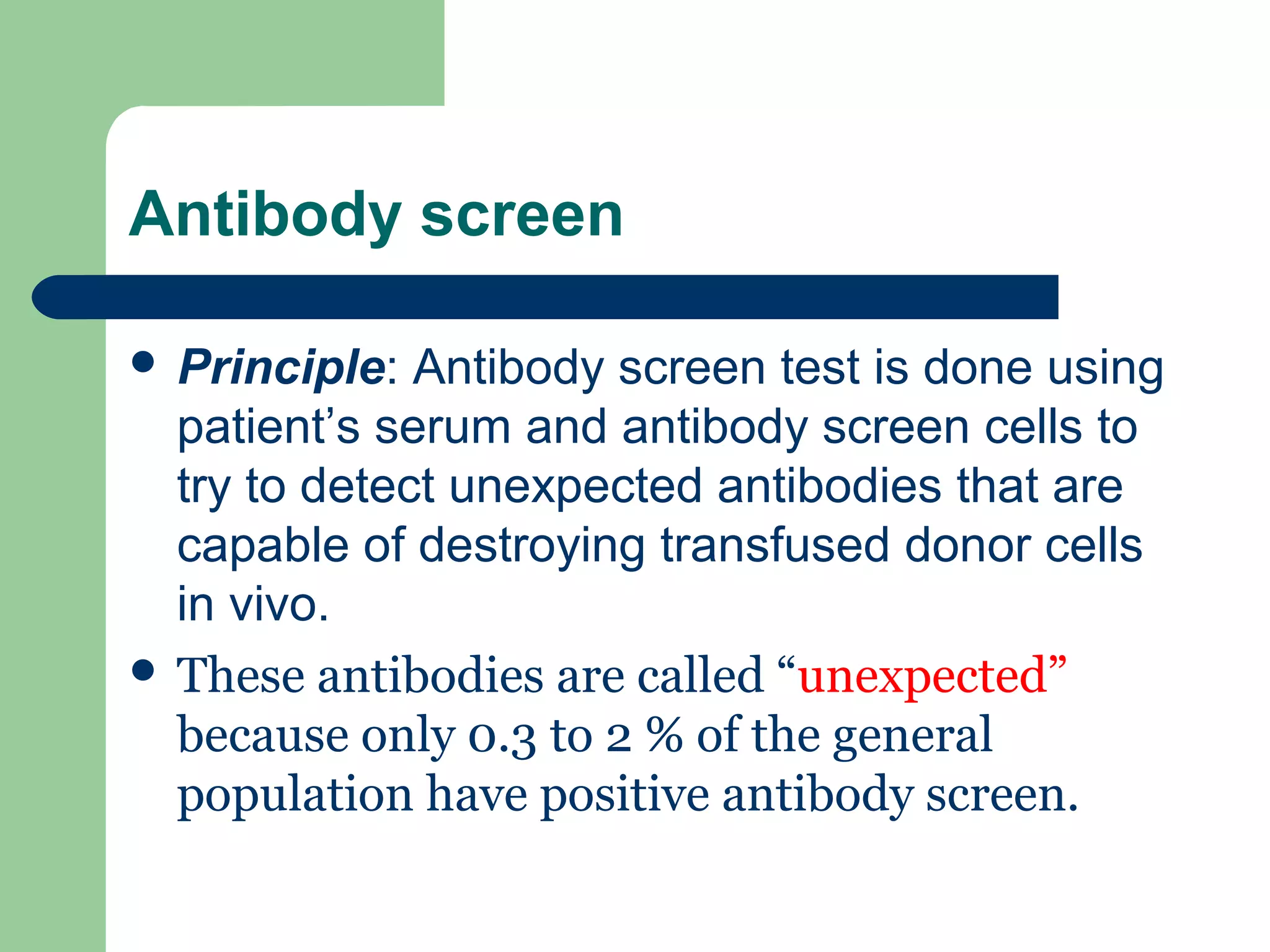
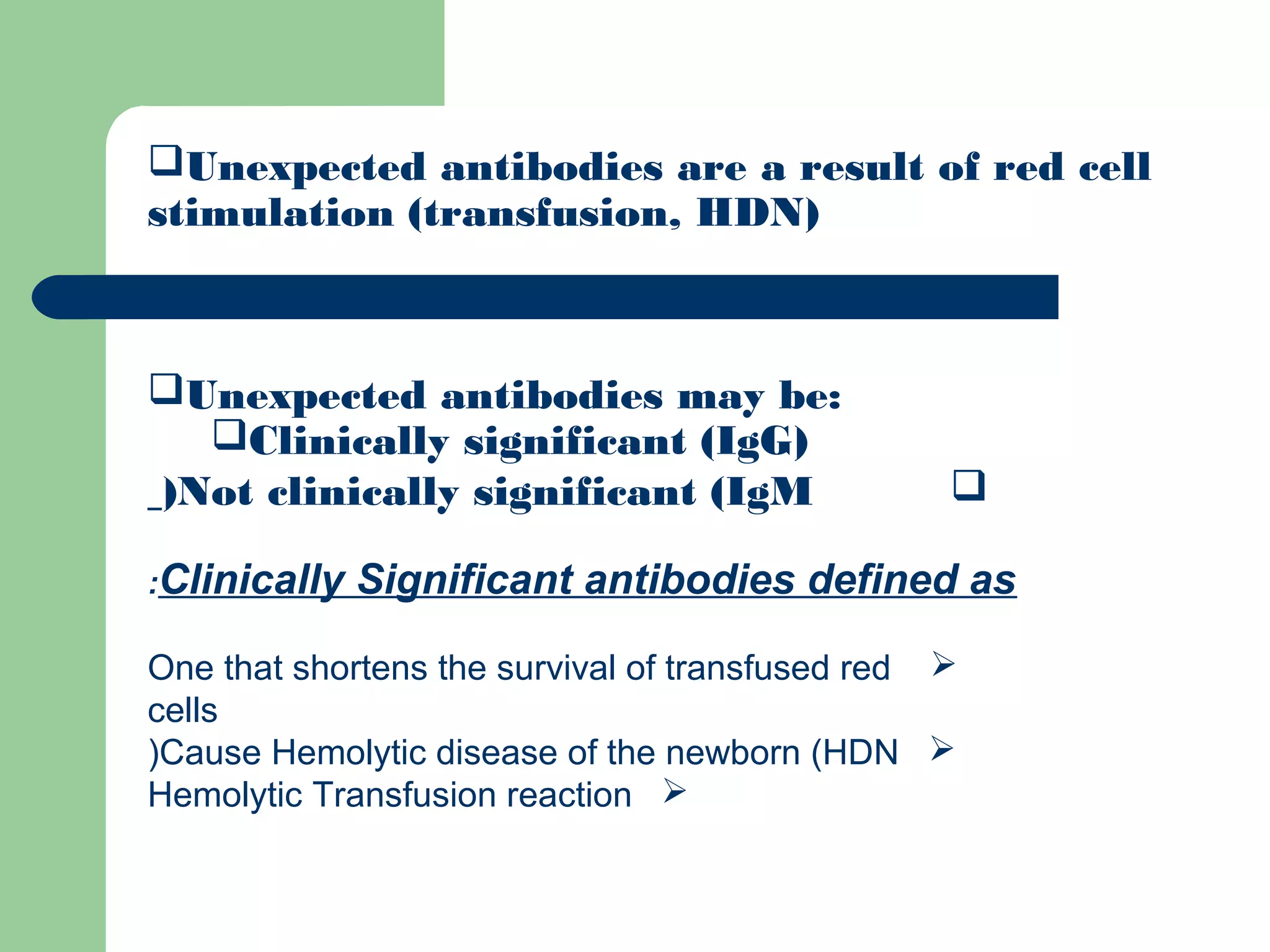
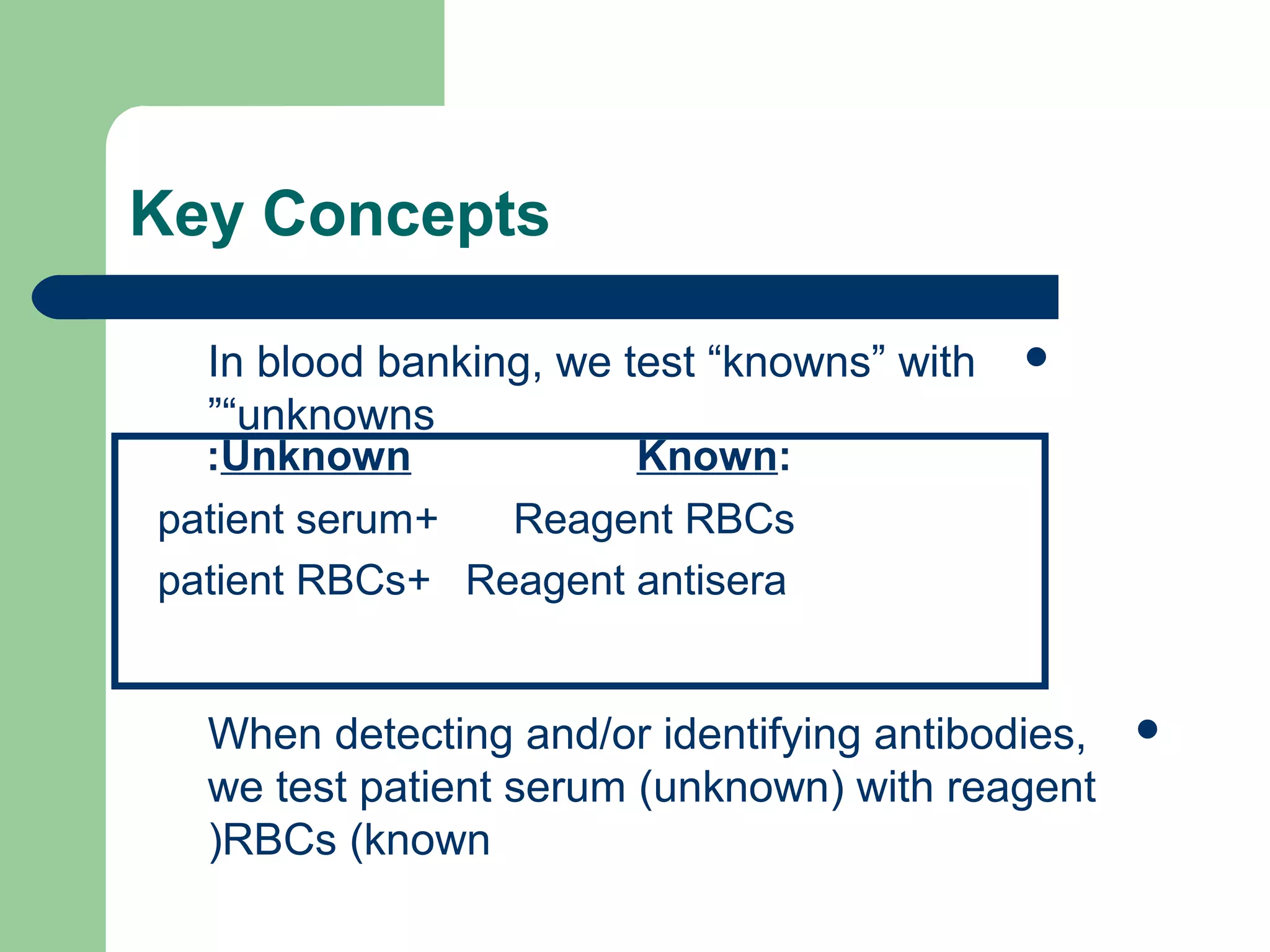
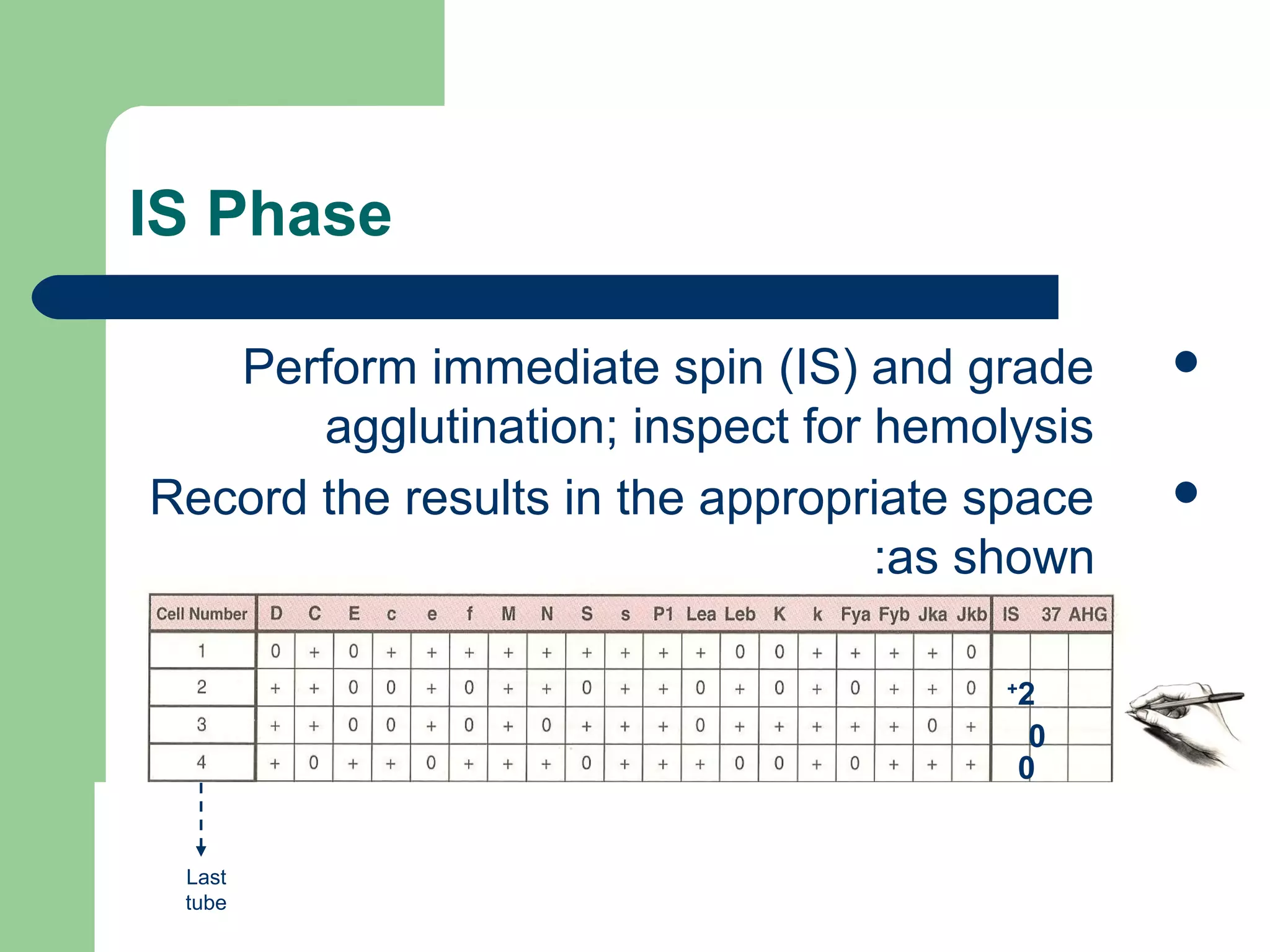
