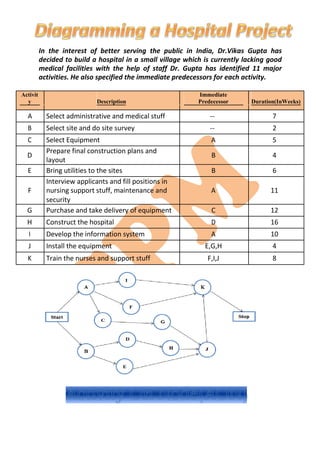
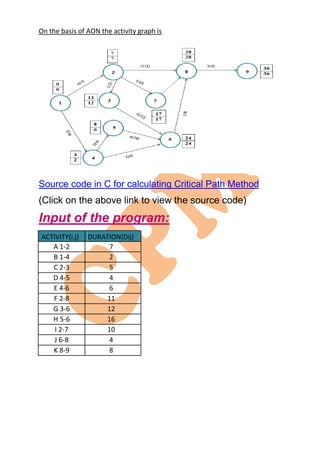
The document discusses project management methodologies, focusing on the Critical Path Method (CPM) and the Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), which help in scheduling and controlling project activities. It outlines phases of project management including planning, scheduling, and controlling, as well as guidelines for network construction and the determination of critical paths. Additionally, it provides a practical example of building a hospital with various tasks and their dependencies, concluding with the calculation of the critical path and estimated completion times.




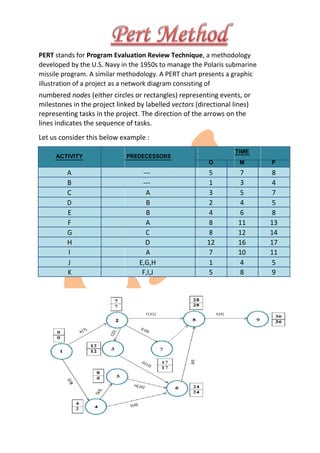
![Formulas:-
Mean:-
Te=(To+4Tm+Tp)/6
Variance:-[(Tp-To)/6]2
ACTIVITY TIME MEAN DURATION VARIANCE
O M P
A 5 7 8 6.8 0.25
B 1 3 4 2.8 0.25
C 3 5 7 5 0.44
D 2 4 5 3.8 0.25
E 4 6 8 6 0.44
F 8 11 13 10.8 0.69
G 8 12 14 11.67 1
H 12 16 17 15.5 0.69
I 7 10 11 9.67 0.44
J 1 4 3 3.67 0.44
K 5 8 9 7.67 0.44
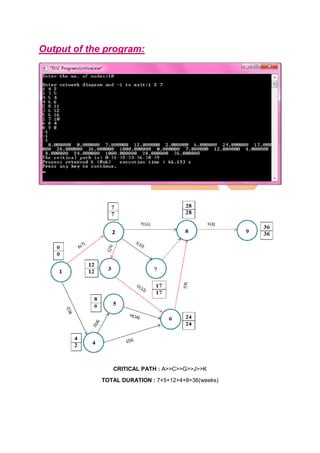
The result of Pert Method is 1>>2>>3>>6>>8>>9
CRITICAL PATH:-A->C->G->J->K
TOTAL DURATION : 7+5+12+4+8=36(weeks)(expected completion time)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spm-200403182706/85/Spm-9-320.jpg)
![Activity Mean Duration Variance
A 9.8 1.25
C 7 1.44
G 11.67 1
J 3.67 1.44
K 9.67 7.67
41.81 12.8
ᶮ=squareroot(12.8)=3.609weeks
P(x≤50)=p[(x-µ)/ᶮ≤(50-41.81)/3.609]
P[z≤2.26]=0.9447
This valueis obtained from std. normal distribution table Therefore the probability
of computing project on or before 50 weeks is 0.9447 i.e 94.47%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spm-200403182706/85/Spm-10-320.jpg)
![REFERENCES
[1] Applied Software Project Management by By Andrew Stellman, Jennifer Greene
[2] Software Project Management In Practice By Pankaj Jalote
[3] Introduction To Software Project Management By Adolfo Villafiorita](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spm-200403182706/85/Spm-11-320.jpg)