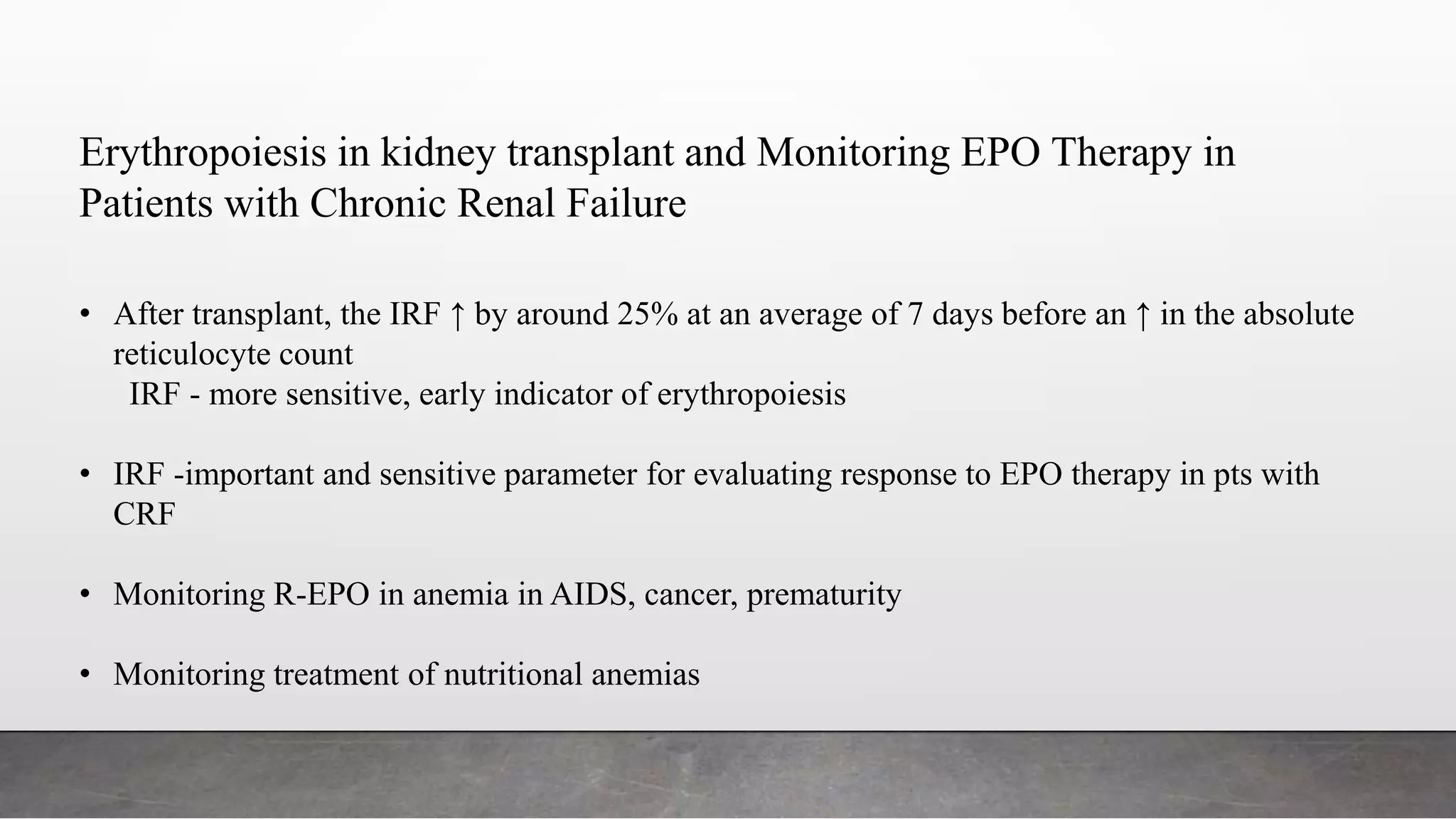
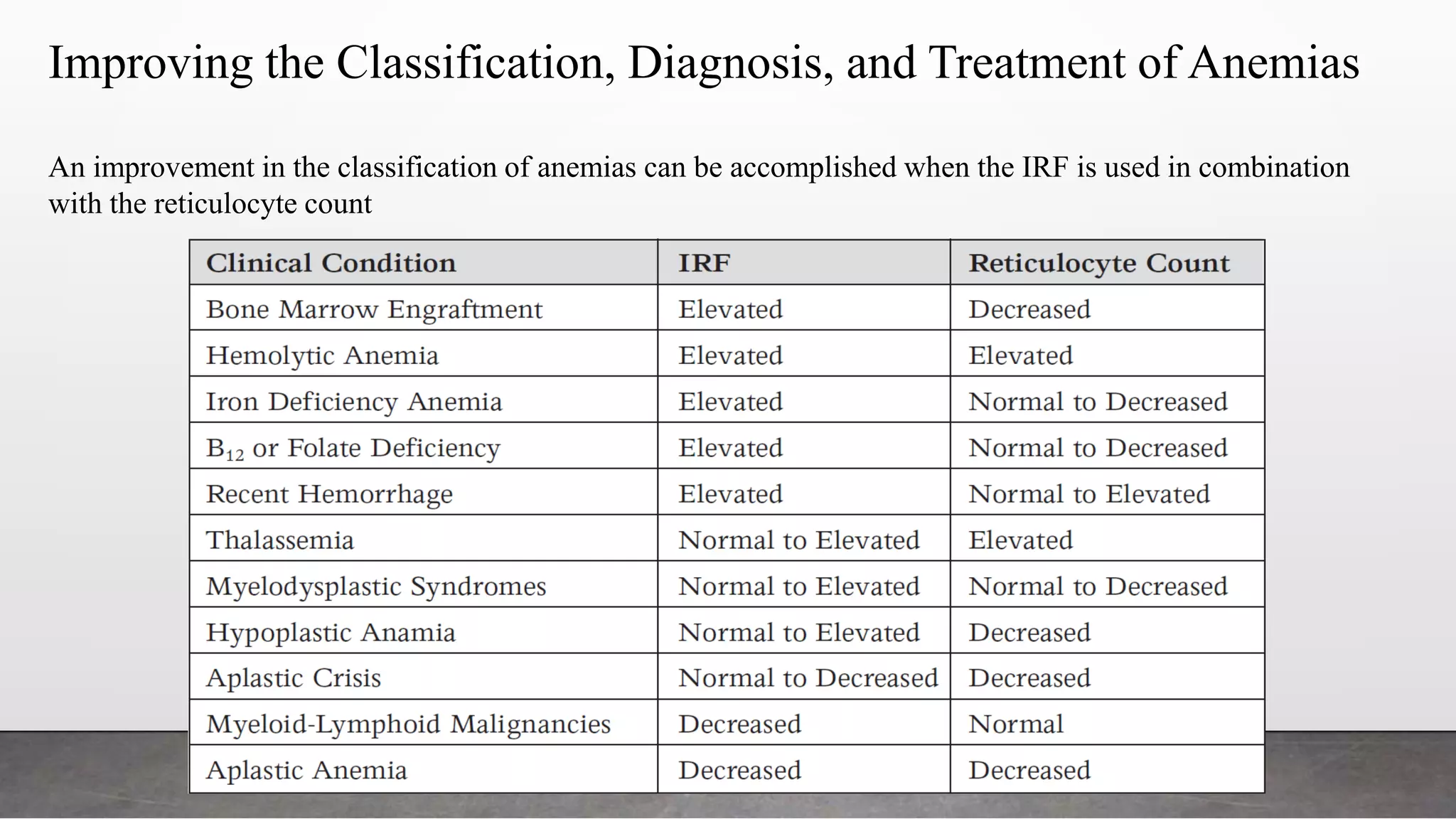
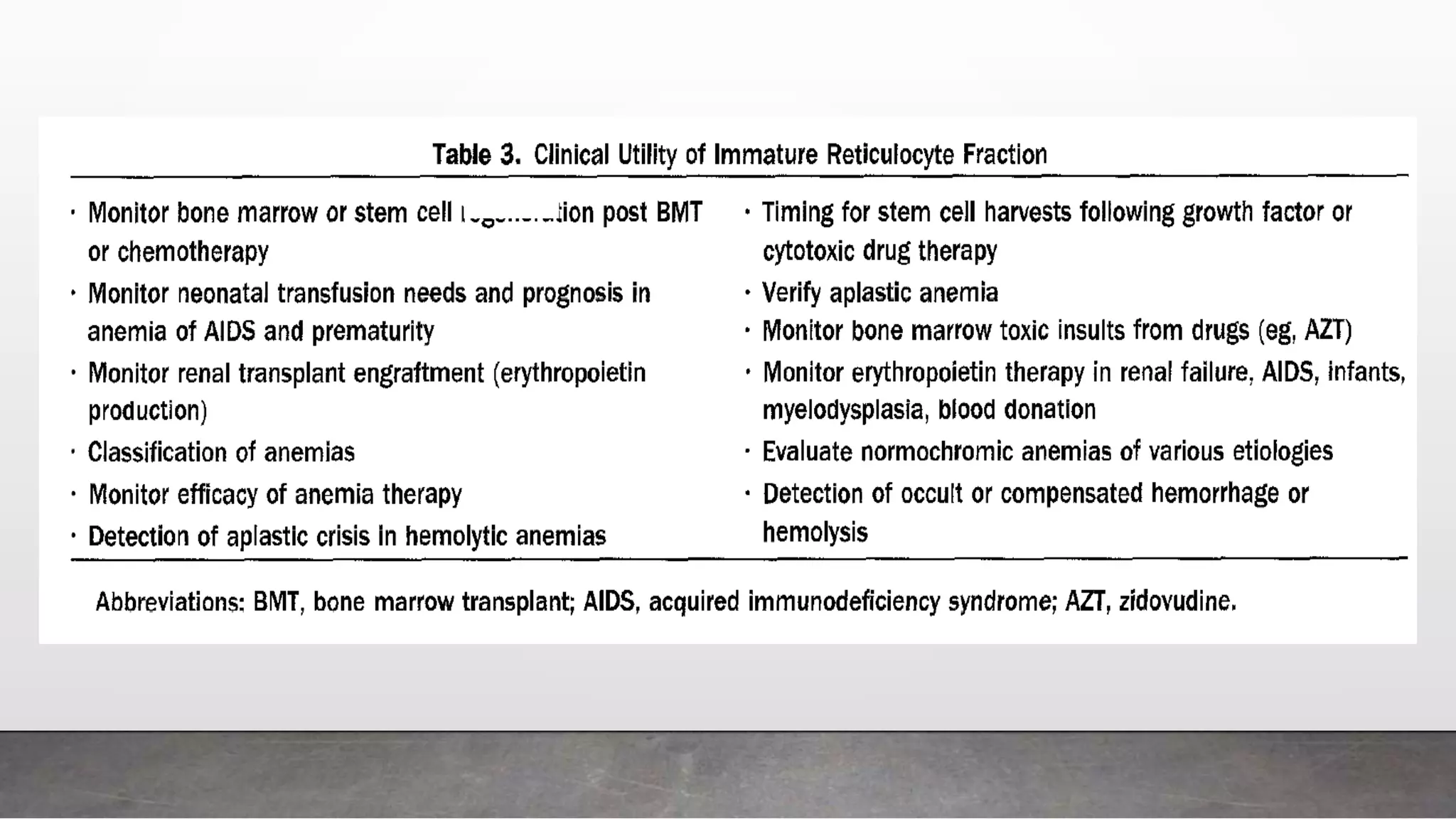
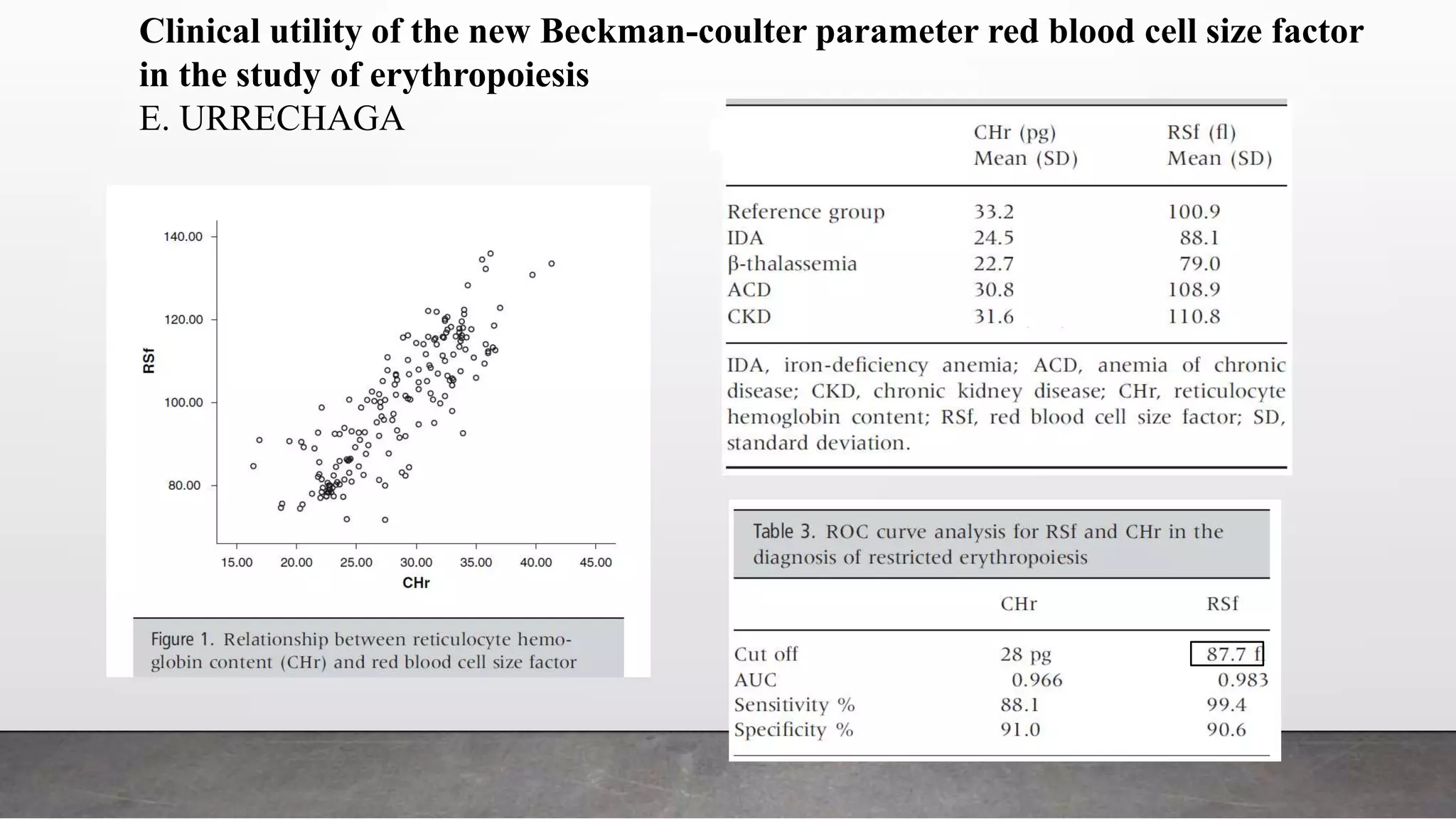
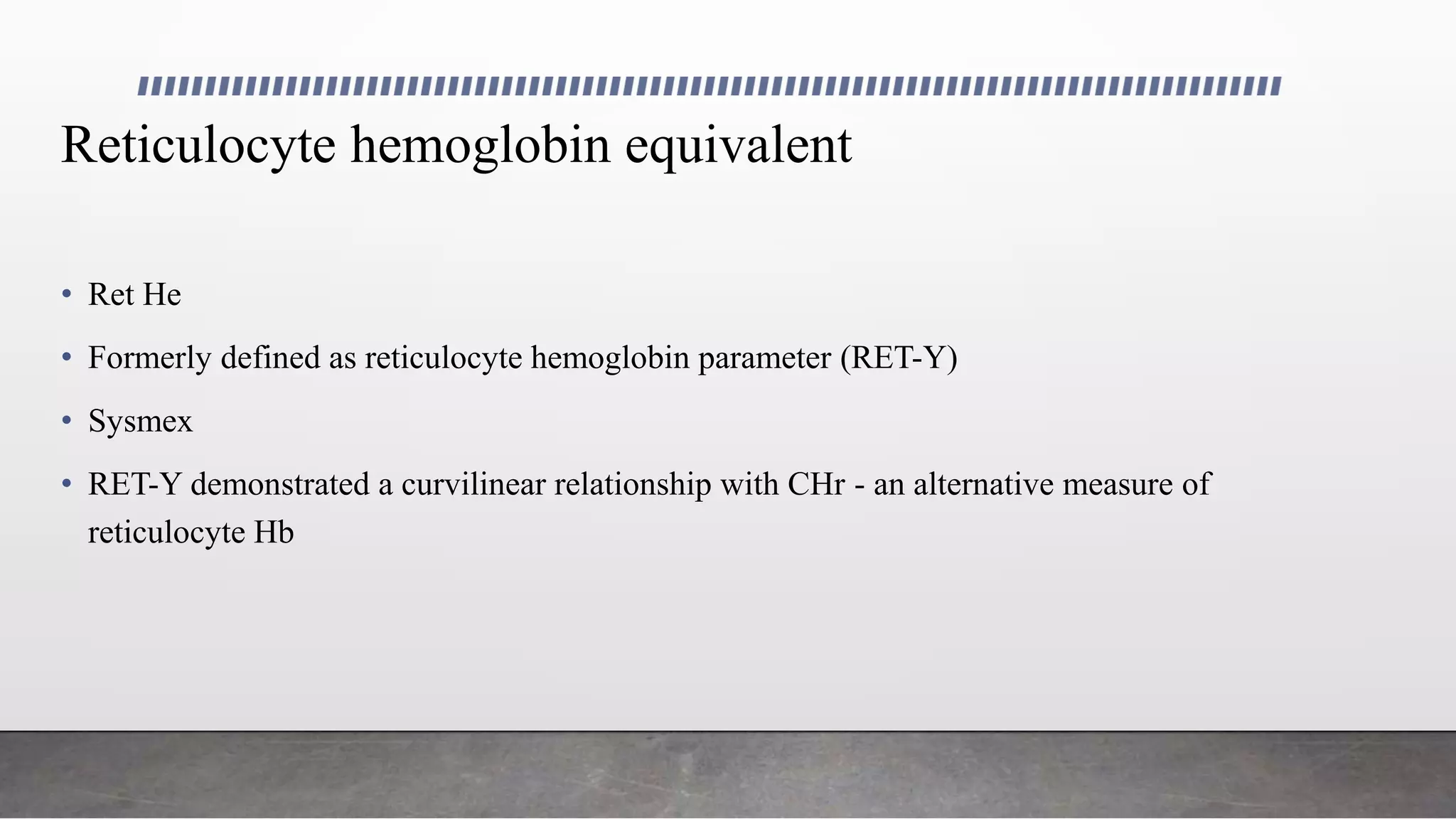
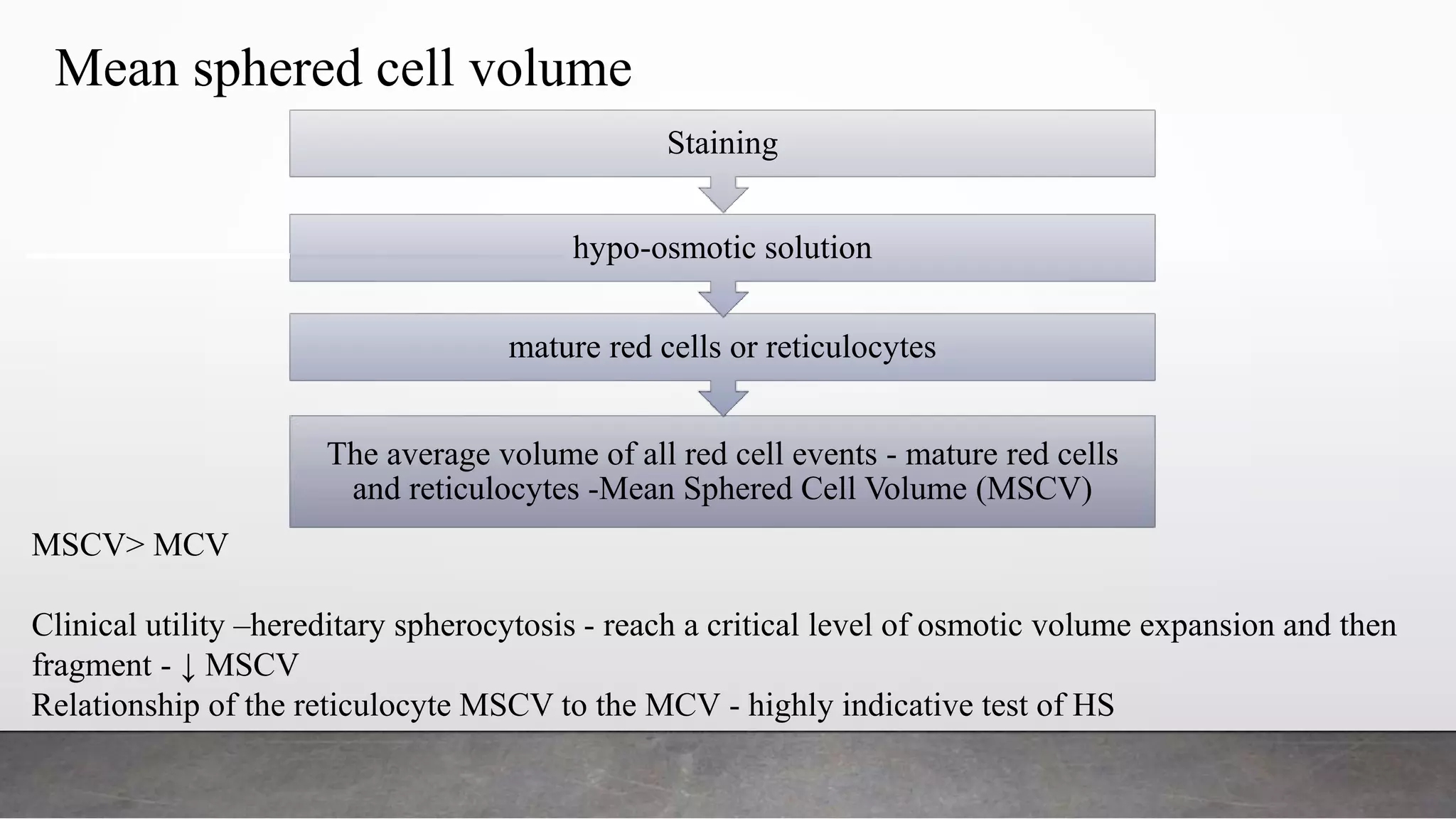
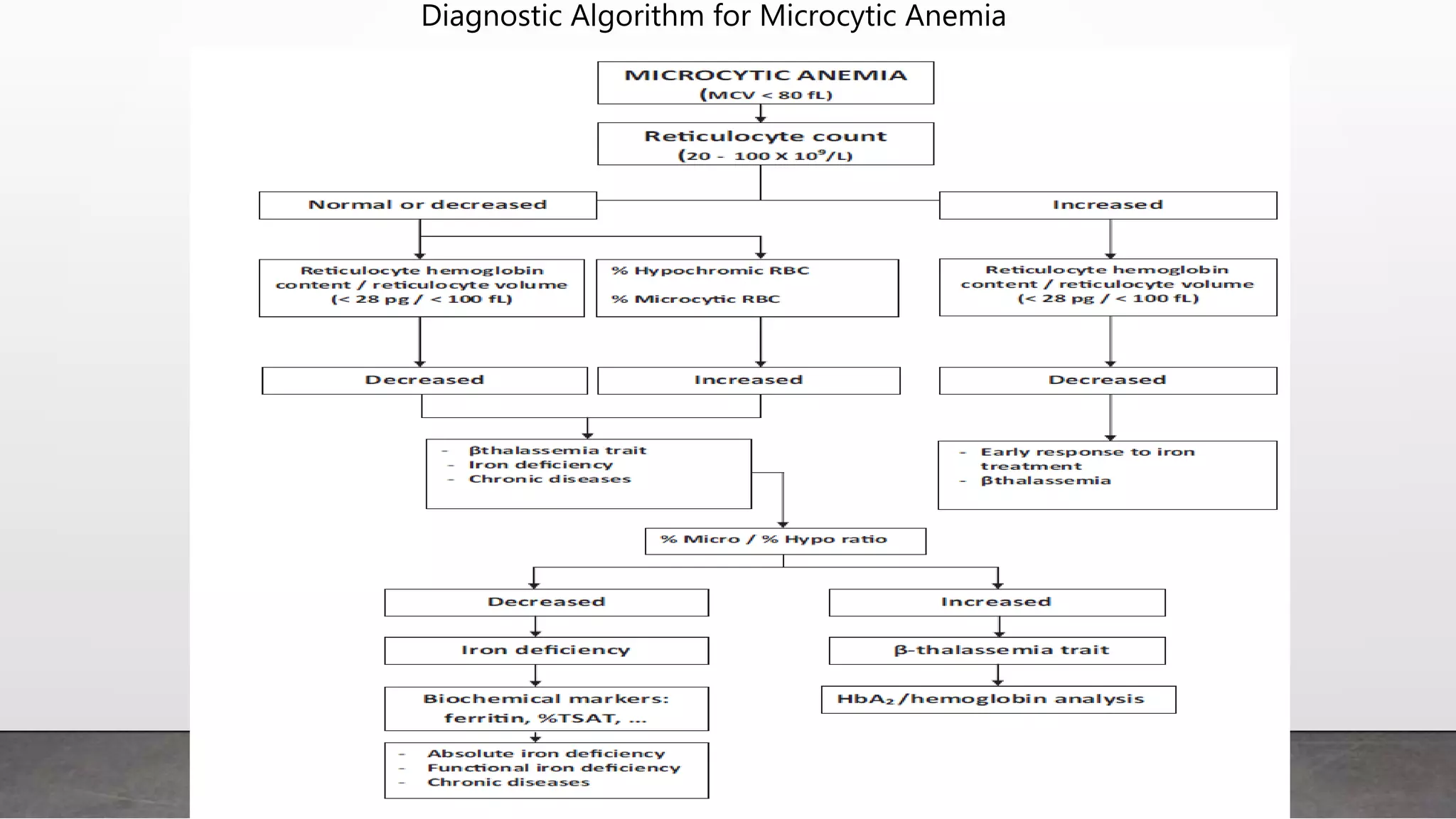