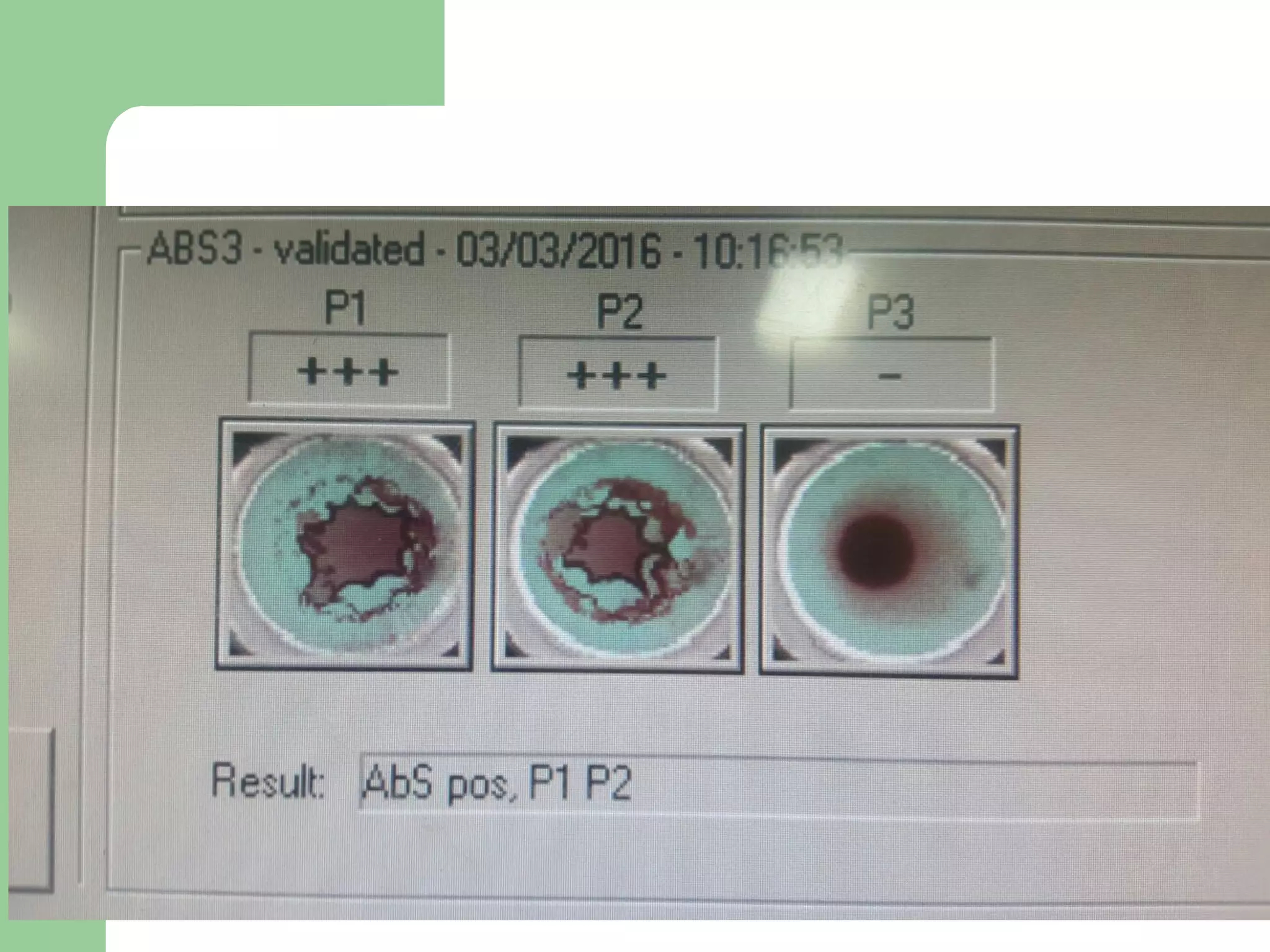
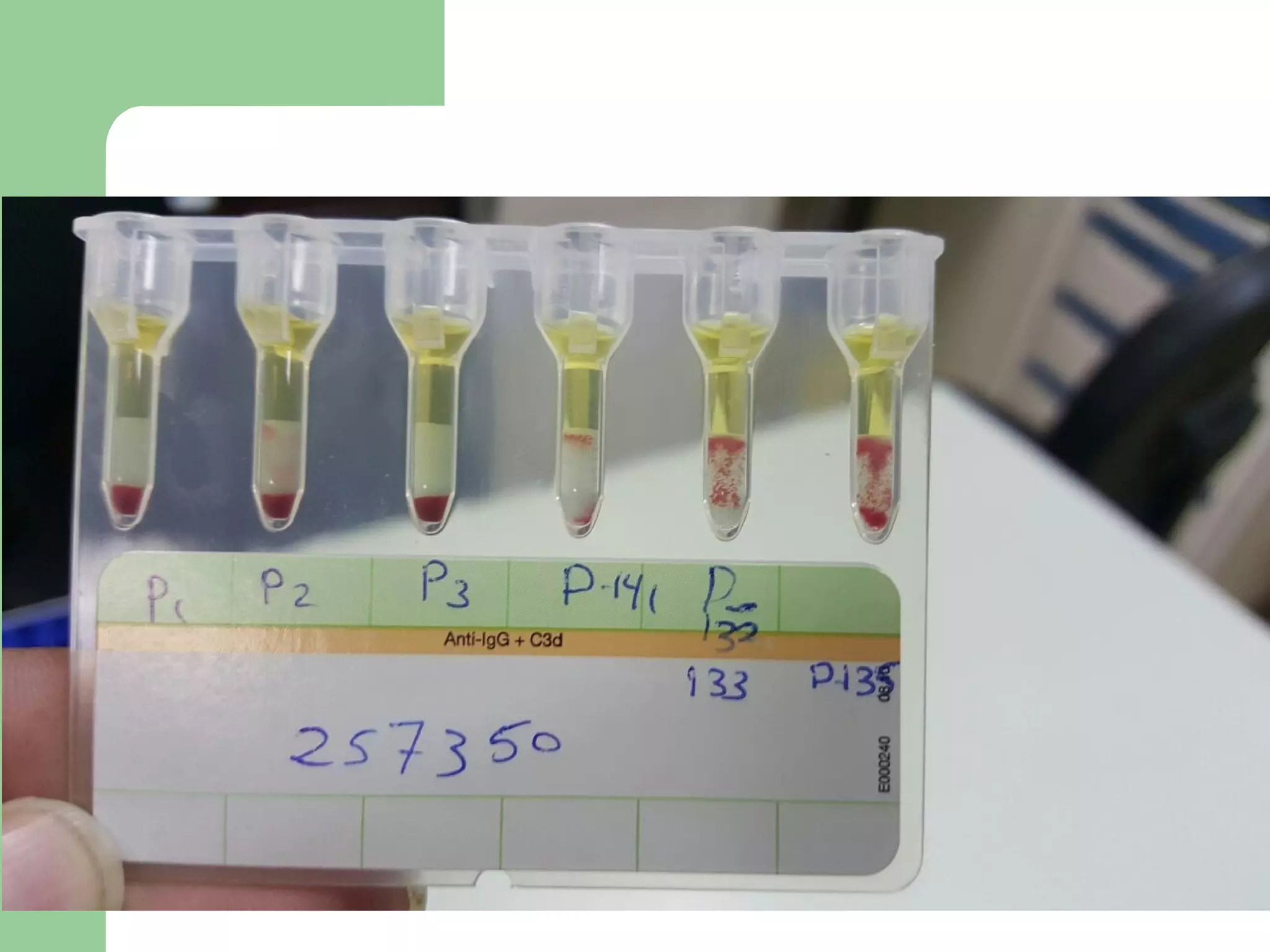
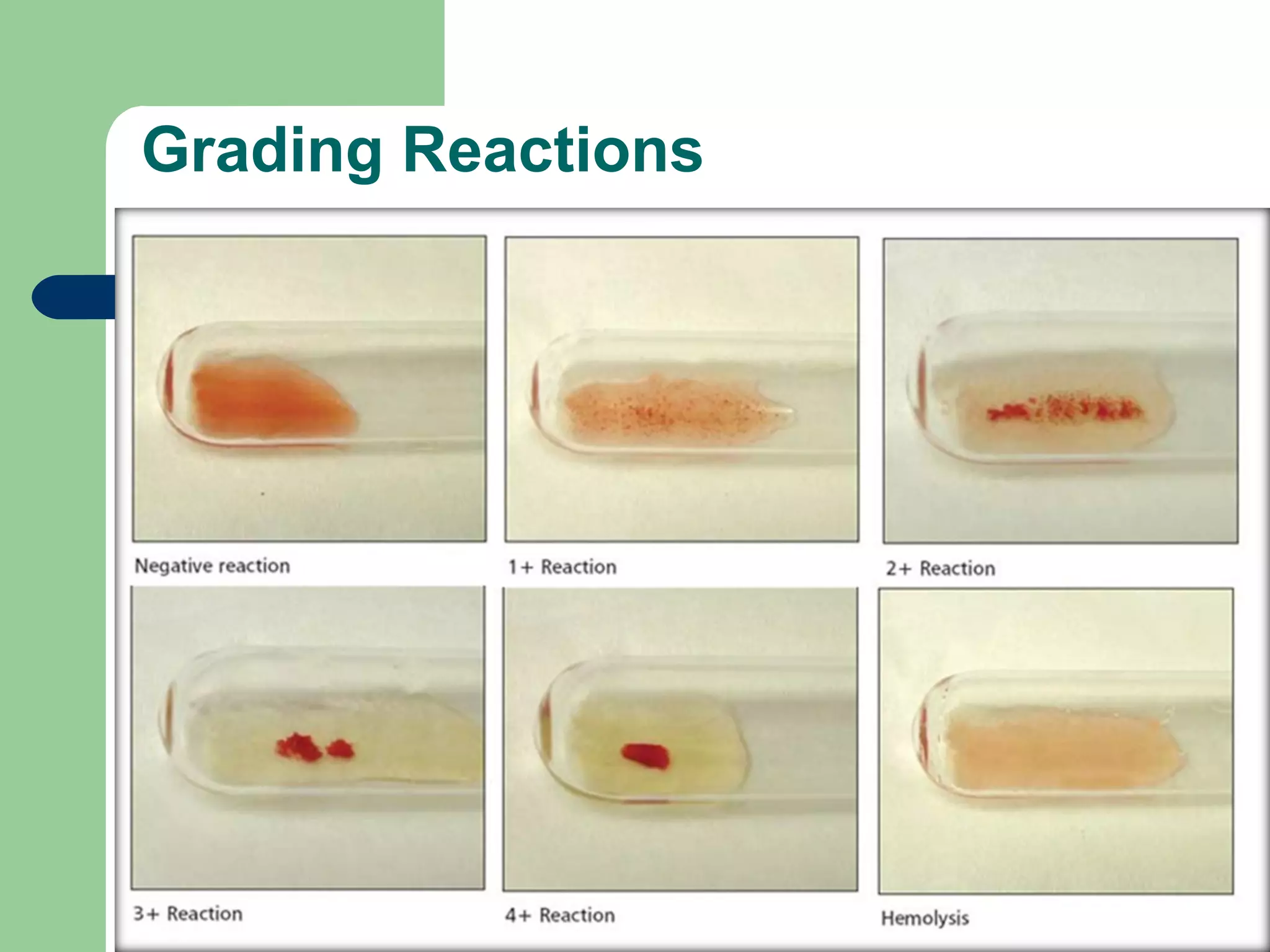
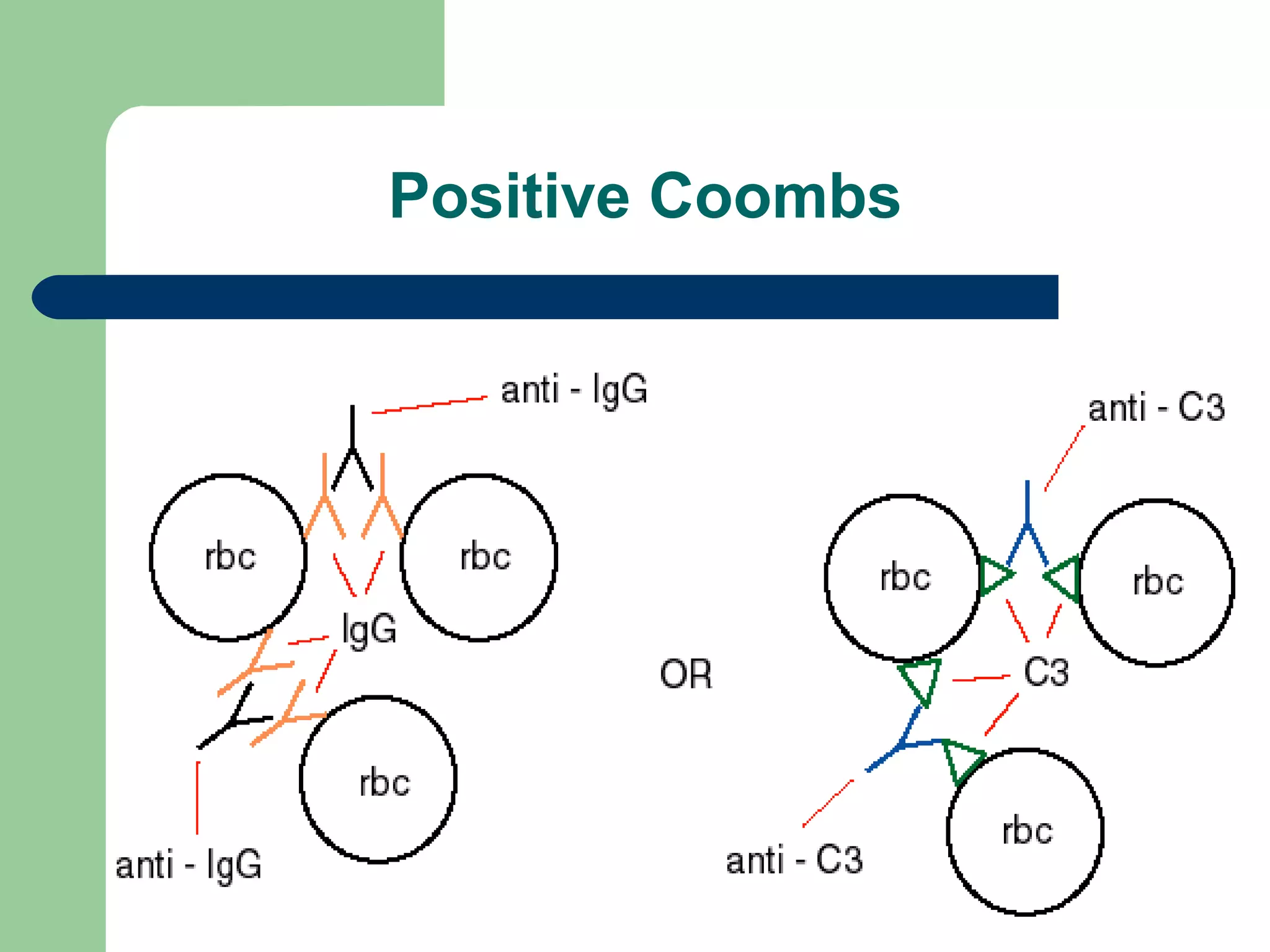
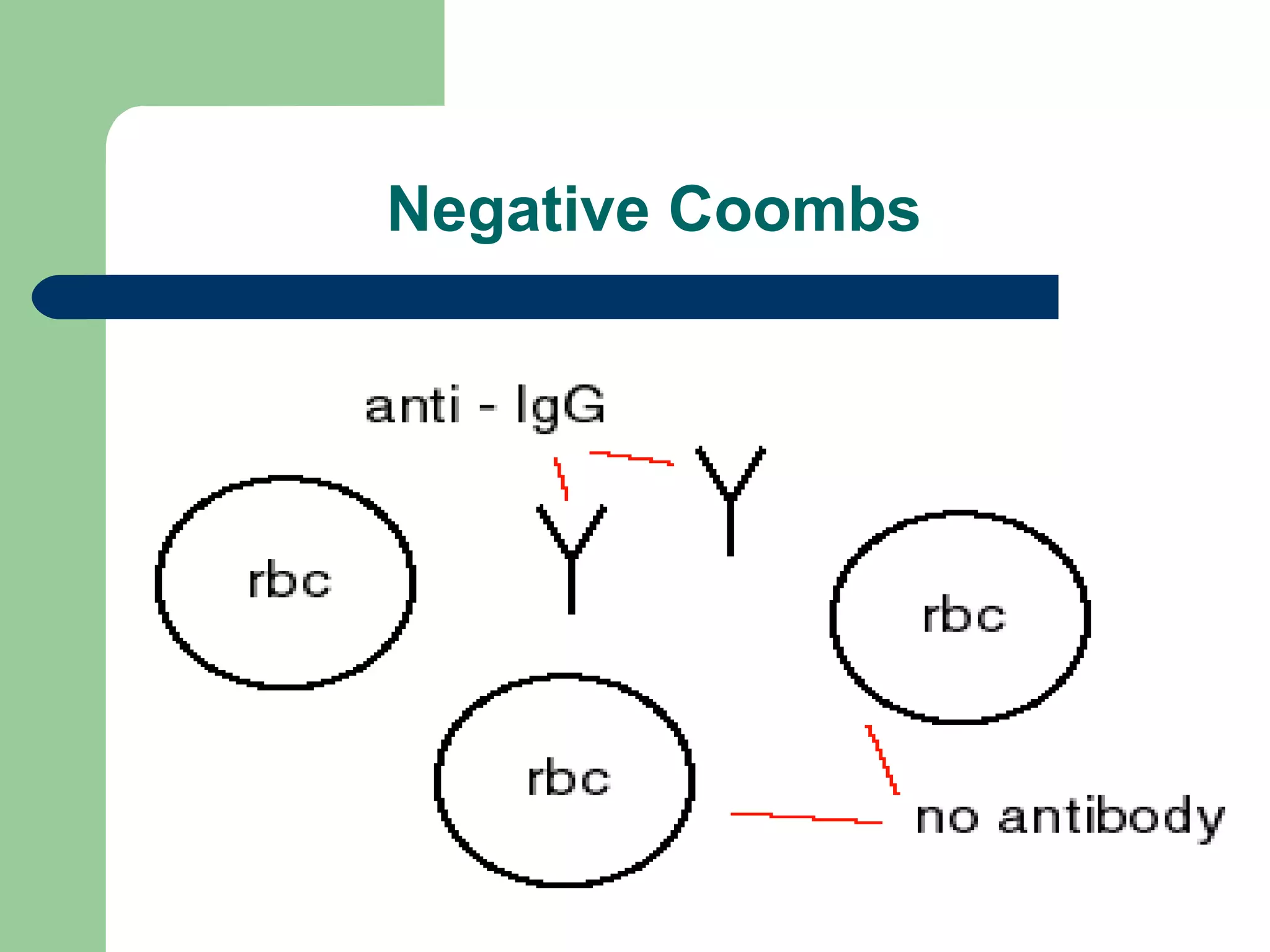
