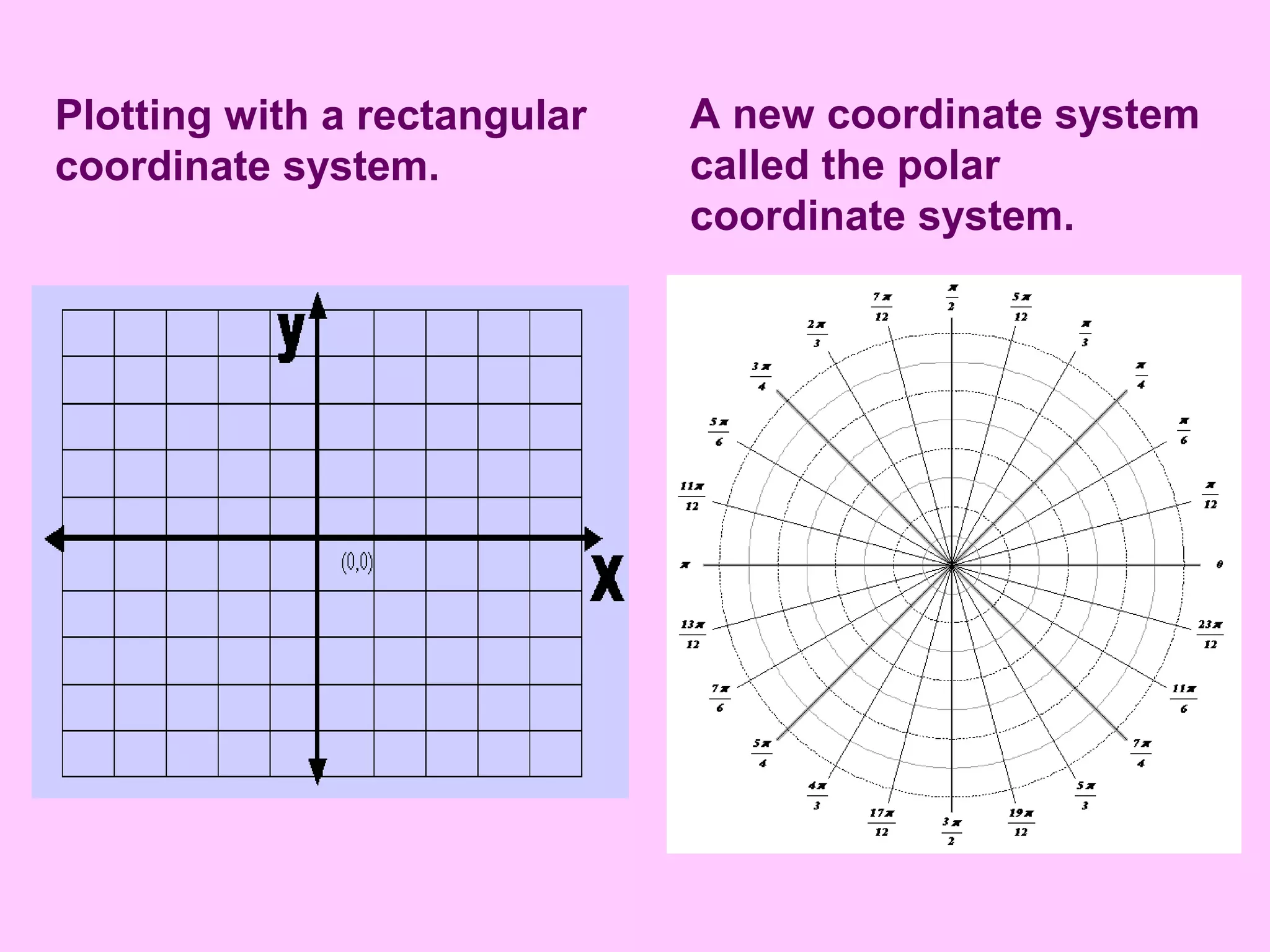
- The document introduces polar coordinates as an alternative coordinate system to Cartesian coordinates.
