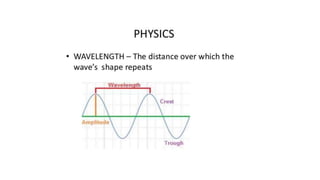
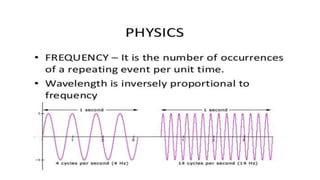
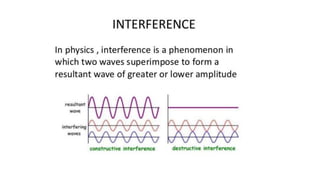
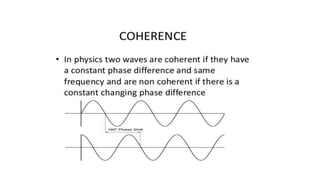
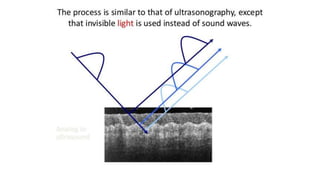
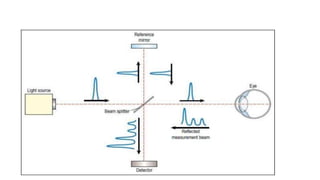
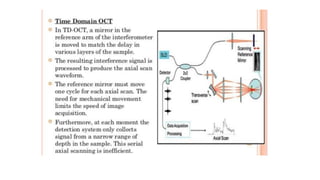
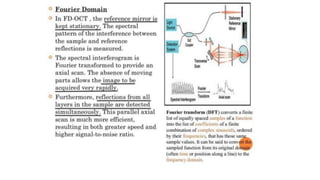
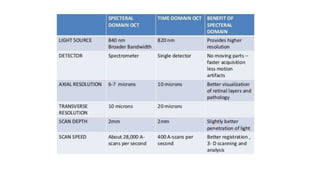
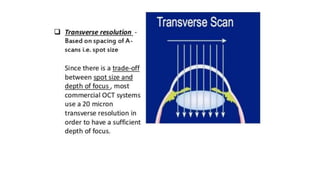
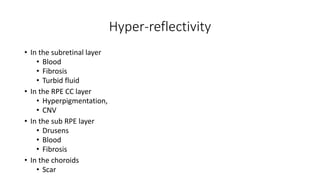
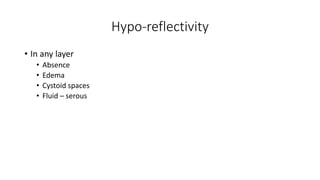
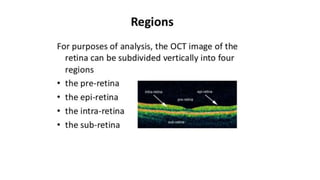
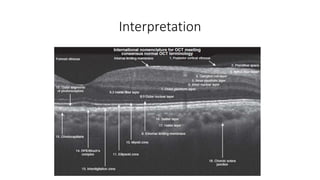
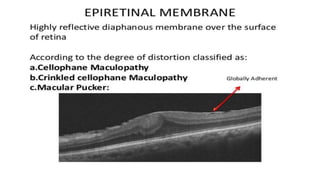
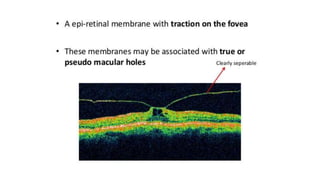
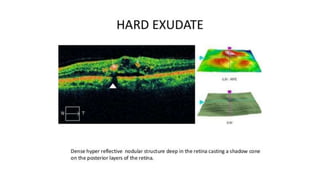
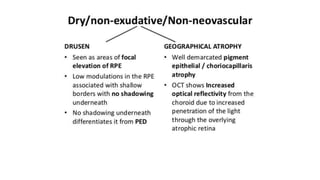
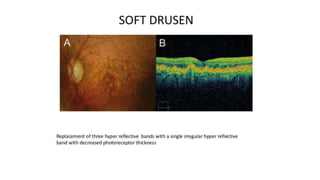
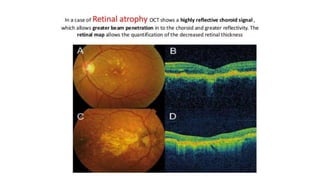
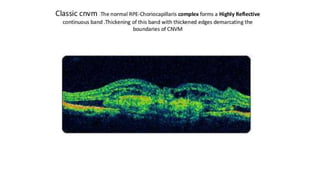
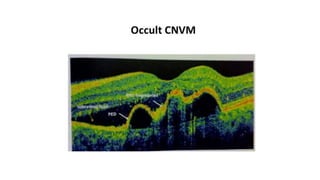
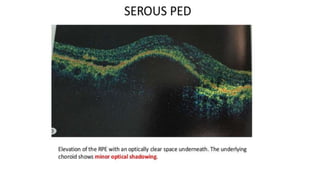
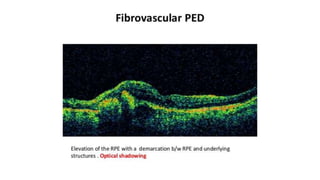
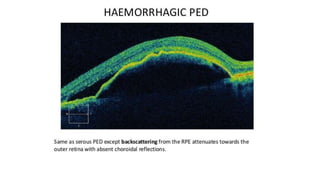
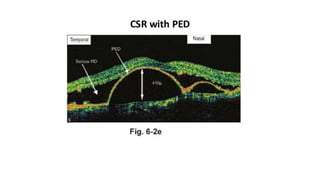
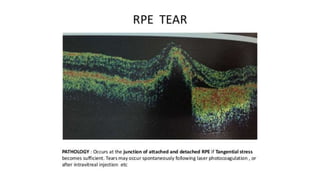