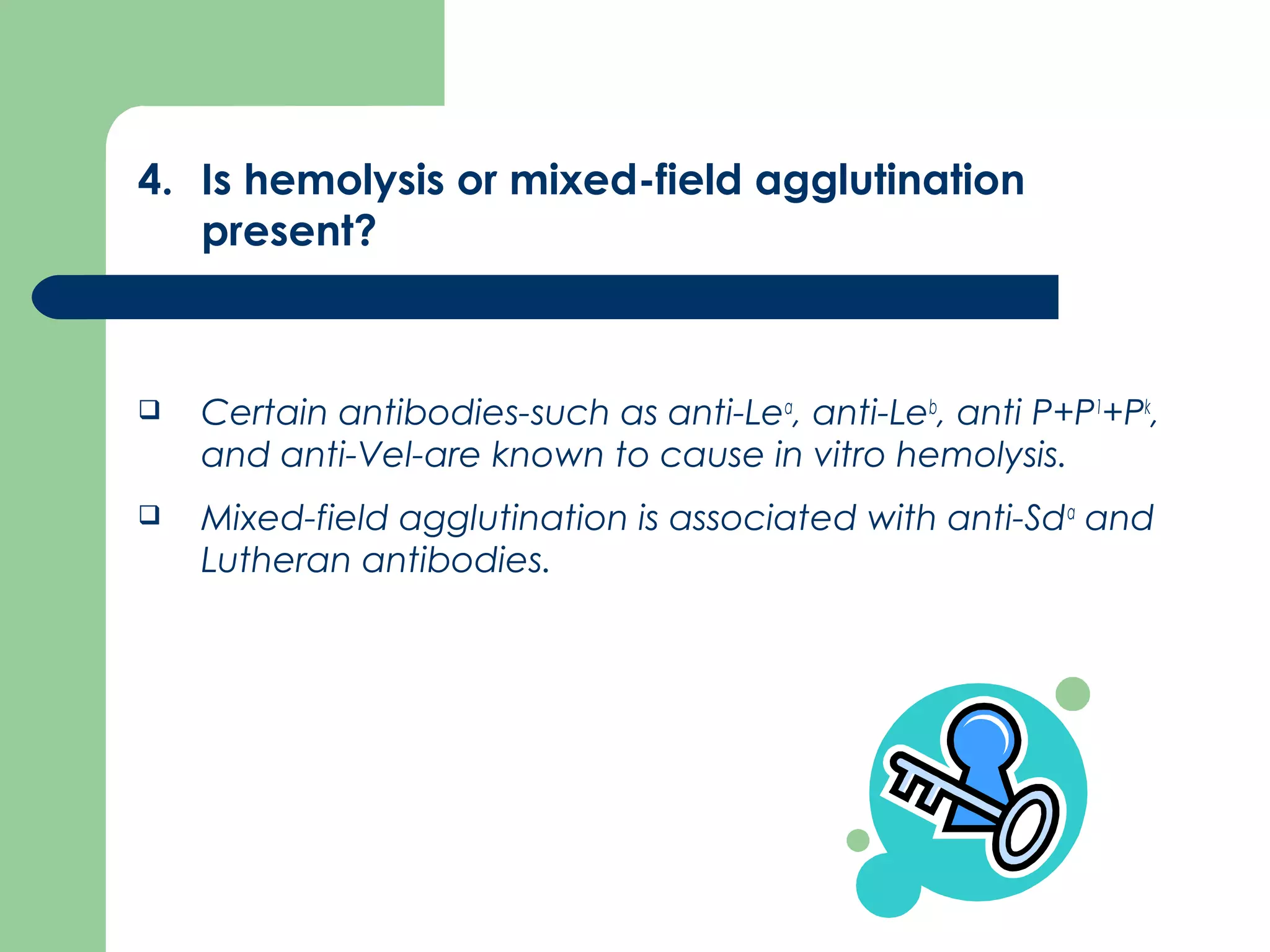
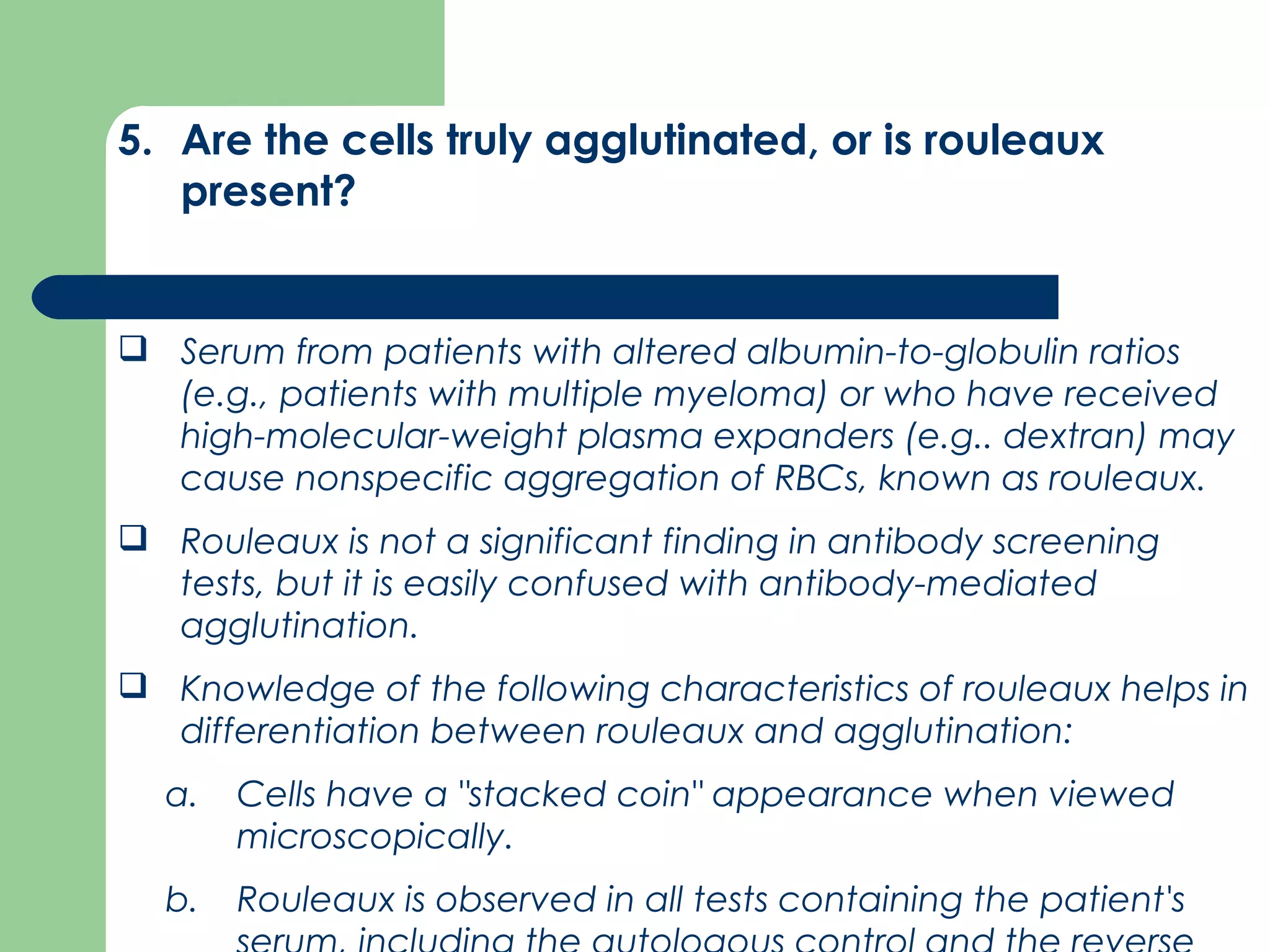
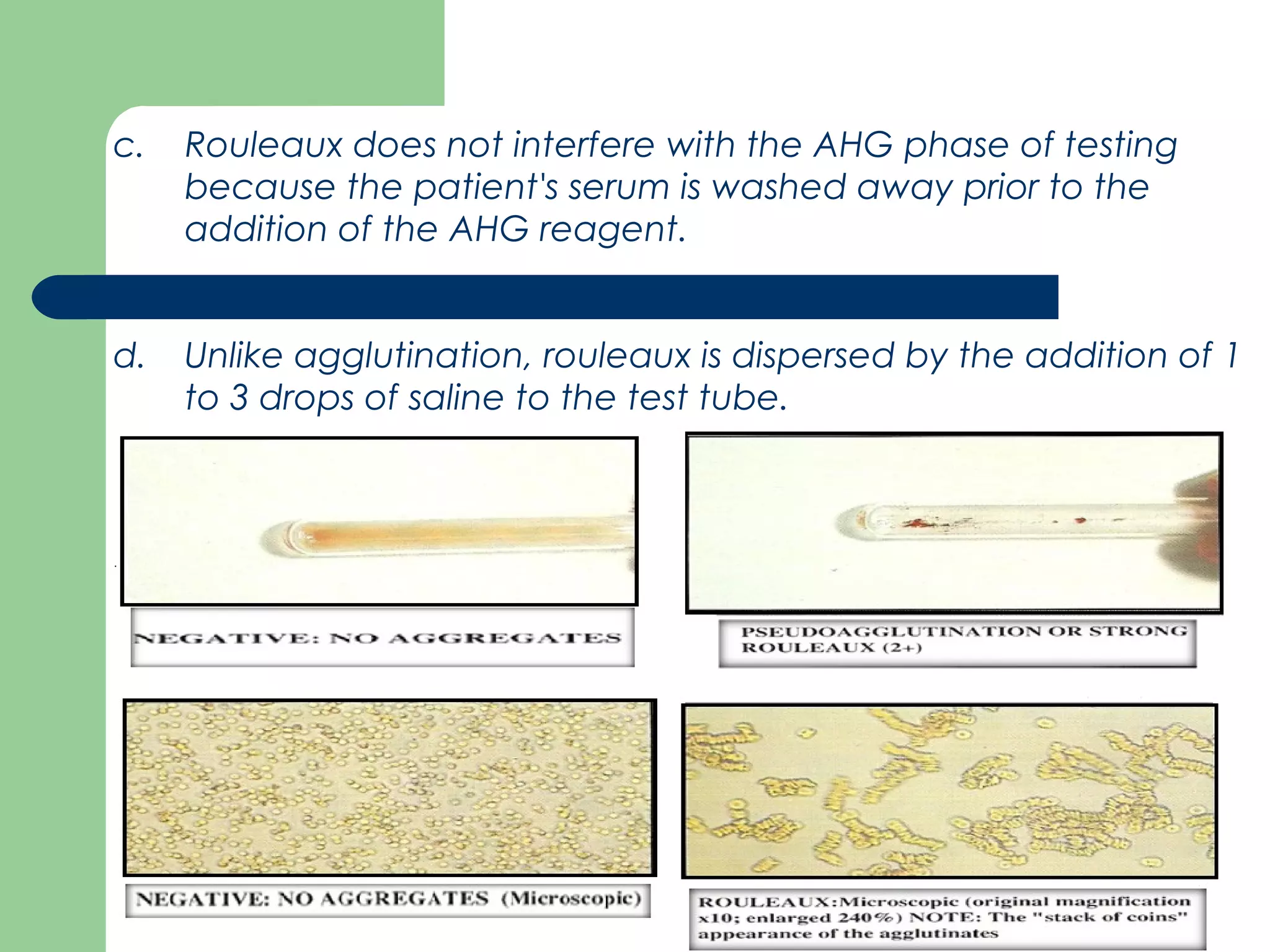
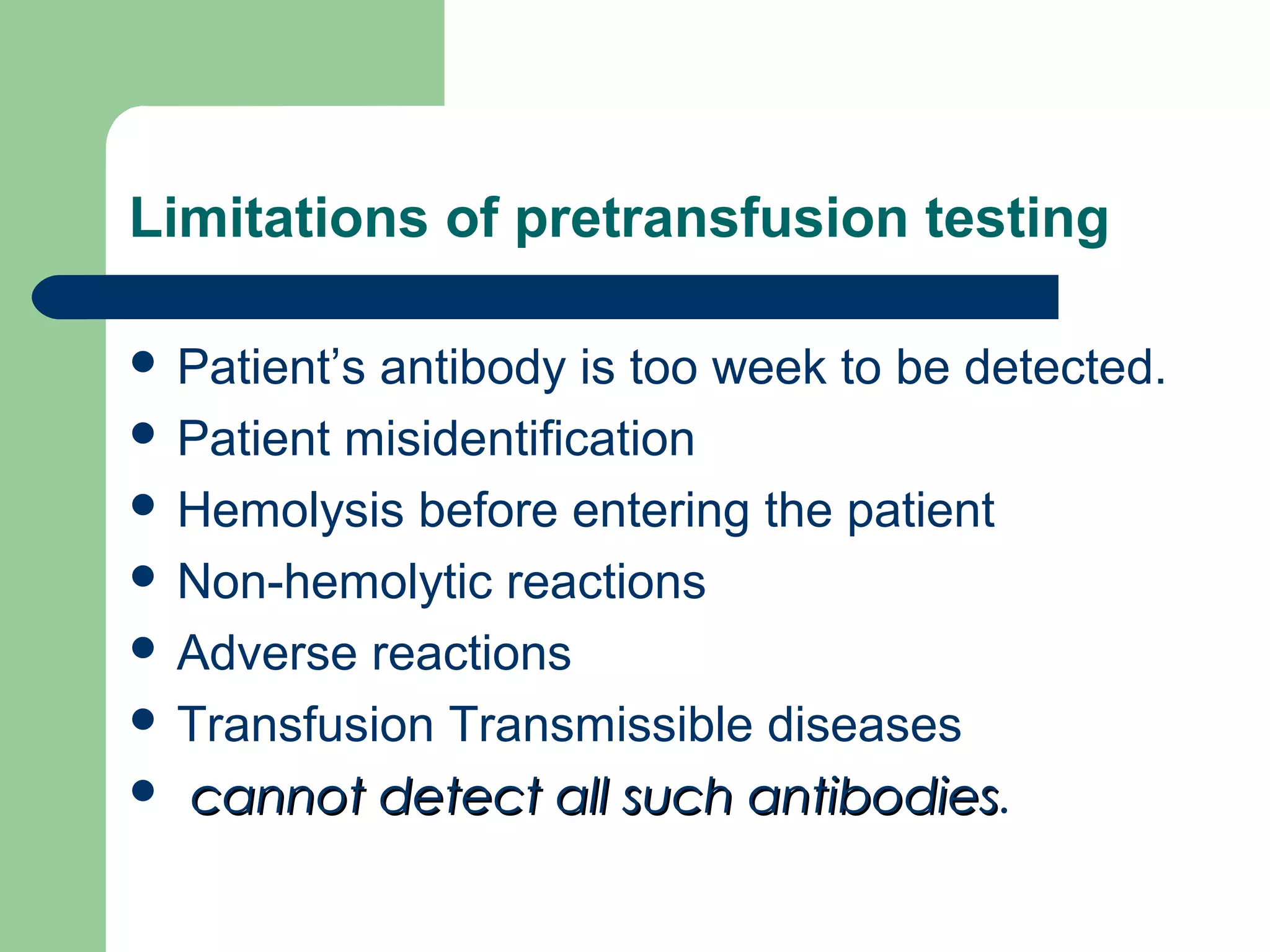
