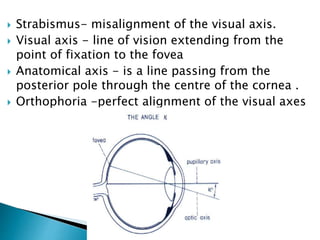
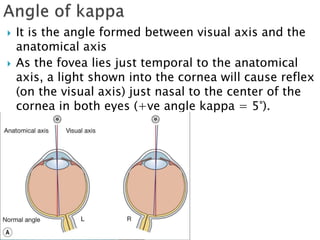
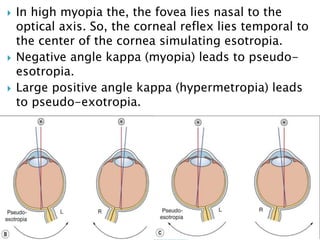
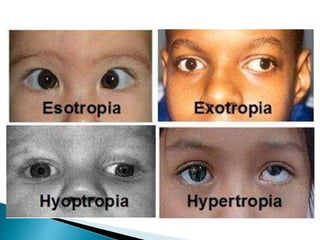
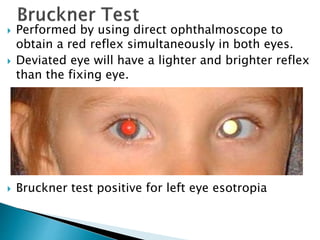
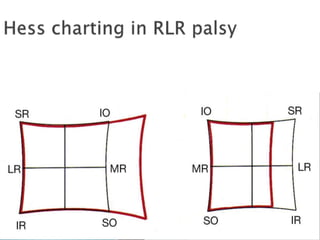
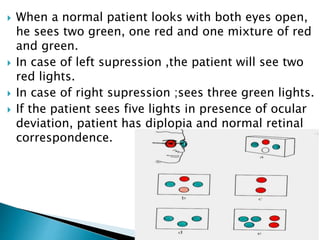
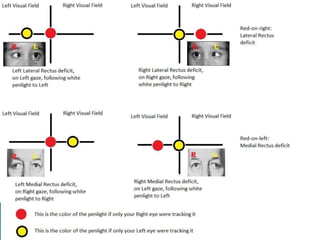
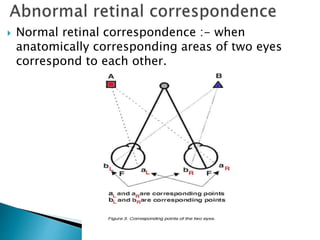
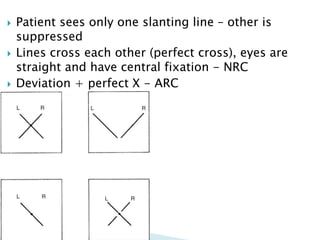
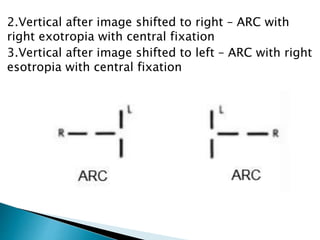
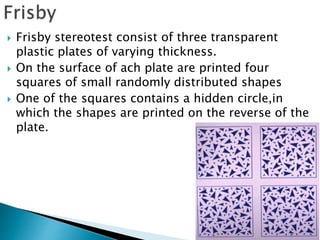
This document summarizes key concepts related to strabismus and eye movement examination. It defines terms like strabismus, visual axis, anatomical axis, orthophoria and describes tests to evaluate eye alignment and movement including:
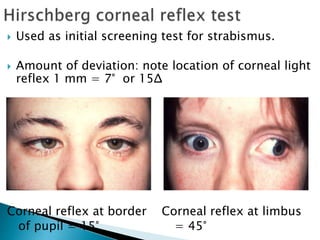
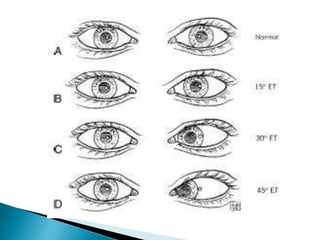
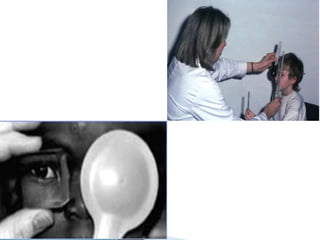