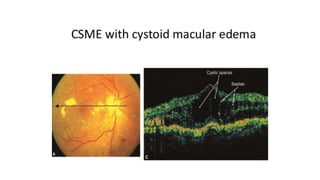
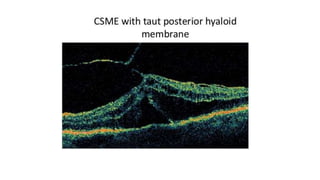
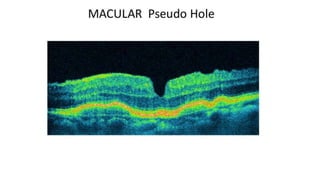
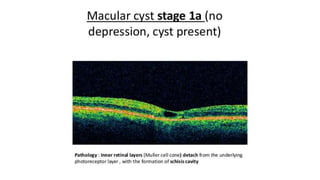
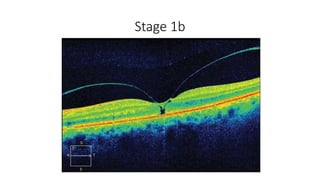
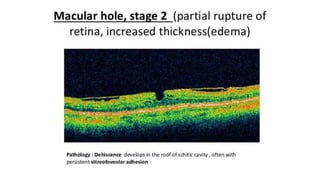
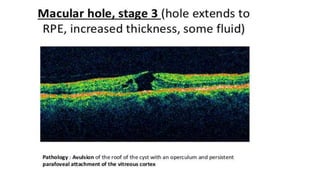
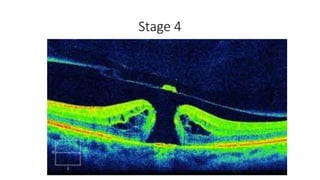
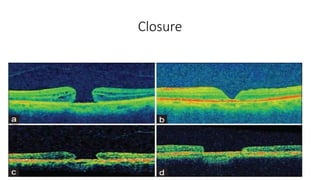
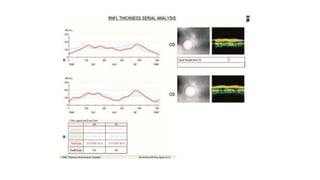
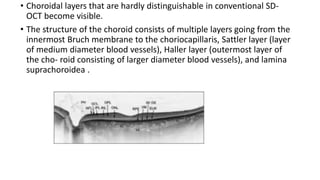
This document discusses optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the retina. OCT uses light instead of a knife to perform a vertical biopsy of the retina, presenting a false-color view with micron-level resolution without physical contact. The document describes various hyper-reflective and hypo-reflective features that can be seen on OCT scans and what they indicate, such as blood, exudates, cysts, edema, and more. It also discusses swept-source OCT which overcomes limitations of previous OCT to enable better visualization of deeper structures like choroidal layers and discusses uses of swept-source OCT in glaucoma to examine microstructural changes in the lamina cribrosa.