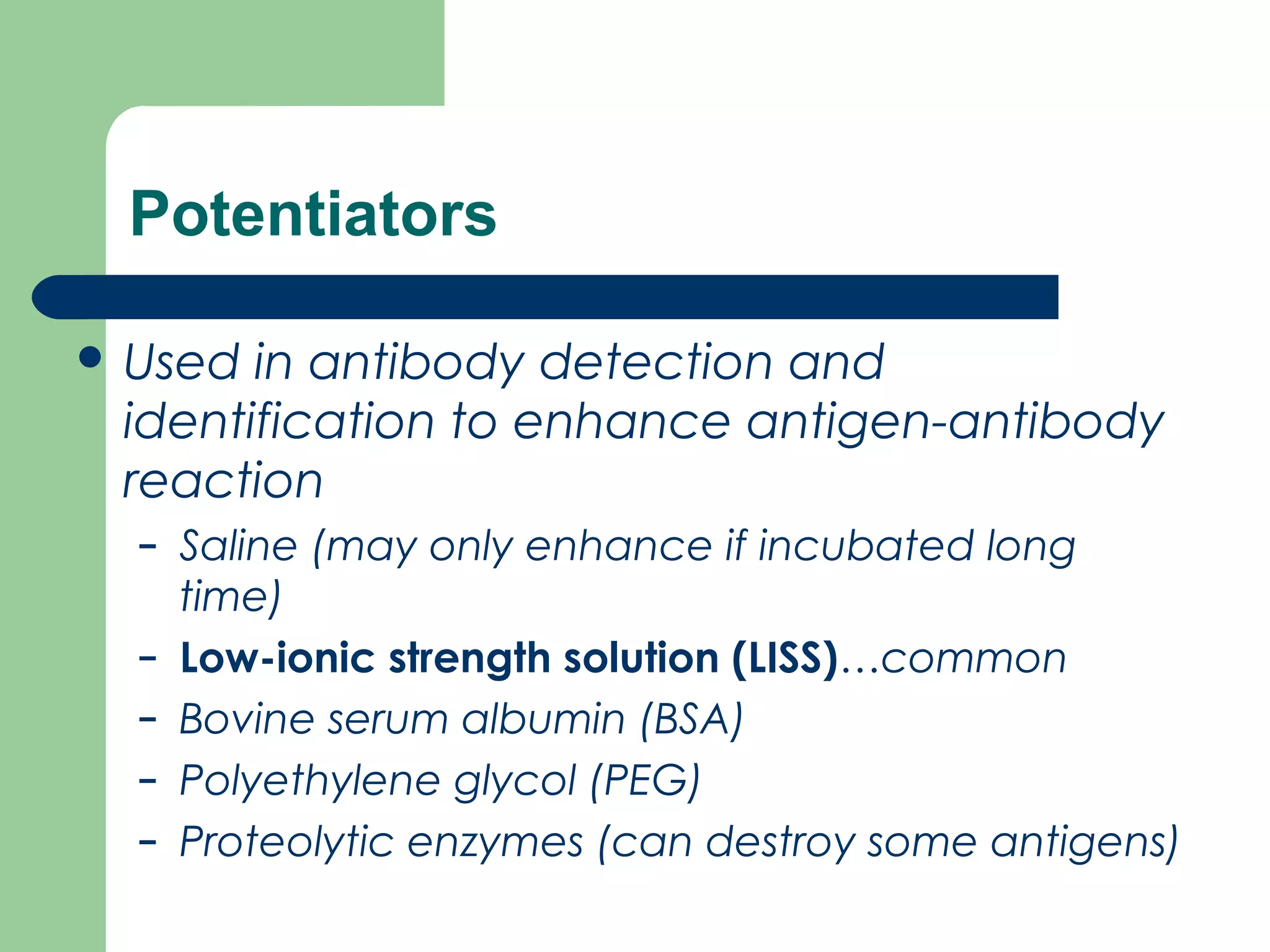
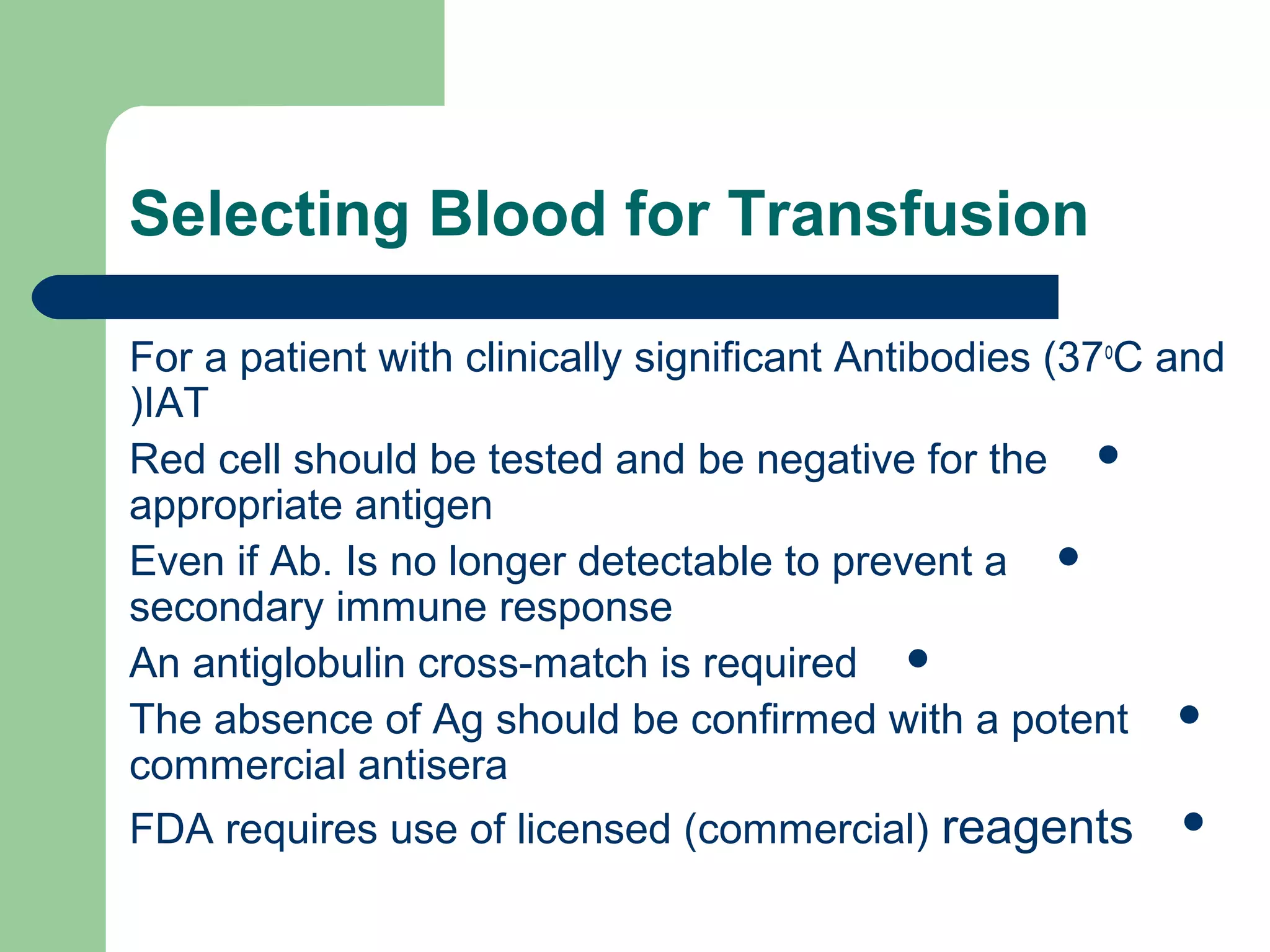
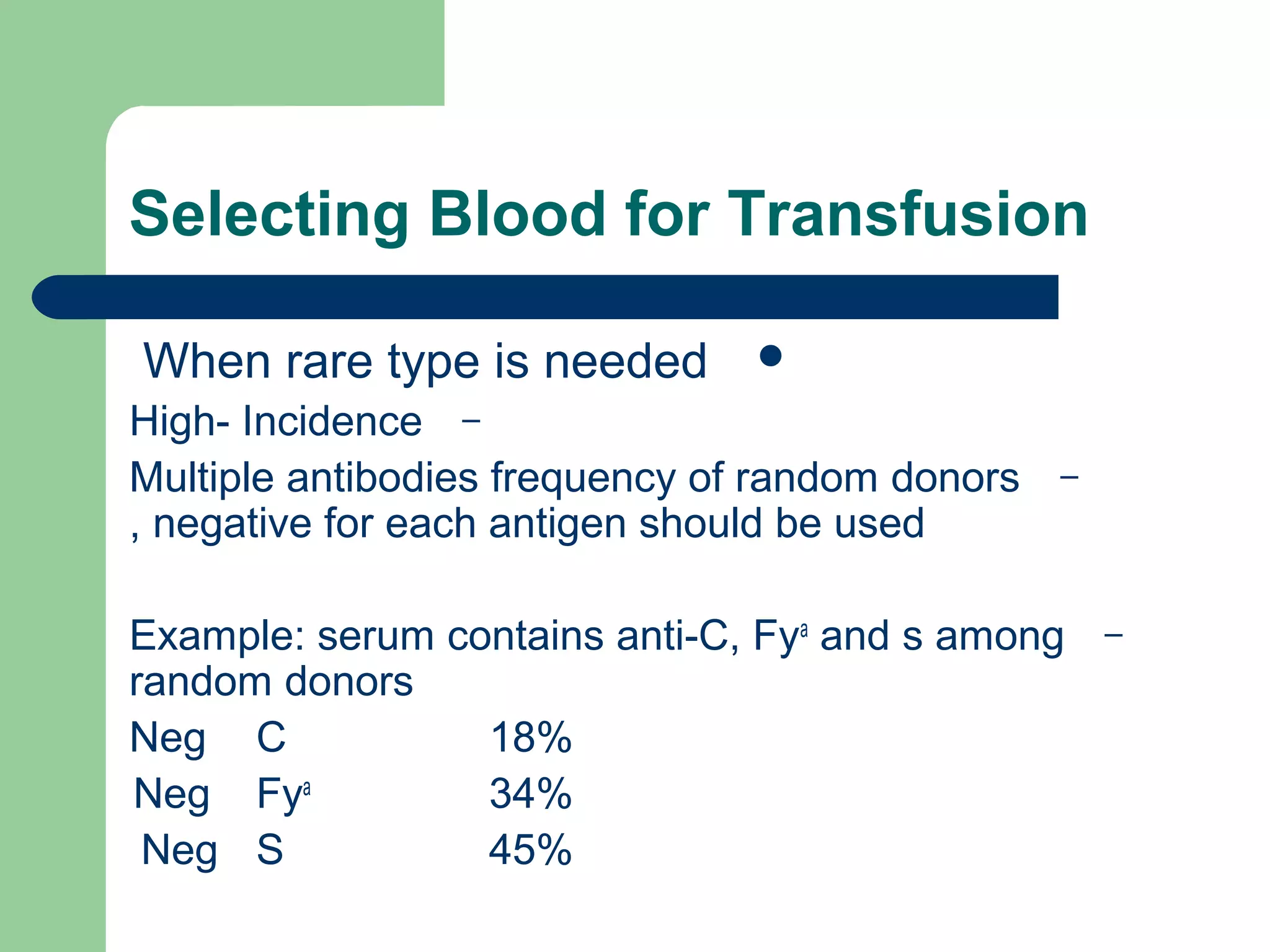
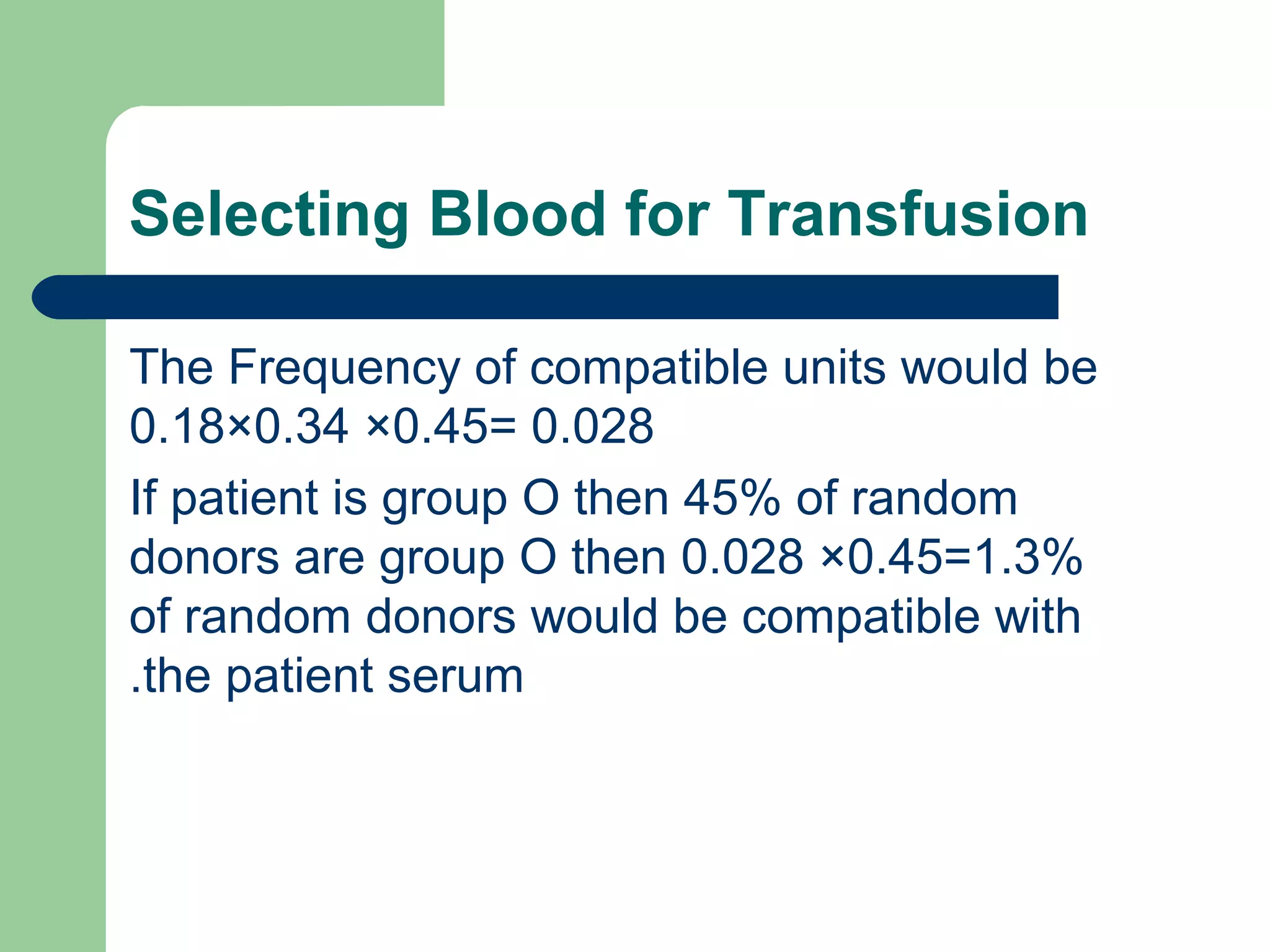