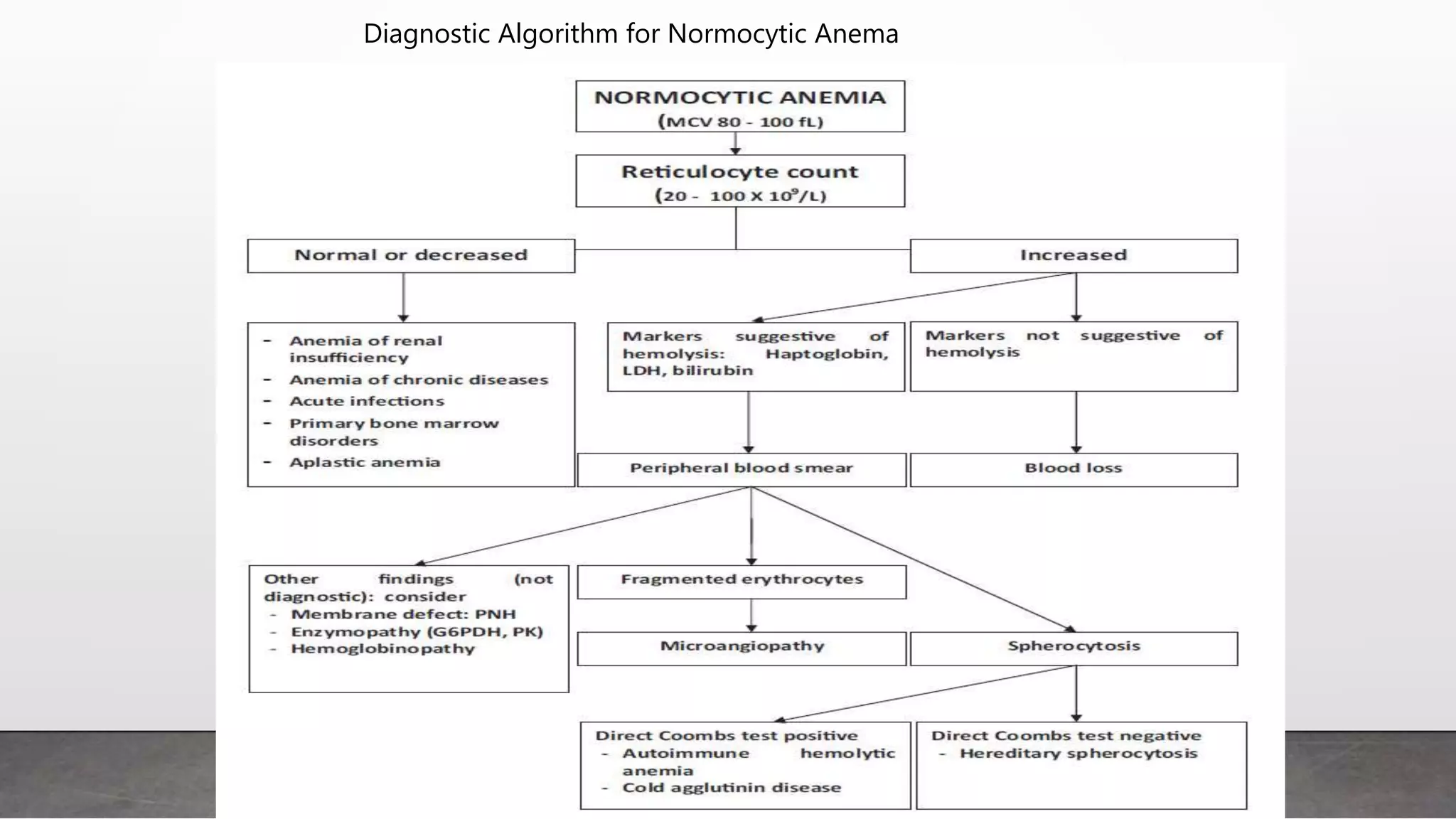
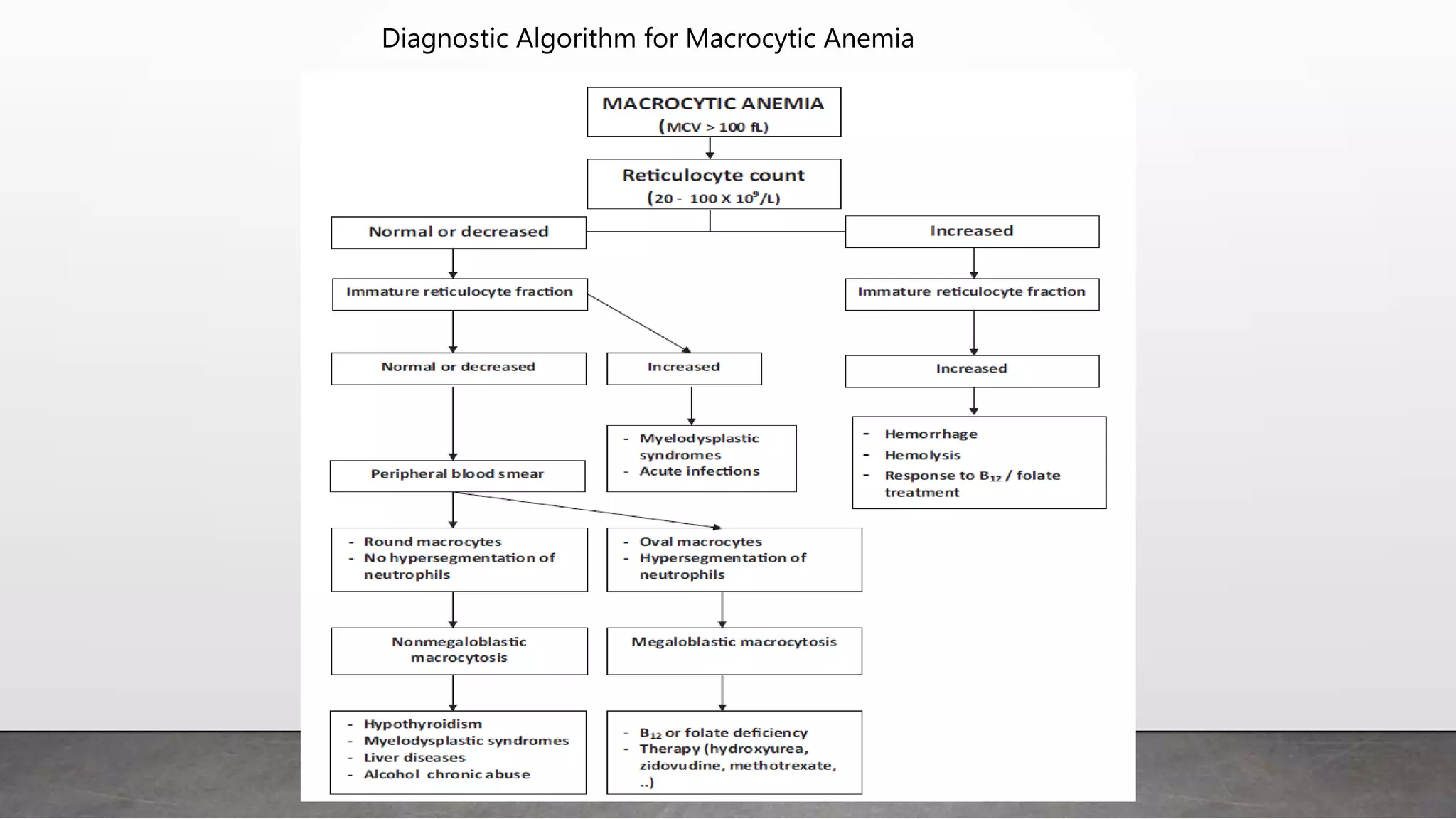
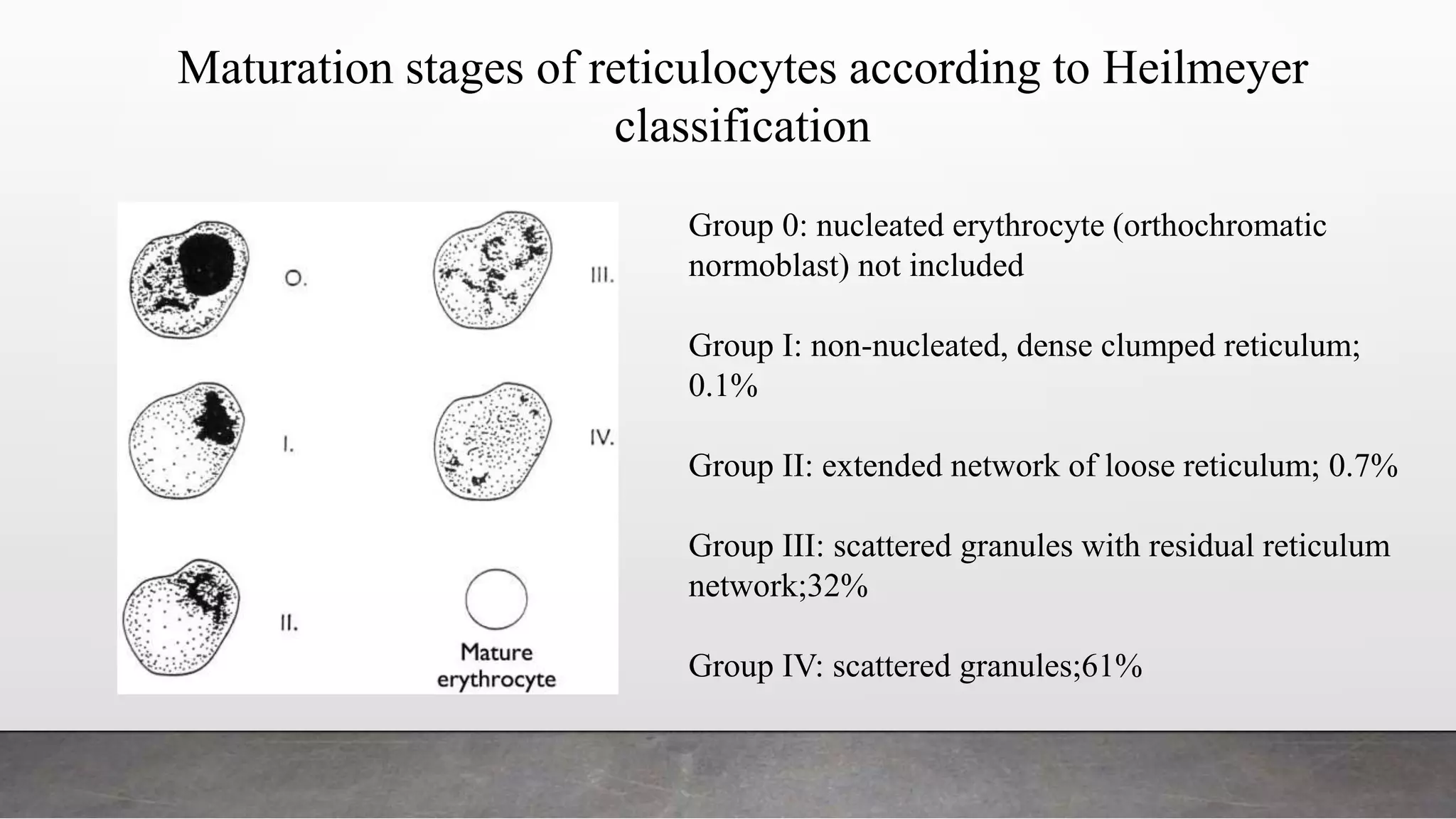
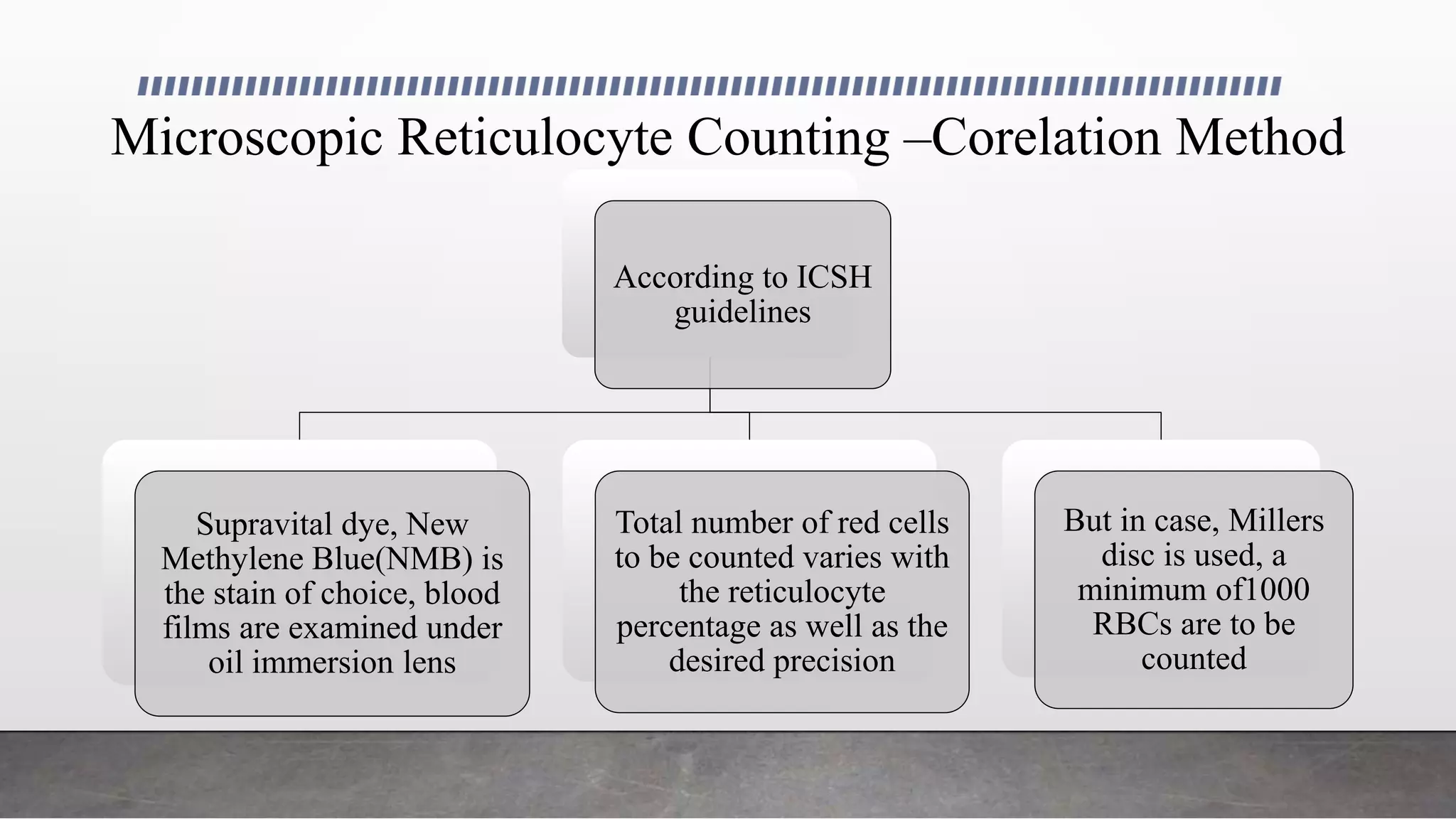
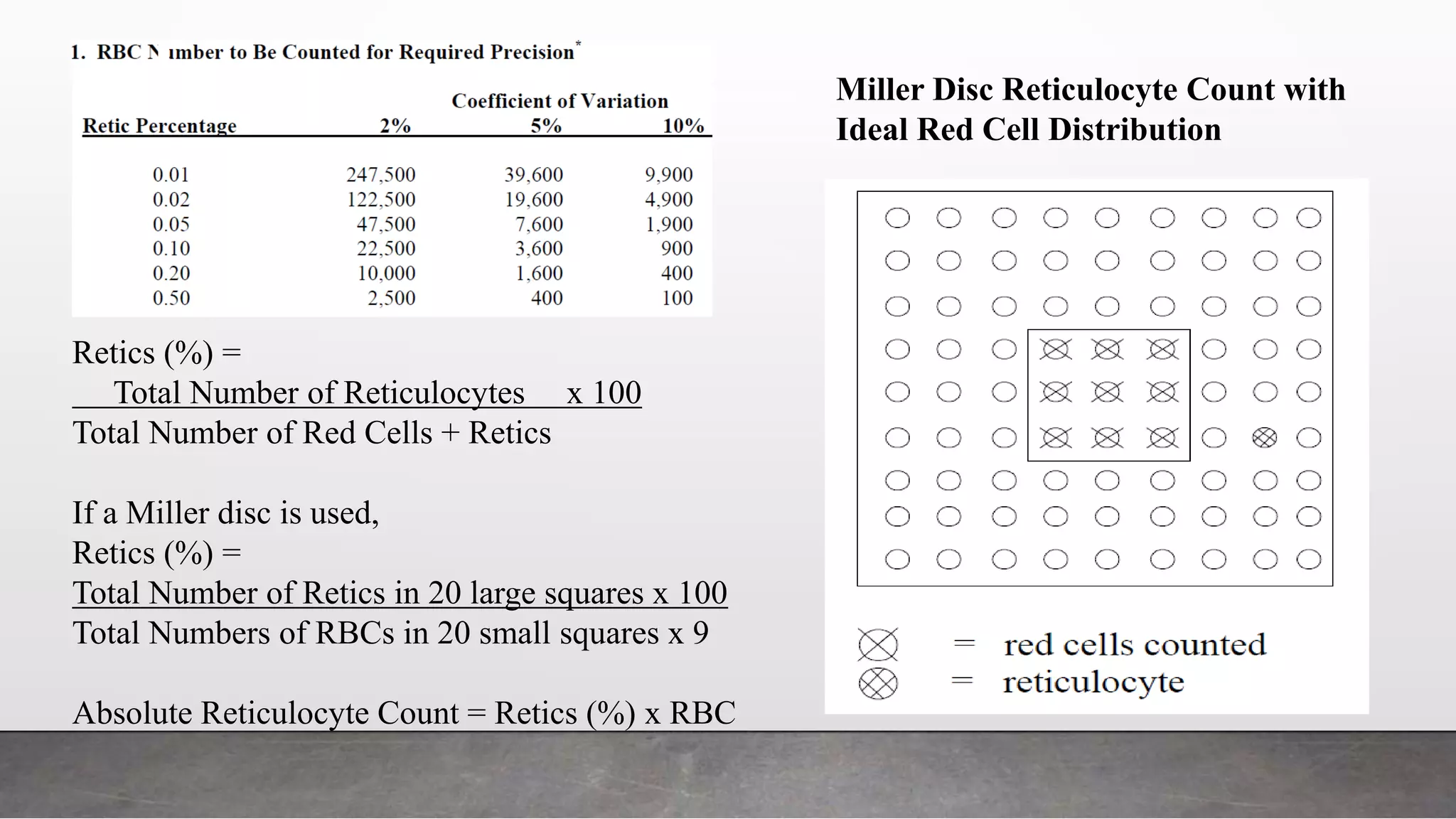
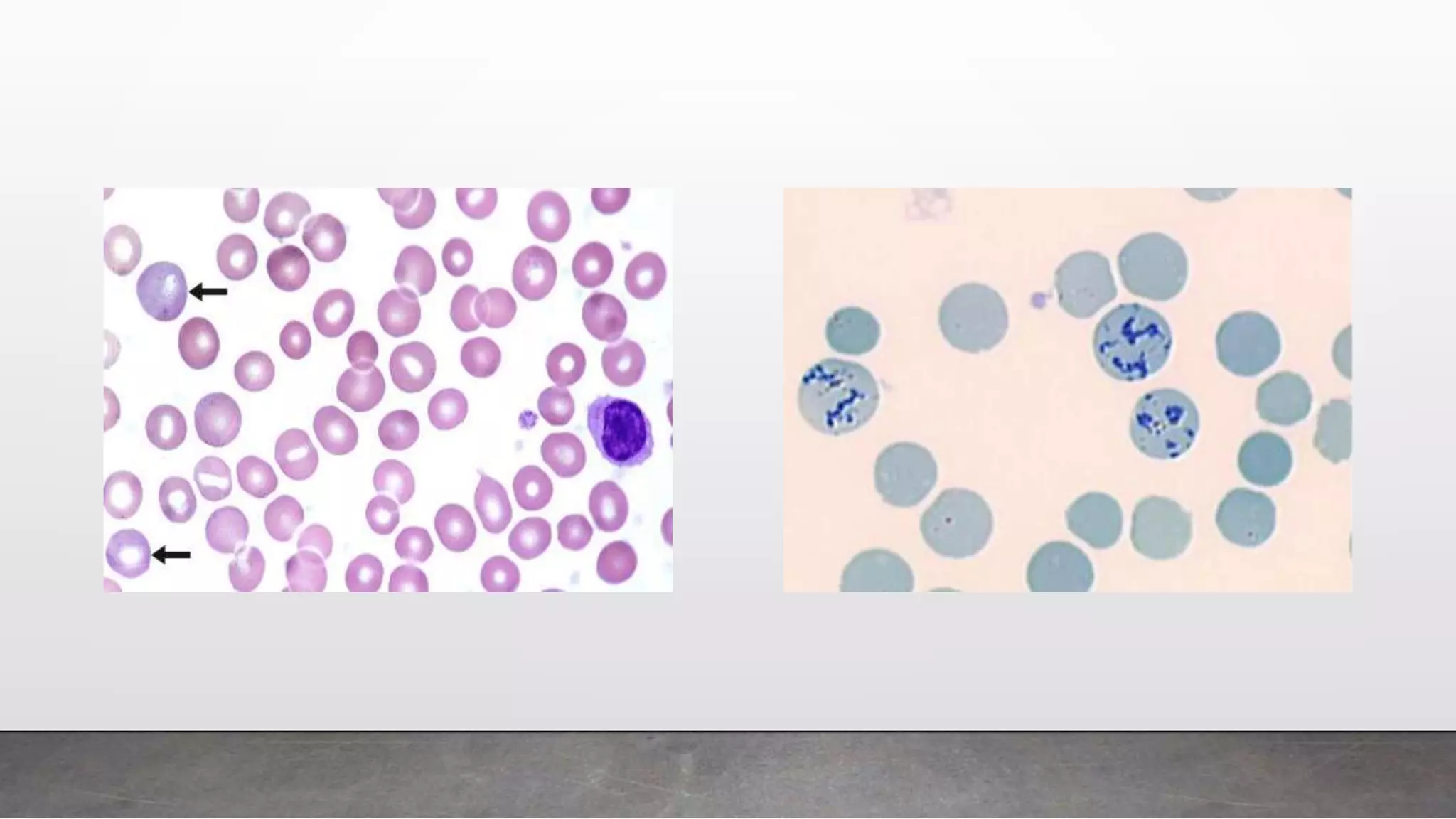
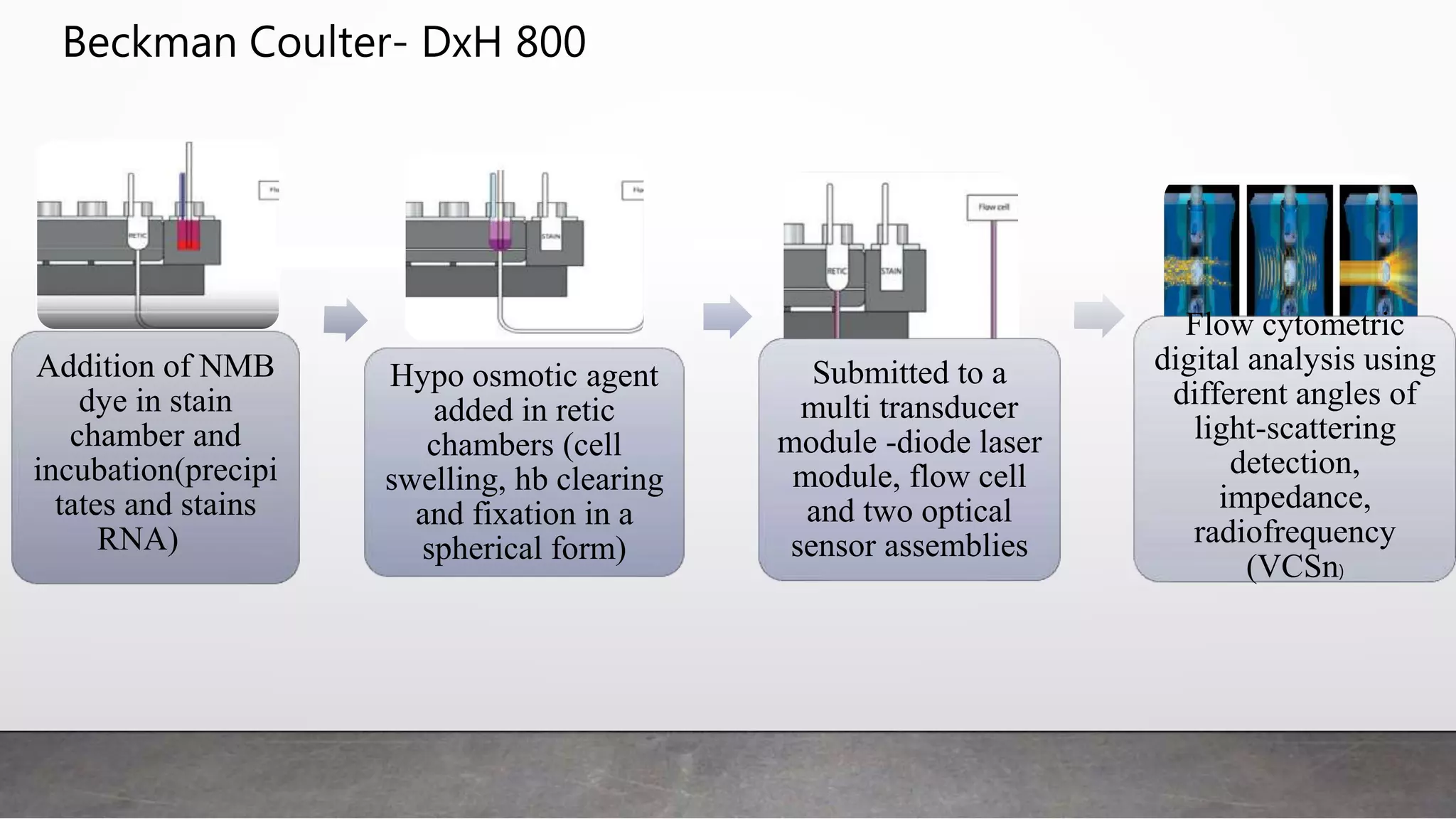
