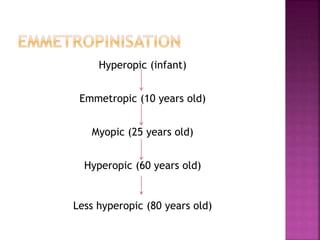
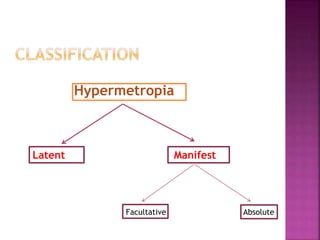
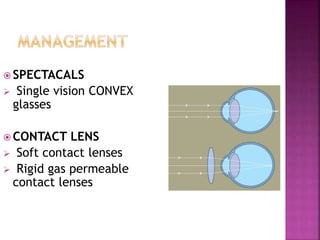
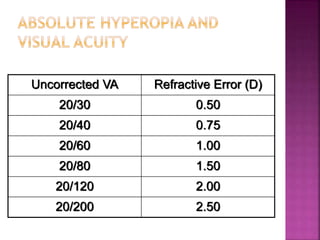
This document discusses hyperopia (farsightedness), which occurs when parallel rays of light focus behind the retina at rest. It defines different types of hyperopia such as physiological and pathological. Symptoms include eye strain, headaches, and blurred near vision. Diagnosis involves visual acuity tests, retinoscopy, and subjective refraction. Treatment options include convex lenses, contact lenses, and refractive surgery like LASIK. The prevalence of hyperopia changes with age, from high levels in infants to low levels in adults that may increase again in older age.