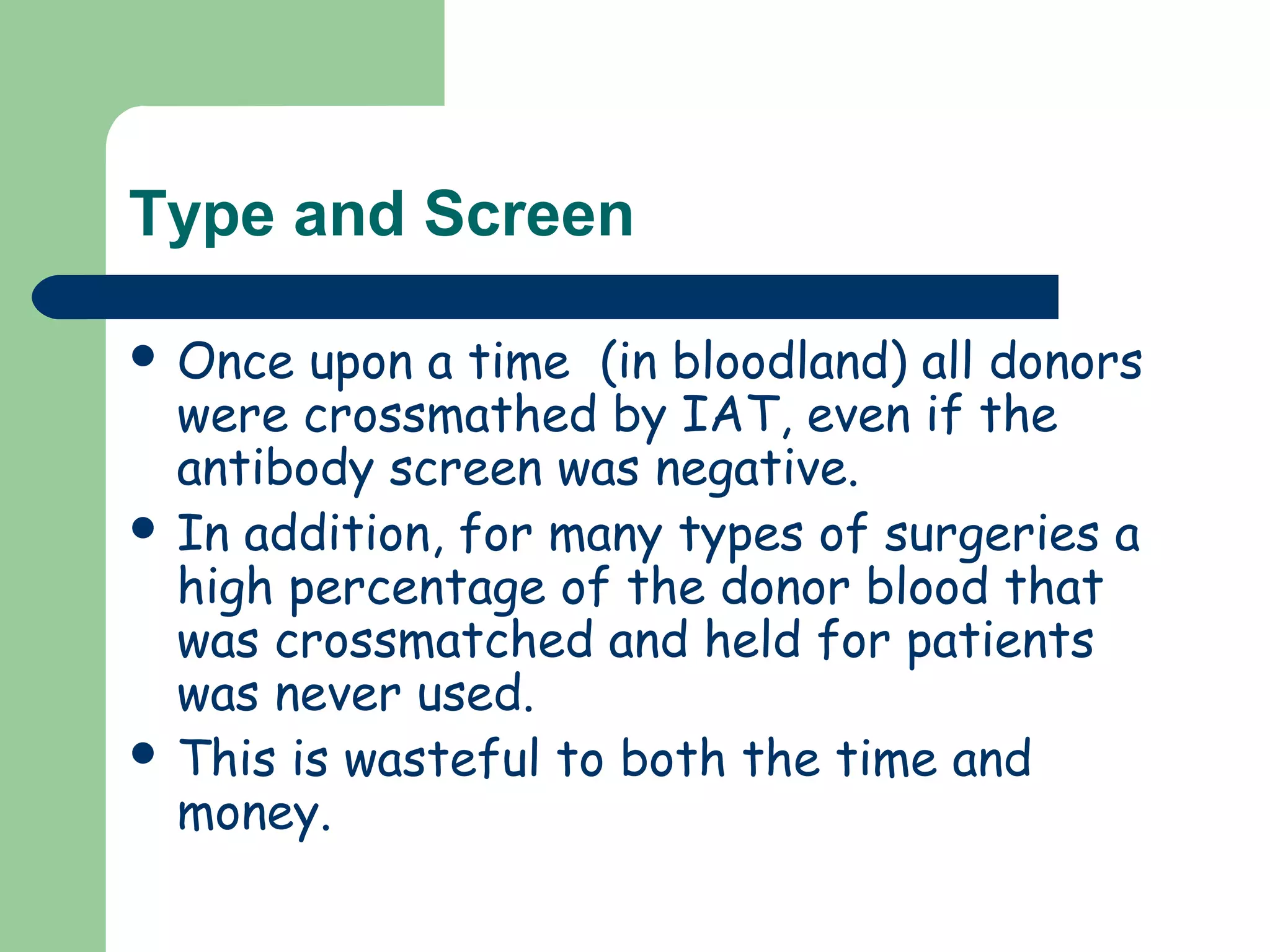
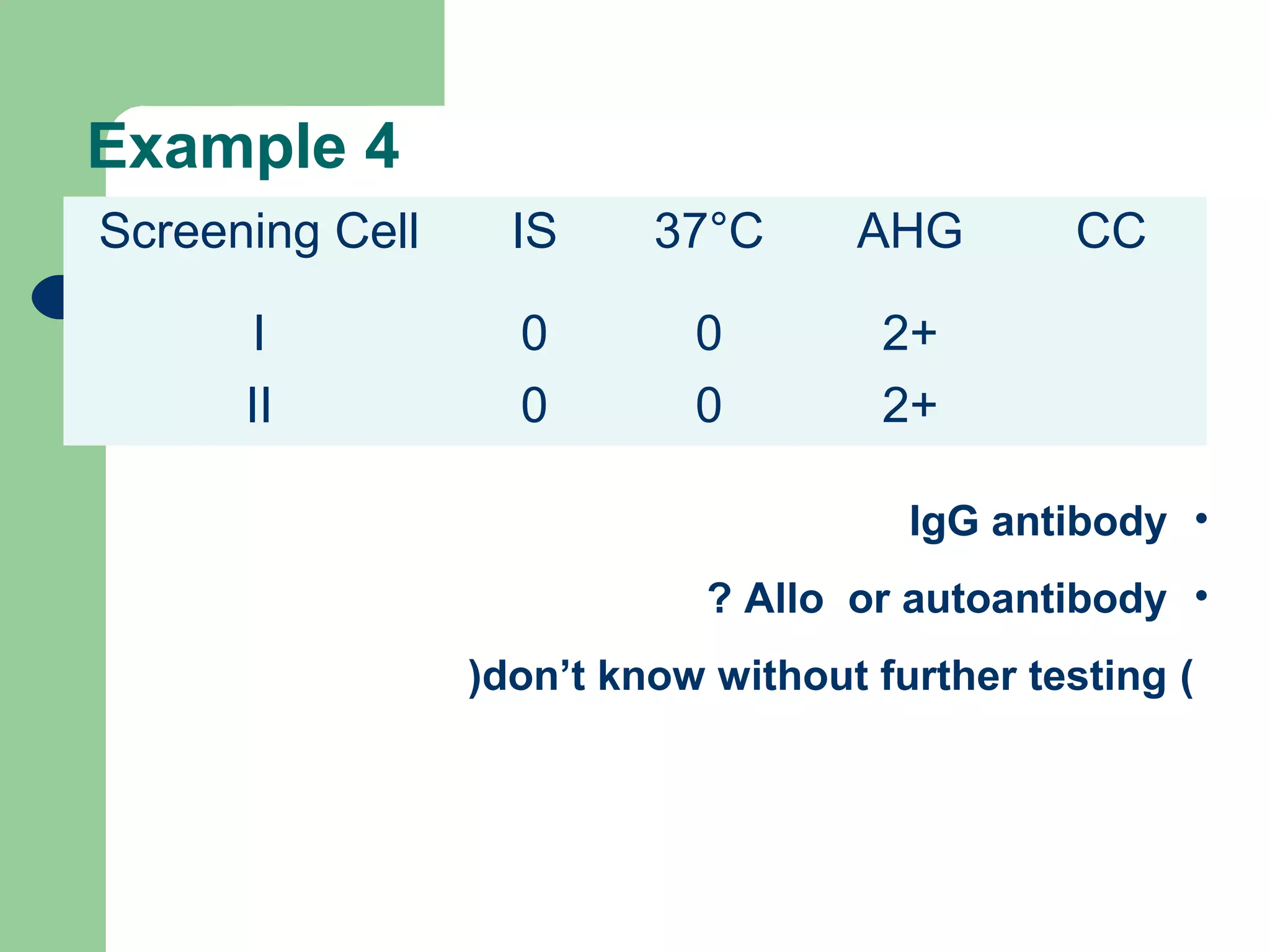
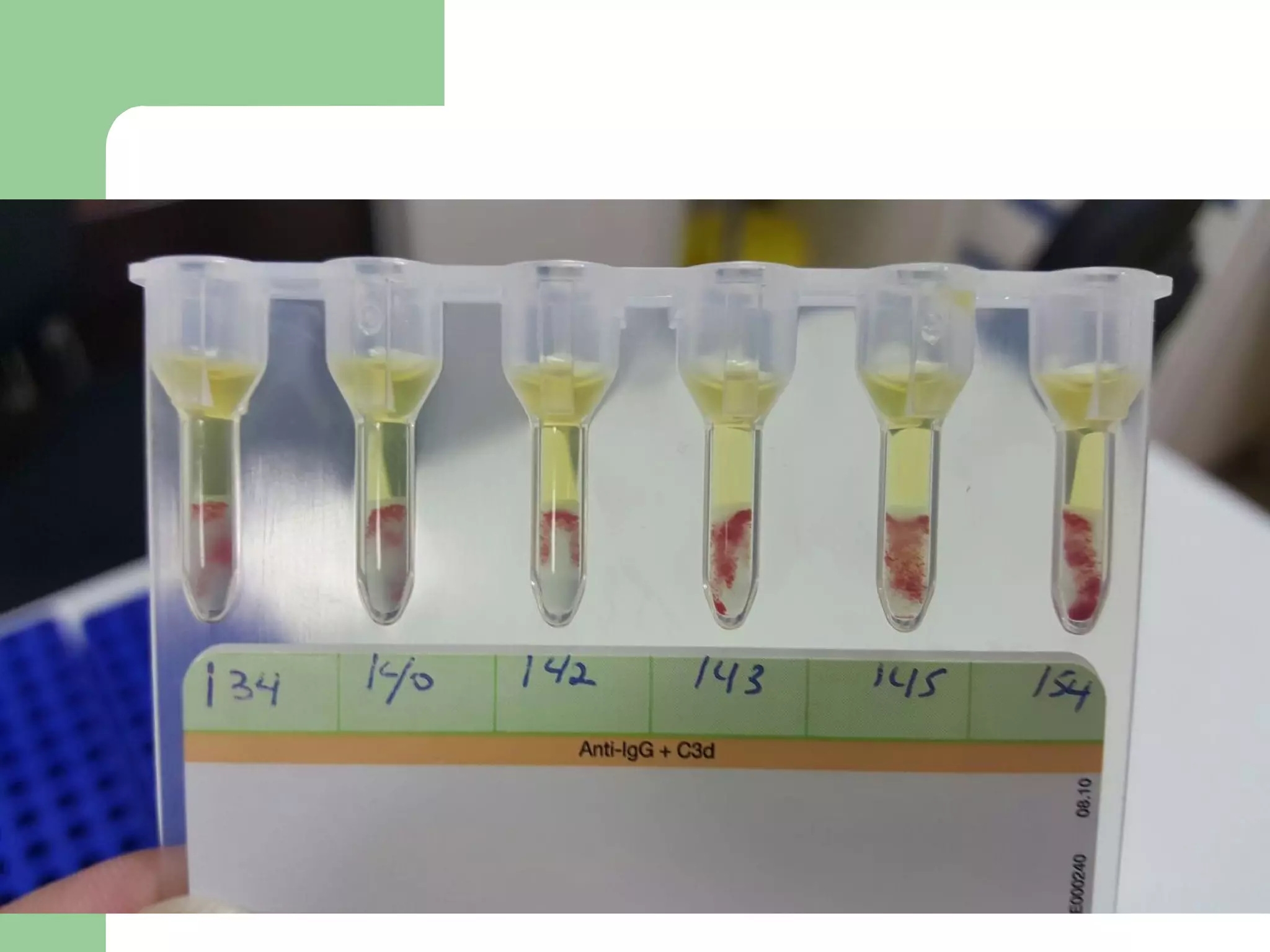
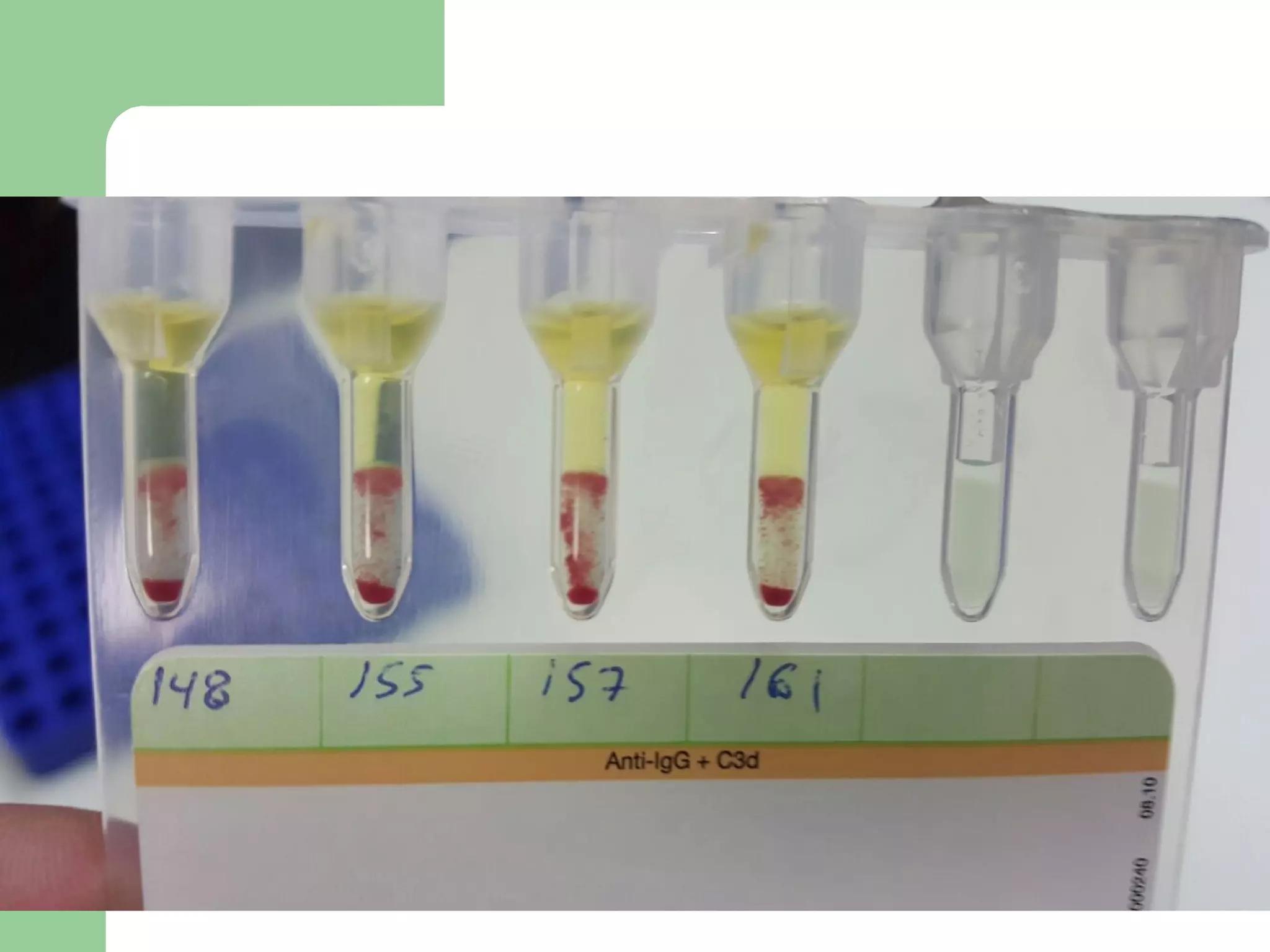
