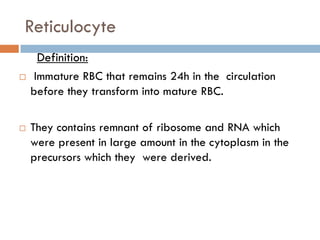
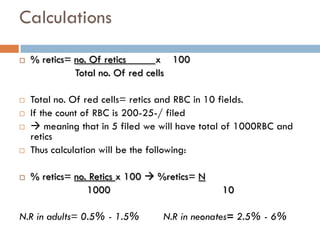
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that remain in circulation for 24 hours before maturing into full red blood cells. A reticulocyte count helps monitor anemic patients under treatment and determines bone marrow activity. The test involves staining a blood sample with a supravital dye that binds to ribosomes and nucleic acids in reticulocytes. Stained reticulocytes appear blue and are counted under a microscope to calculate the percentage of reticulocytes compared to total red blood cells, indicating bone marrow response to anemia or treatment.