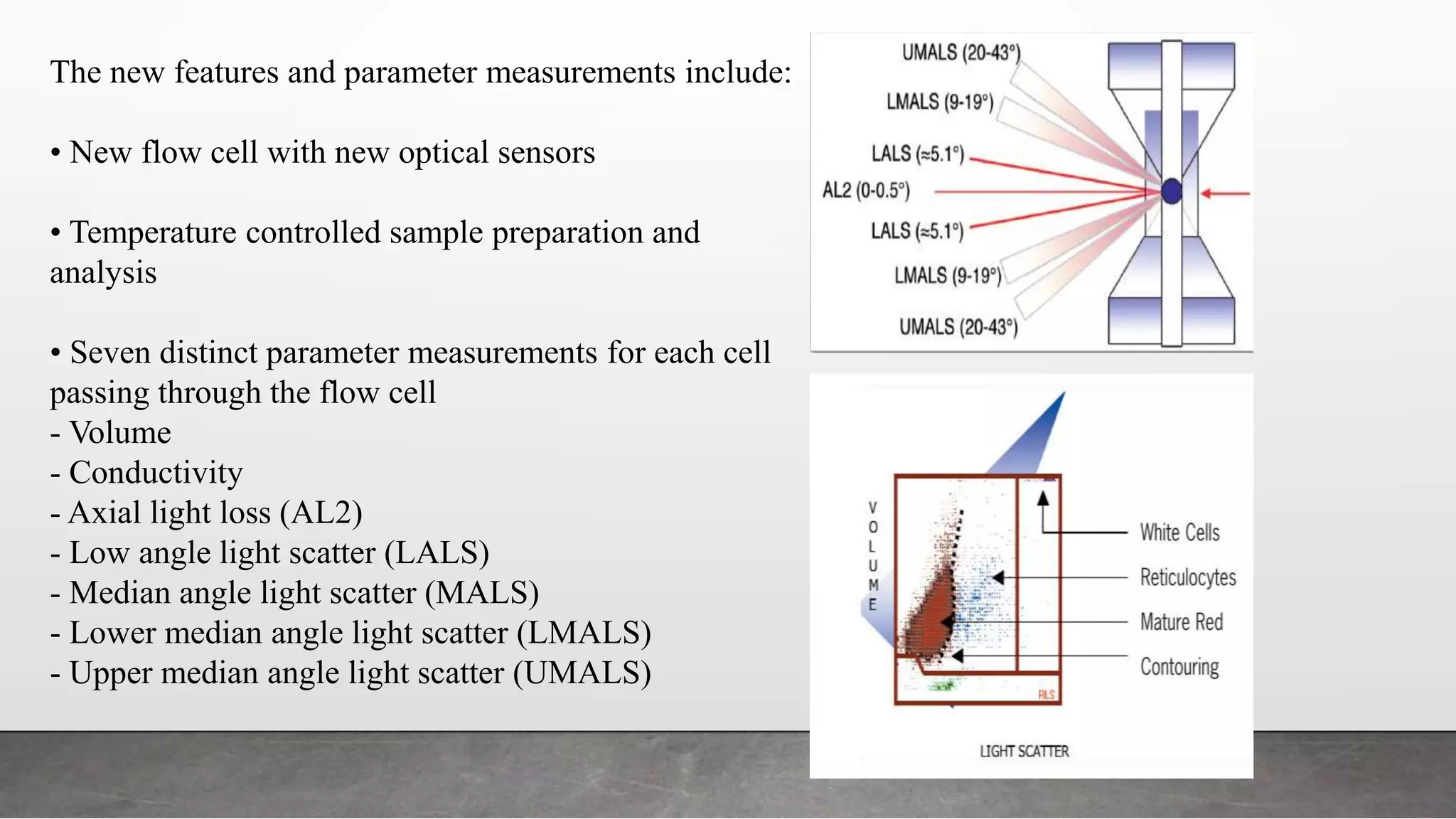
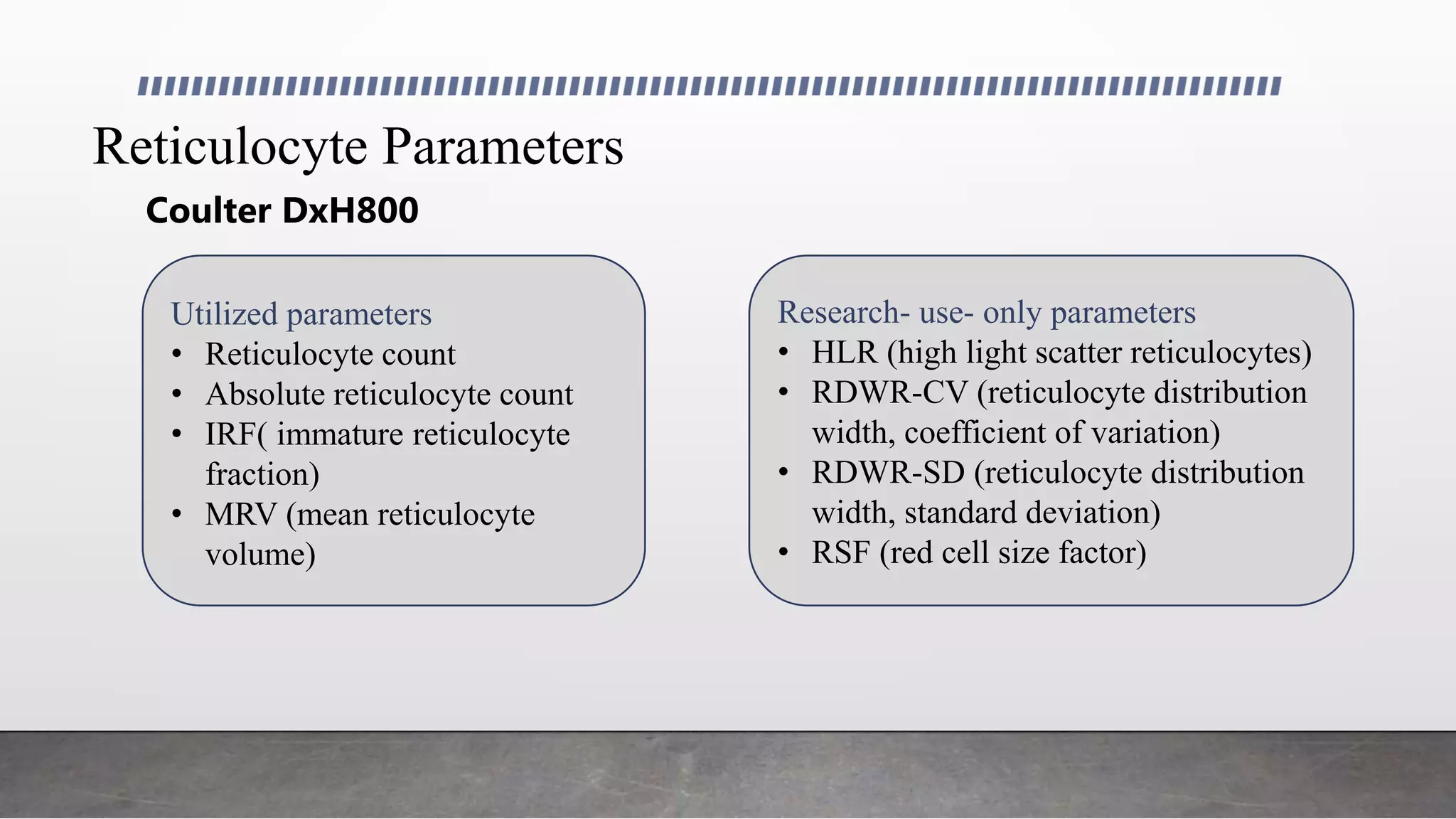
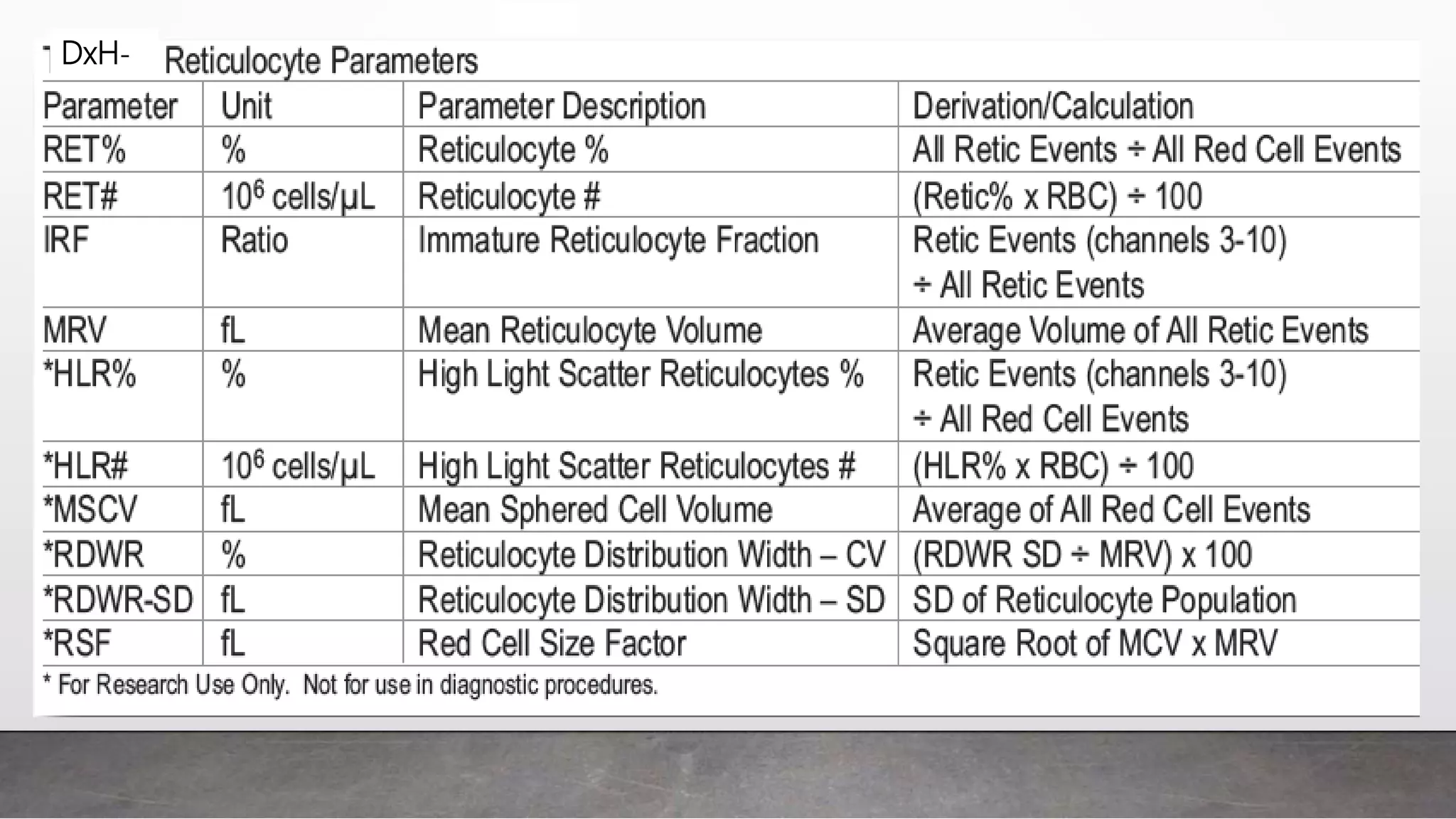
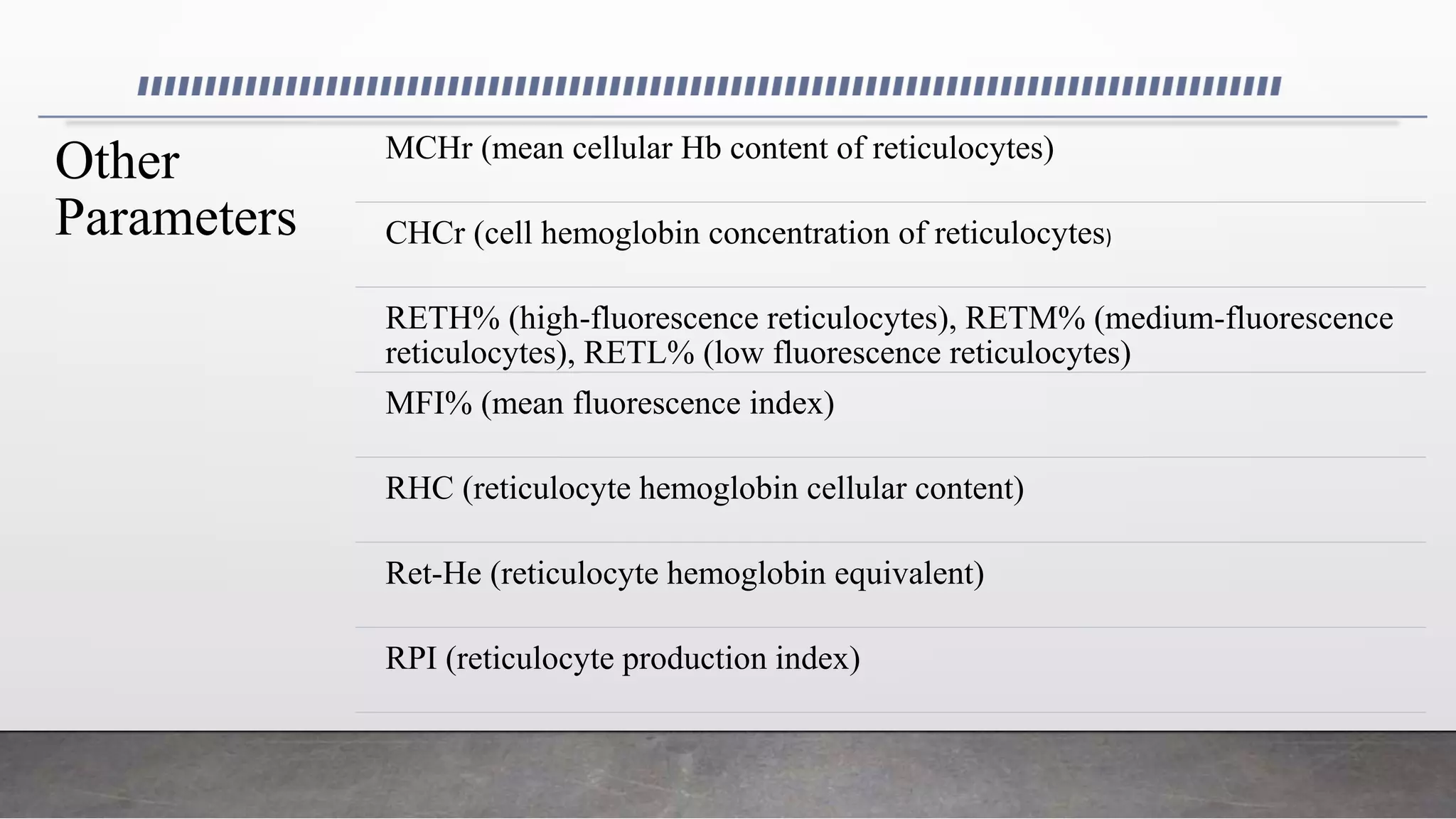
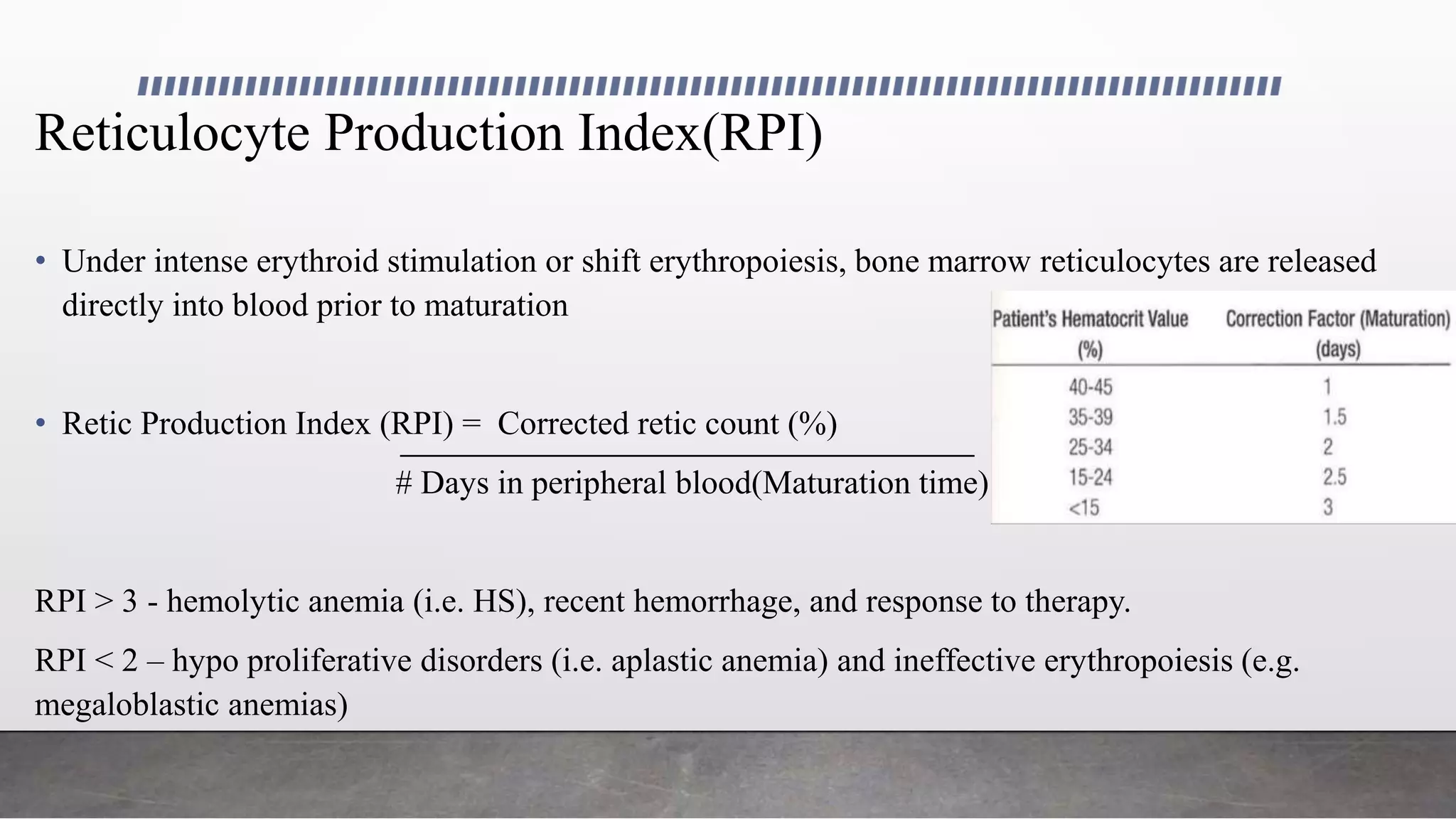
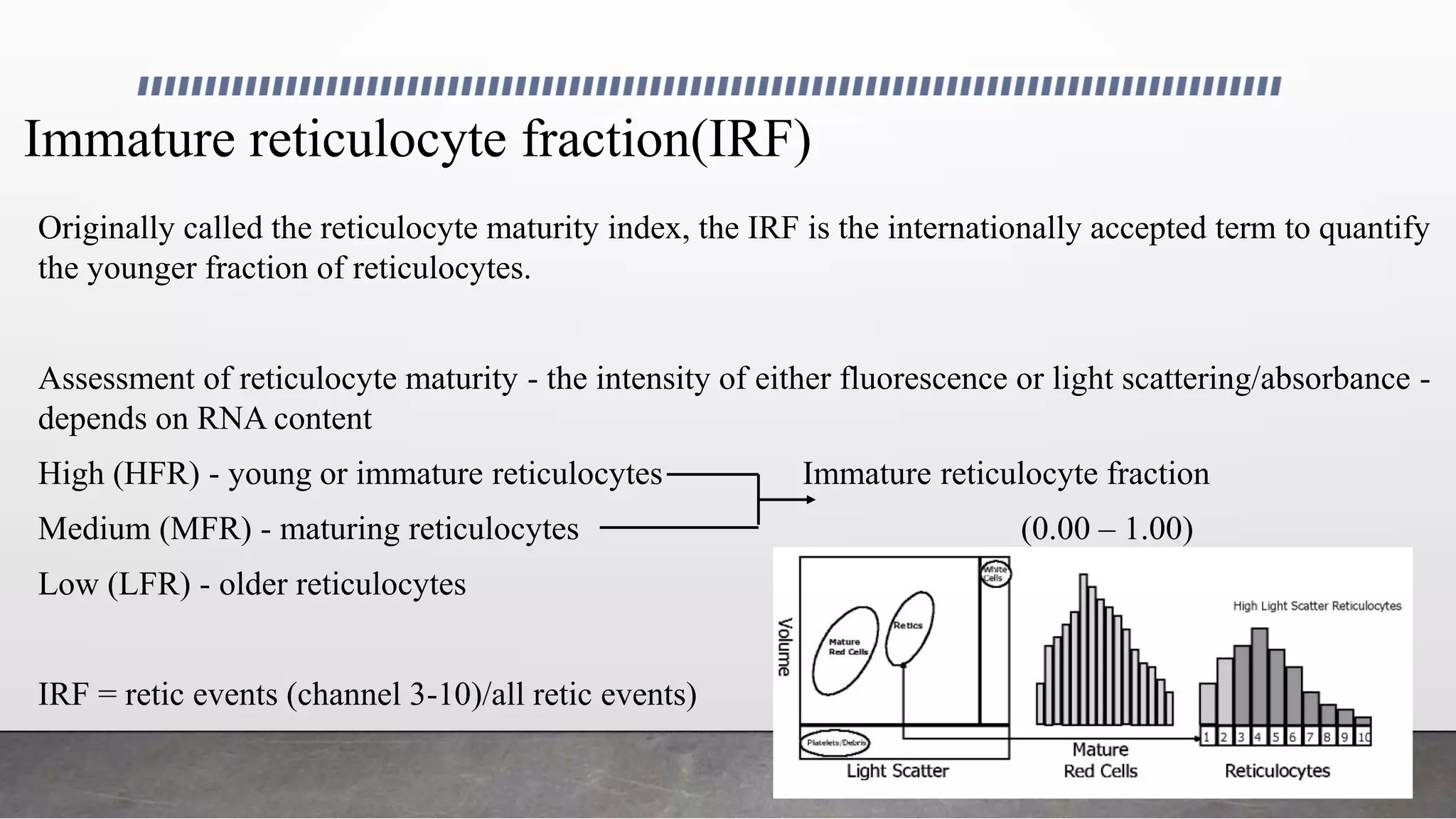
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that