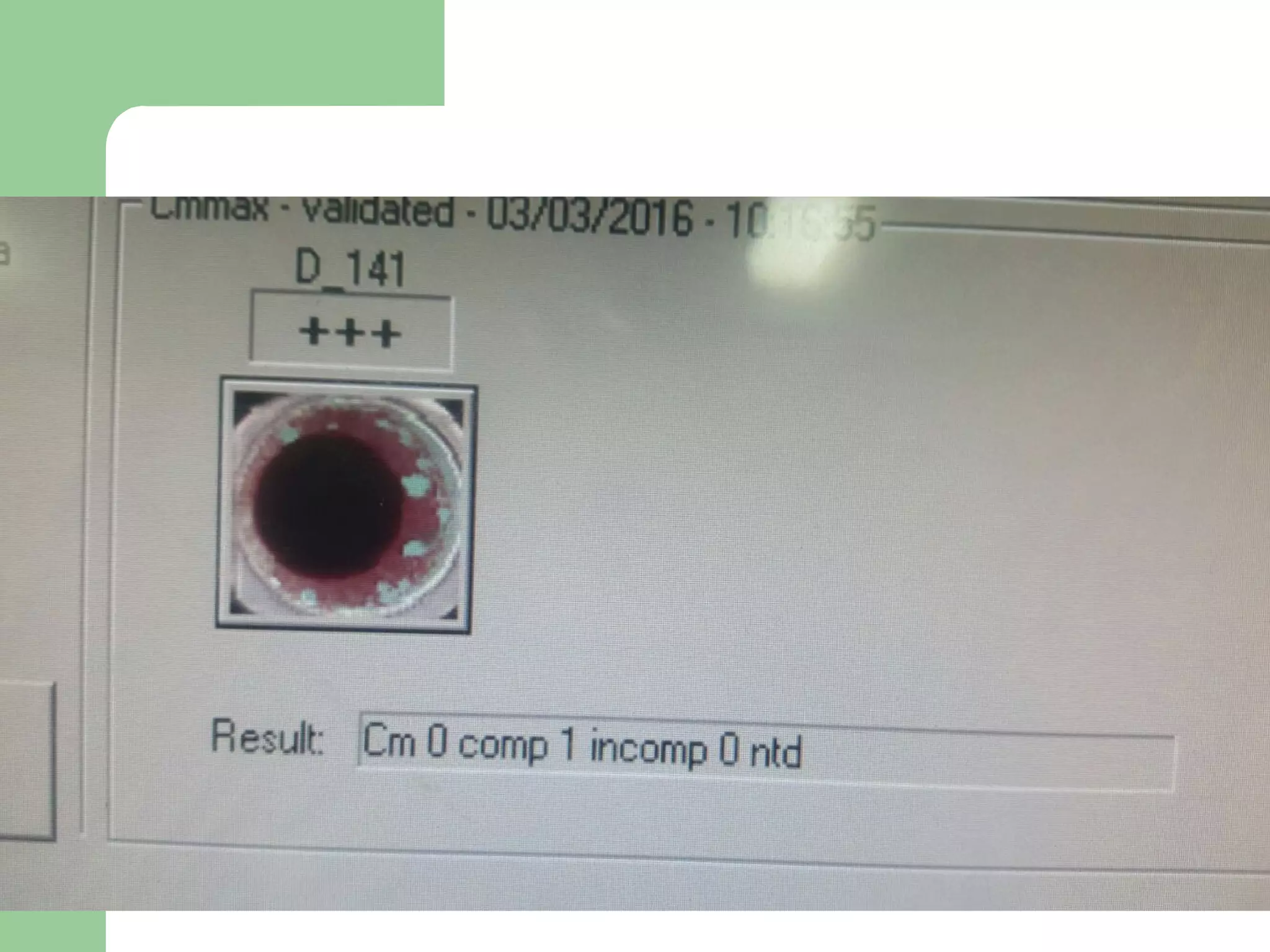
1. Antibody screening tests patient serum against reagent red blood cells to detect unexpected antibodies that could destroy transfused donor cells.