- Hirschberg test to measure strabismus angle
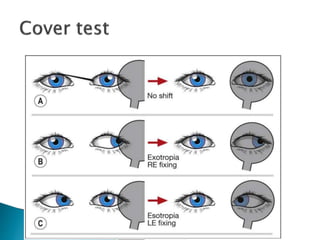
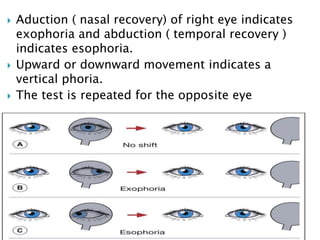
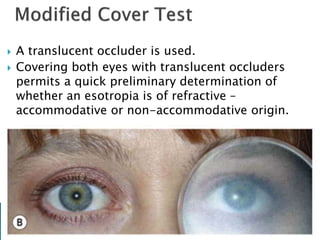
- Cover-uncover test and alternate cover test to detect heterotropia and heterophoria
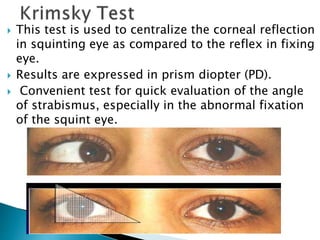
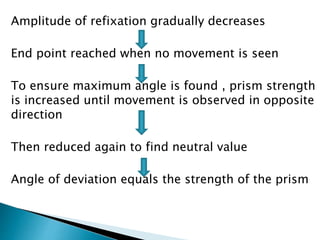
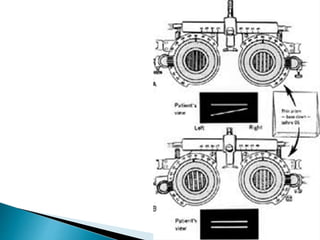
- Prism bar cover test for measuring strabismus angle
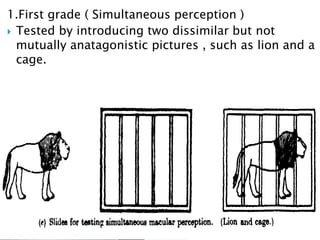
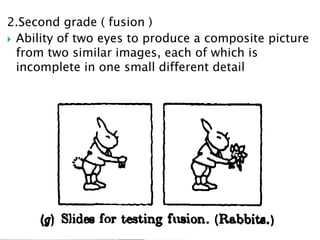
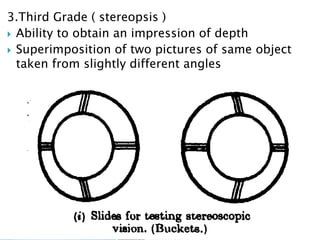
- Synoptophore for grading binocular vision
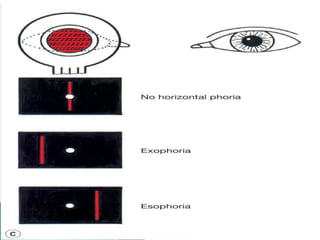
- Maddox rod test for detecting horizontal and vertical phorias
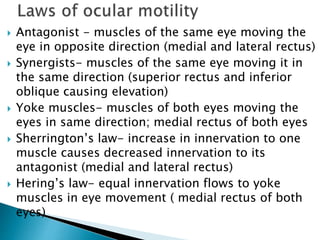
- Extraocular muscle actions and innervations are also summarized.