are released from the bone marrow into circulation during erythropoiesis. Automated analysis of reticulocytes provides several parameters that can help evaluate bone marrow function and iron status. The immature reticulocyte fraction is useful for monitoring bone marrow recovery after chemotherapy or transplant. Reticulocyte hemoglobin content measures like CHr can detect iron deficiency earlier than other tests. Using multiple reticulocyte parameters in diagnostic algorithms helps classify anemias and guide treatment.













![Monitoring Bone Marrow Recovery Following Bone Marrow
Transplant And Following Chemotherapy
• Increase in IRF - indicator of engraftment - precedes - absolute neutrophil counts (ANC),
reticulated platelets (immature platelet fraction [IPF]), or reticulocyte counts
• Post transplantation increase in ANC to 0.5 x109
/L or greater - successful myeloid engraftment
• IRF doubling time (IRF-D) - first of 2 consecutive days during which the IRF value doubles -
predict myeloid engraftment several days before ANC exceeds 0.1 x109/L
IPF - useful indicator - variations - platelet transfusion and complication such as sepsis
• Strong indicator - post chemotherapy aplasia in children with cancer - additional parameter of
impaired bone marrow function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utilityofreticulocyteparameters-180609204036/75/Utility-of-reticulocyte-parameters-25-2048.jpg)