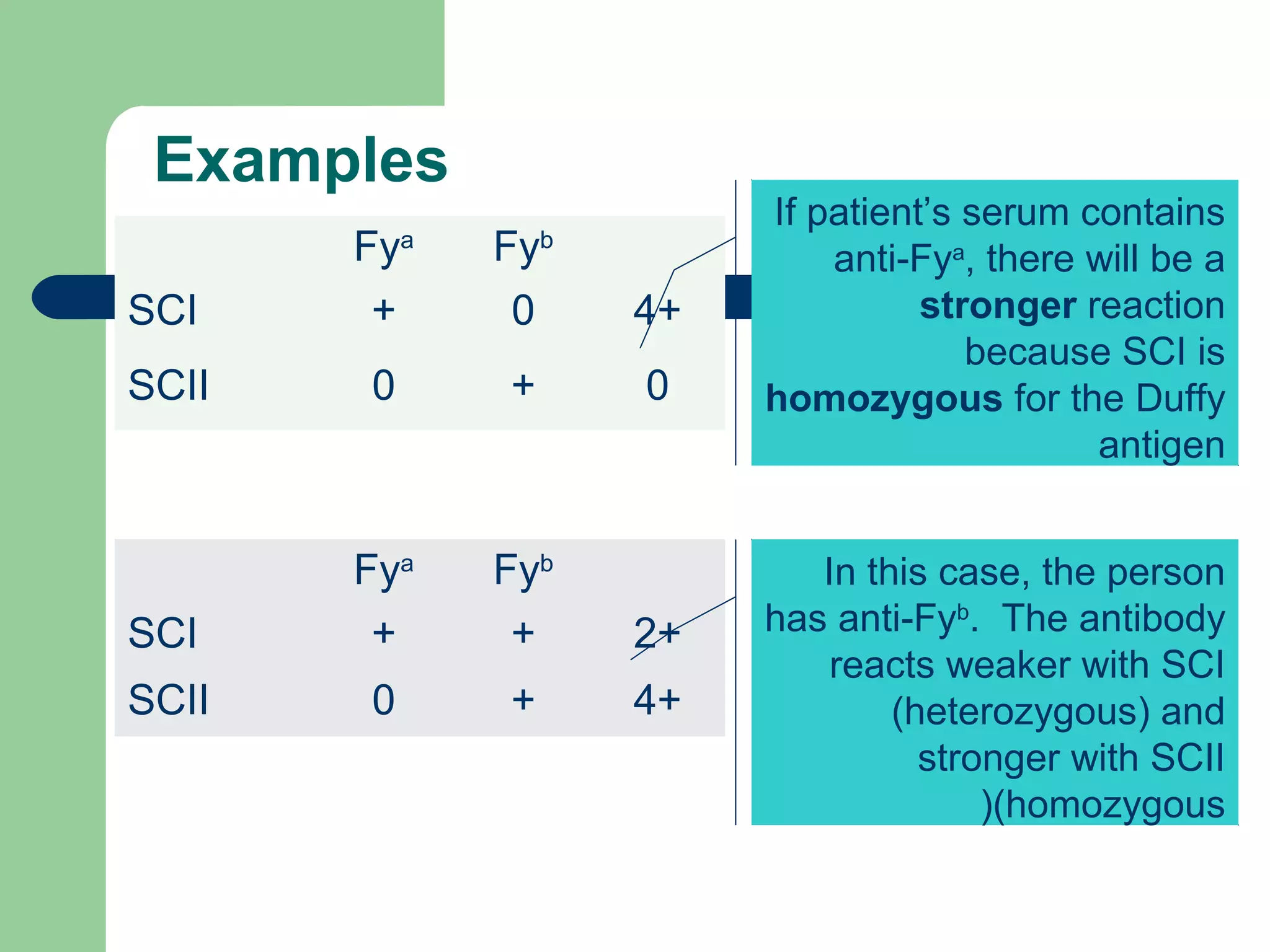
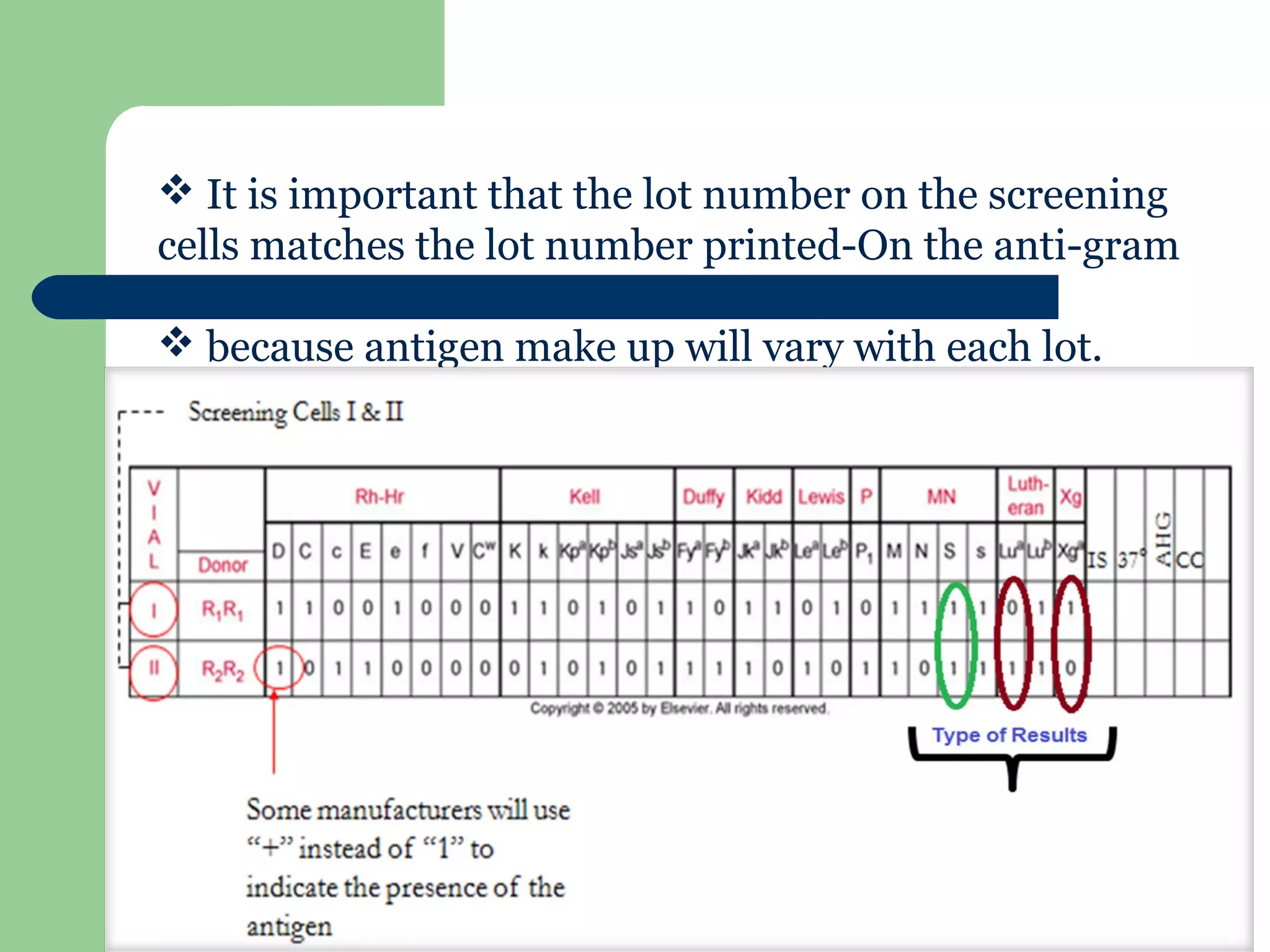
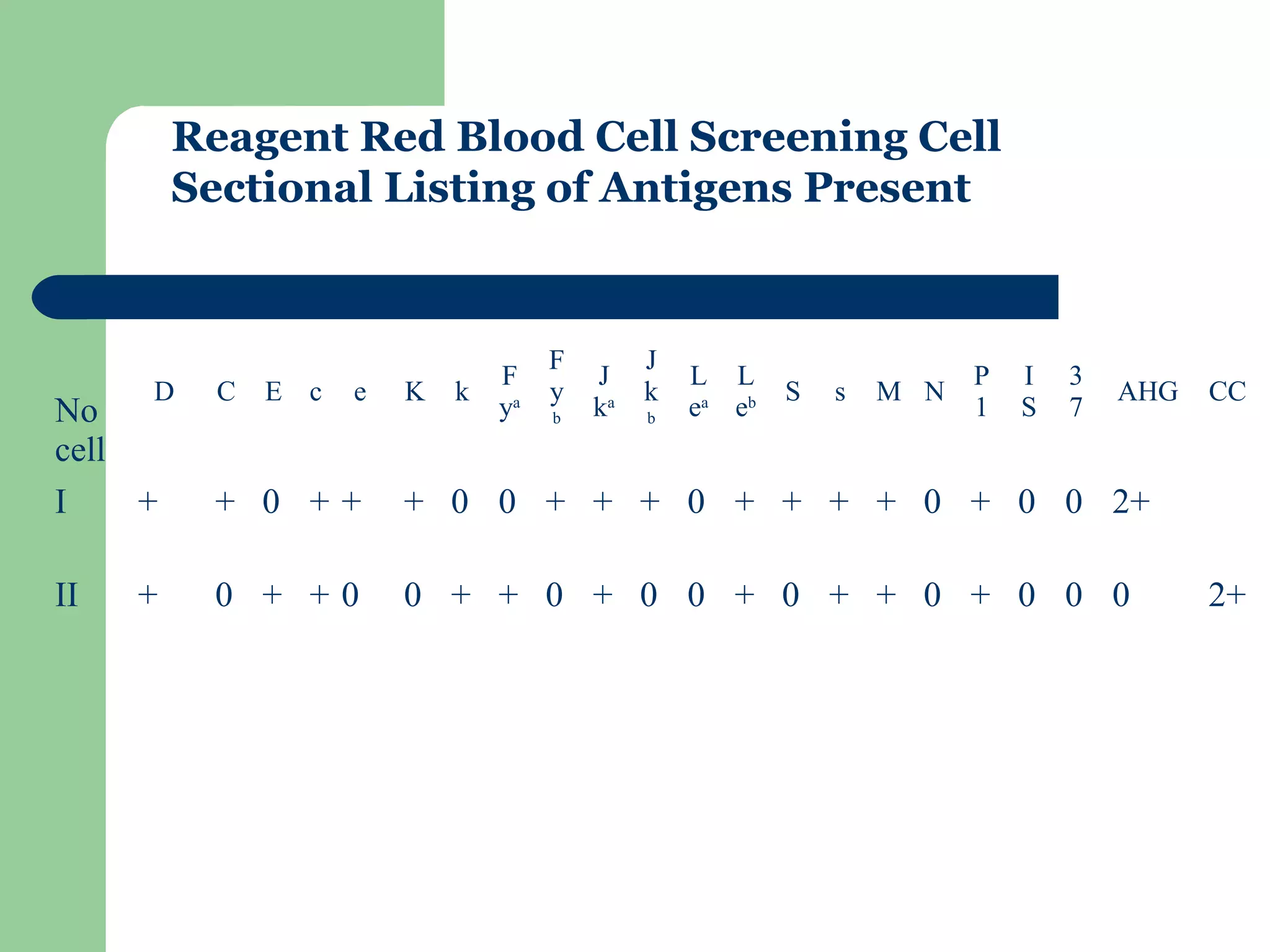
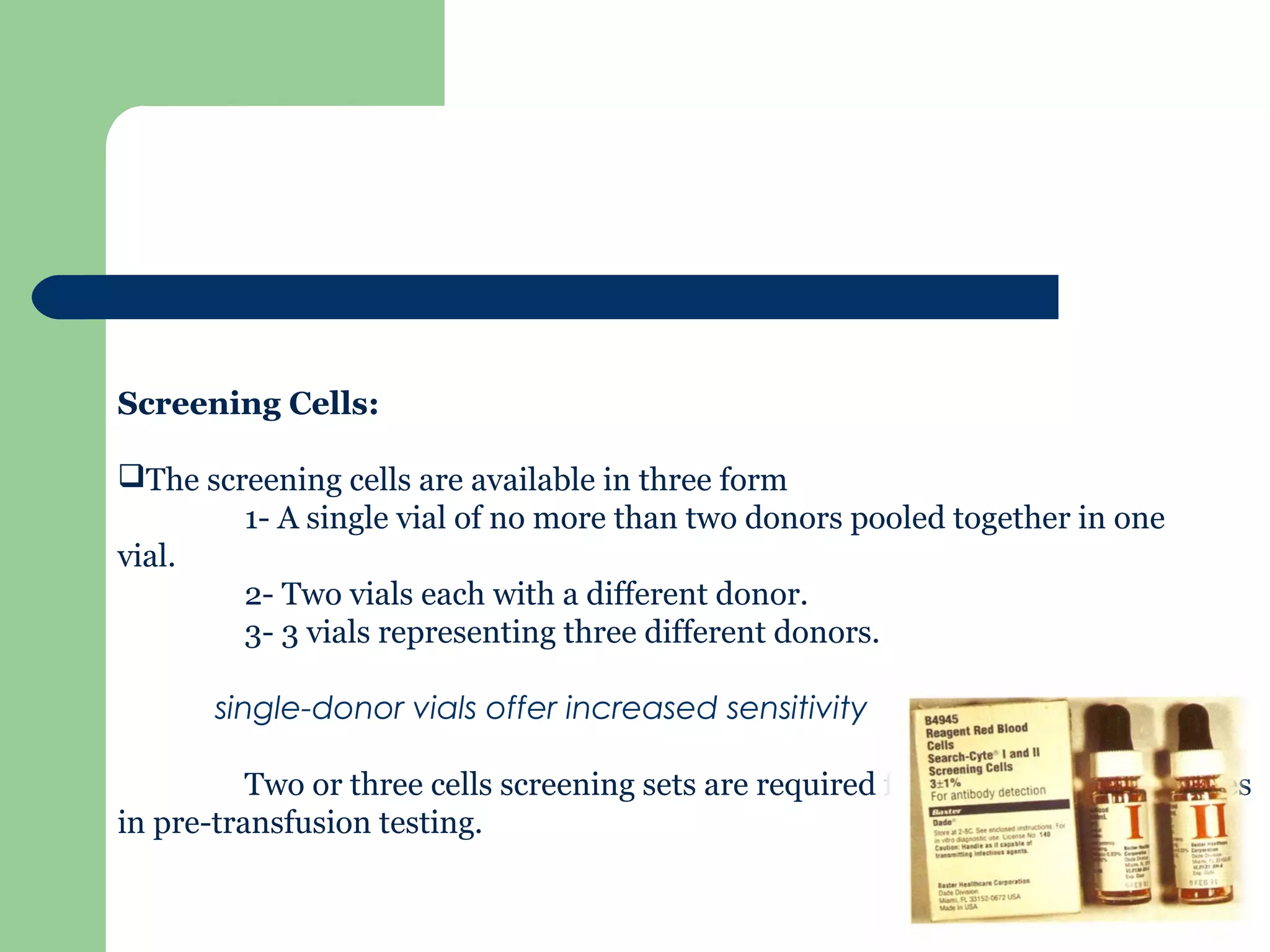
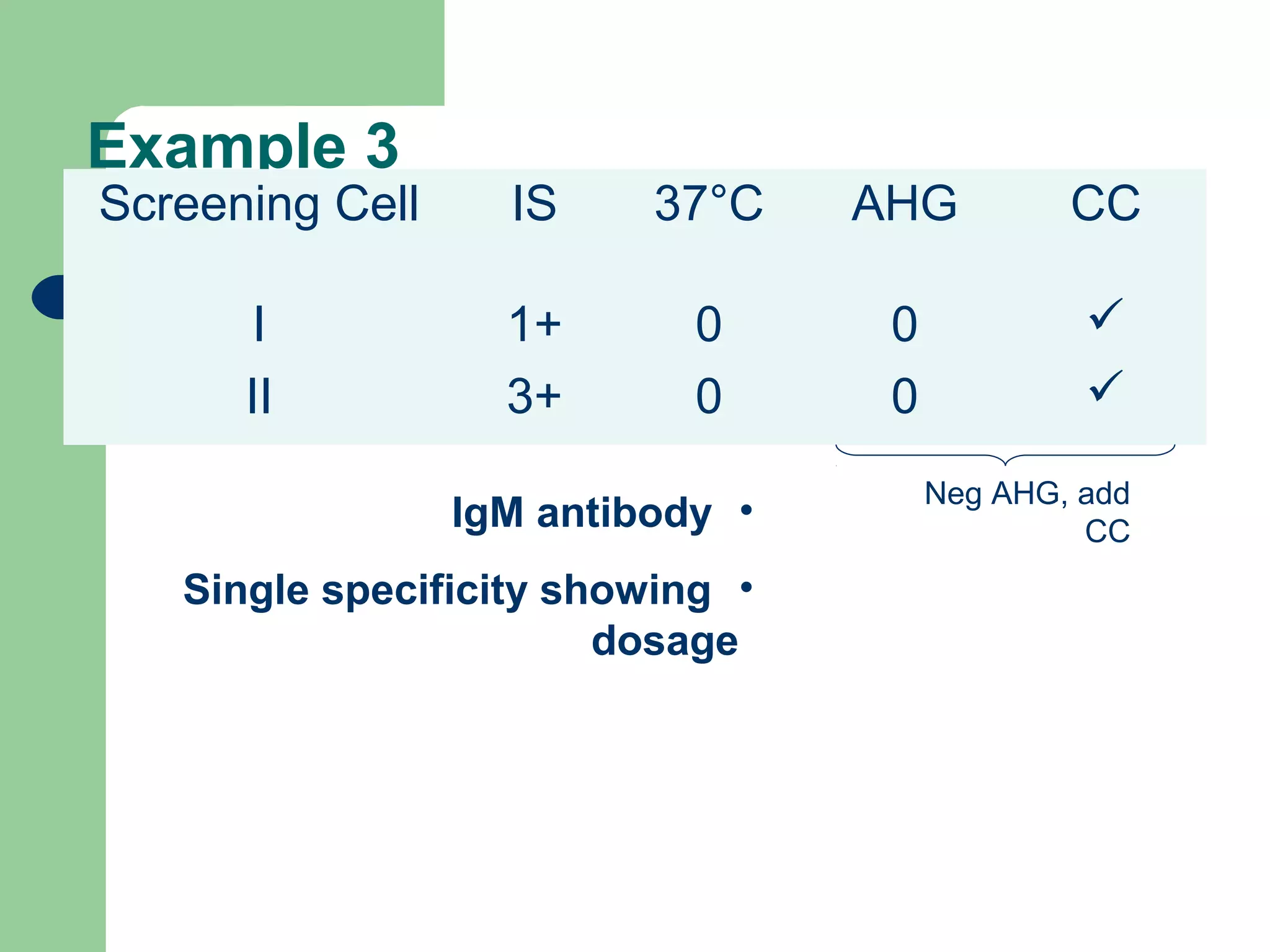
2. Screening cells must contain many common antigens and include some cells with homozygous antigen expression to detect weakly reacting antibodies.
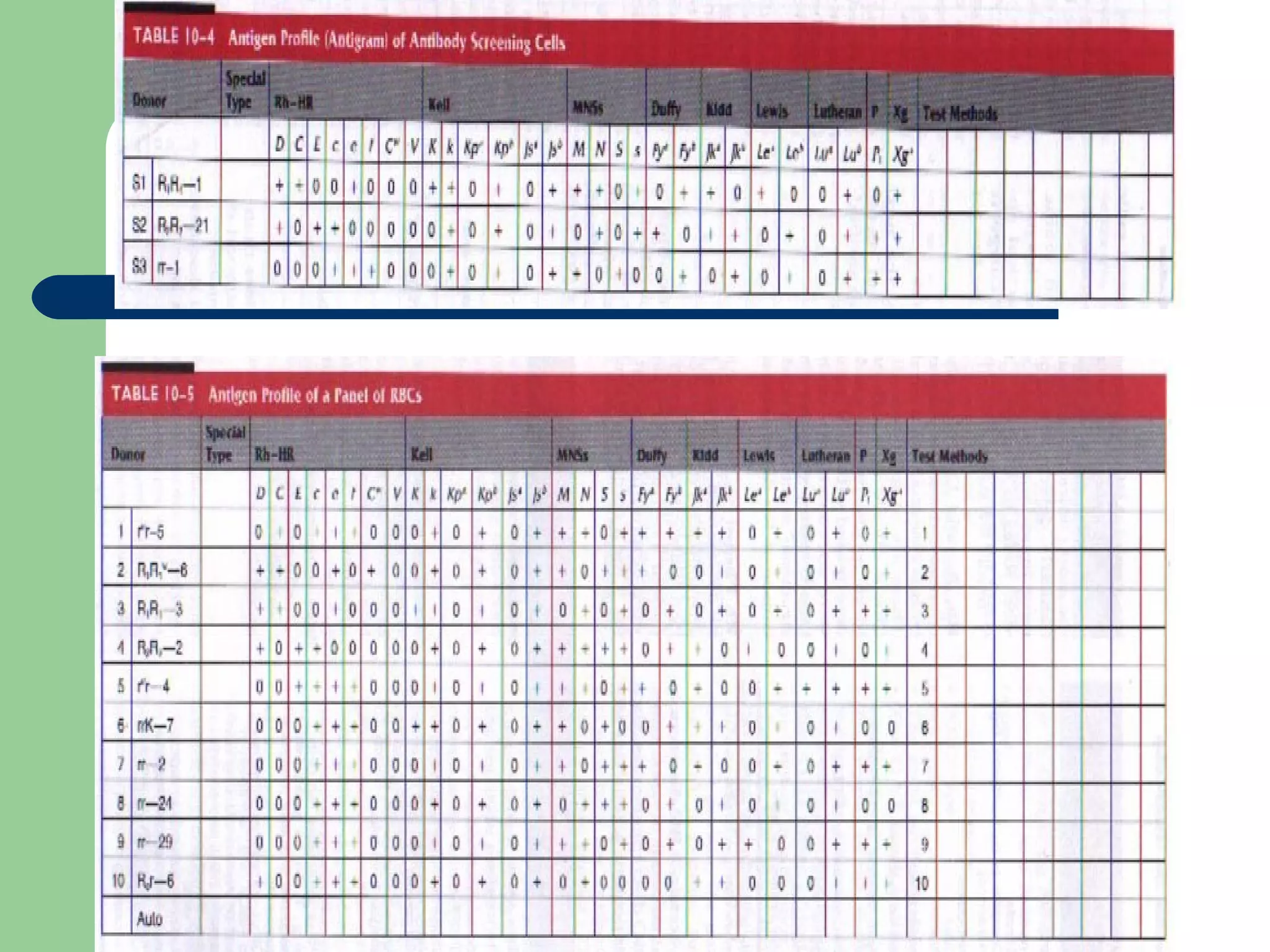
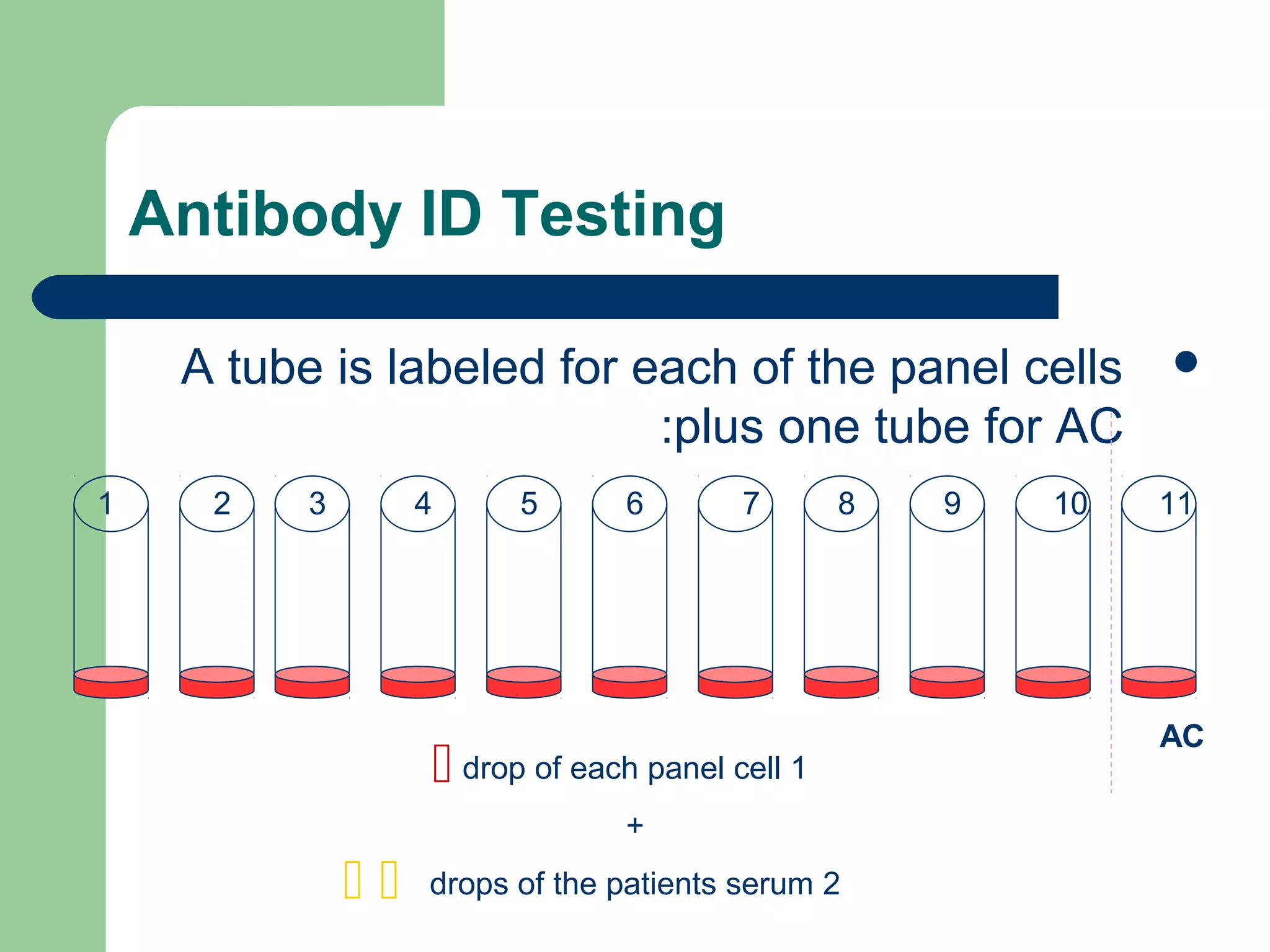
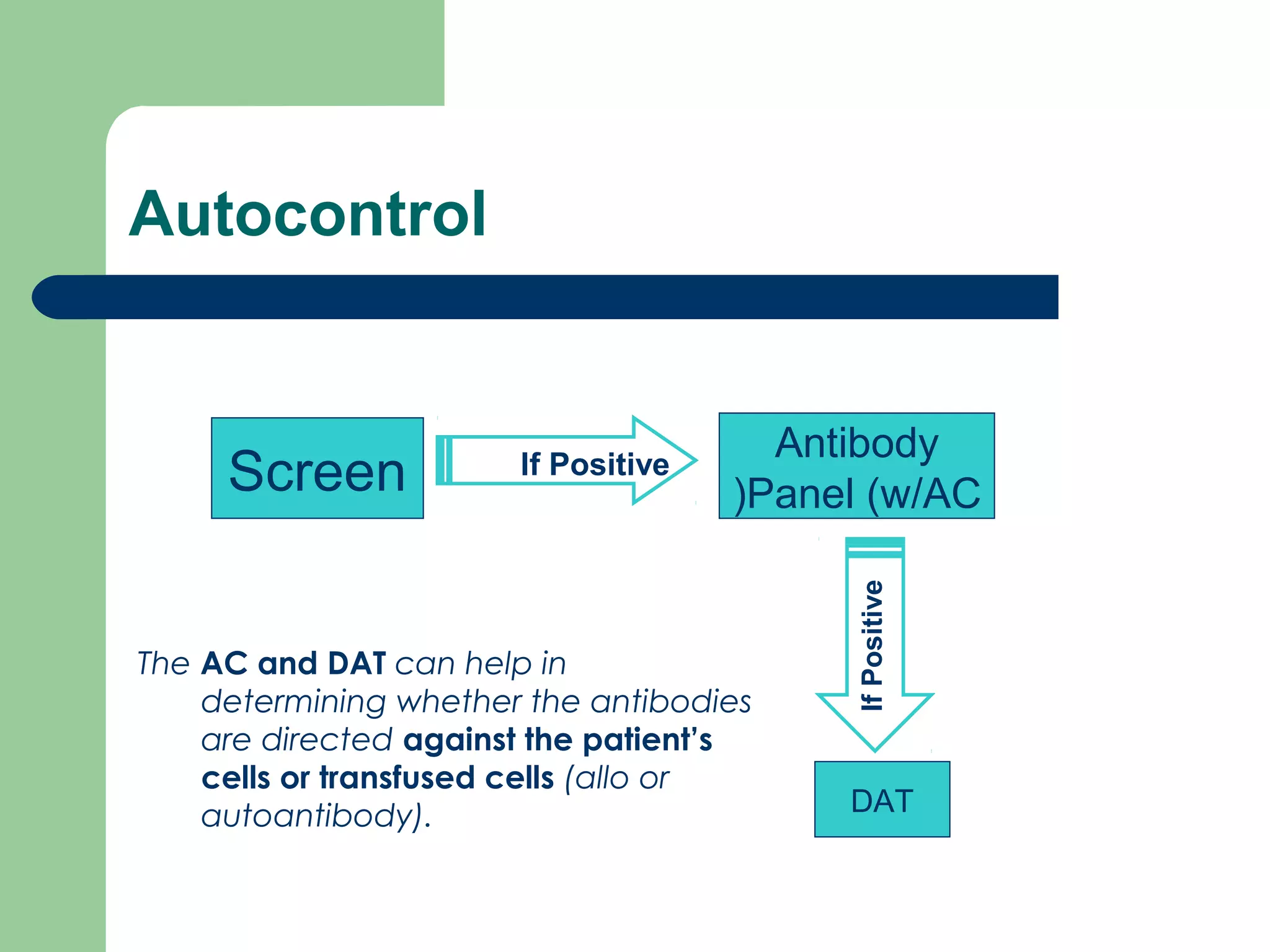
3. A positive antibody screen requires antibody identification testing to determine the antibody specificity so that antigen-negative blood can be transfused.