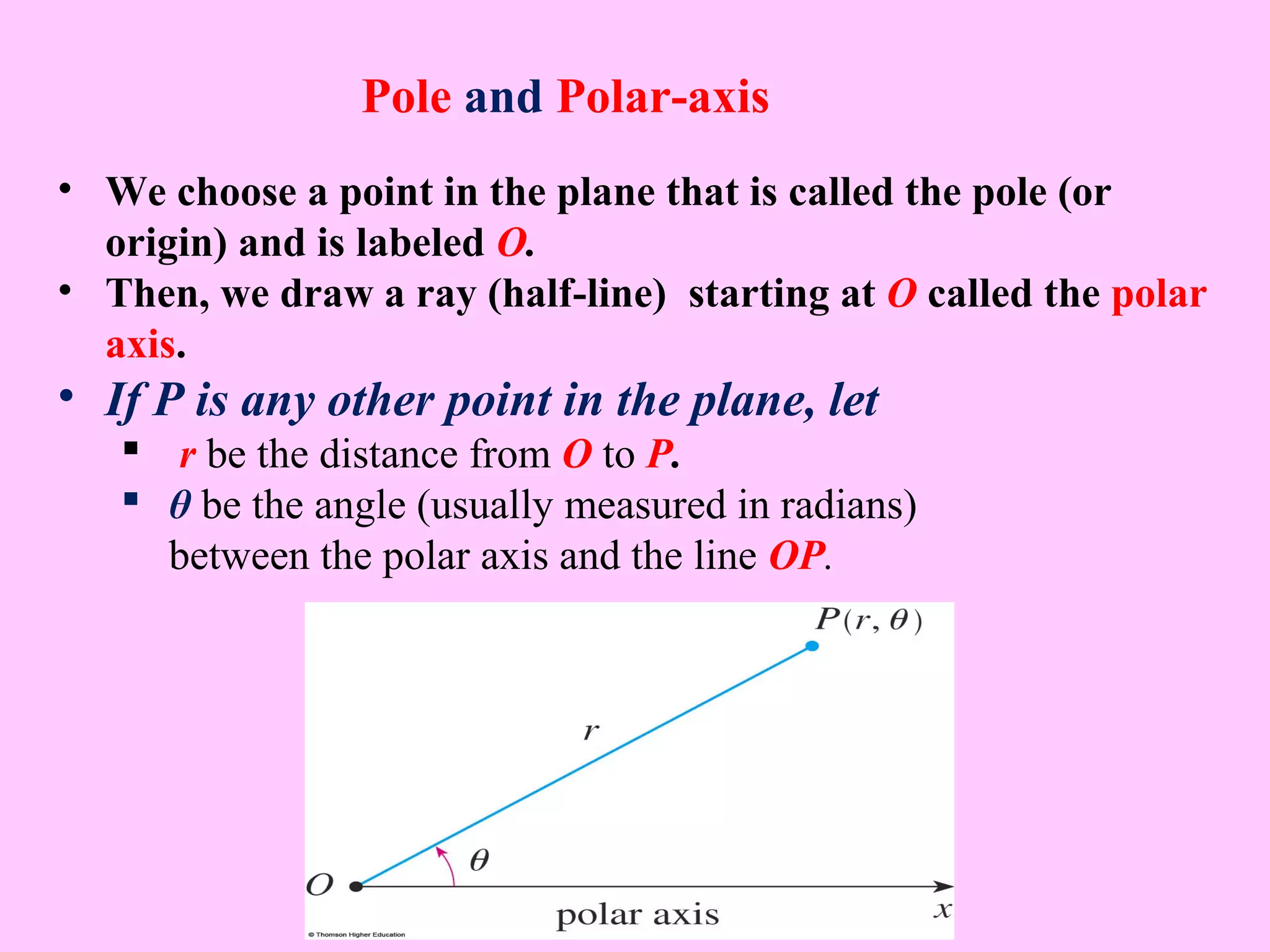
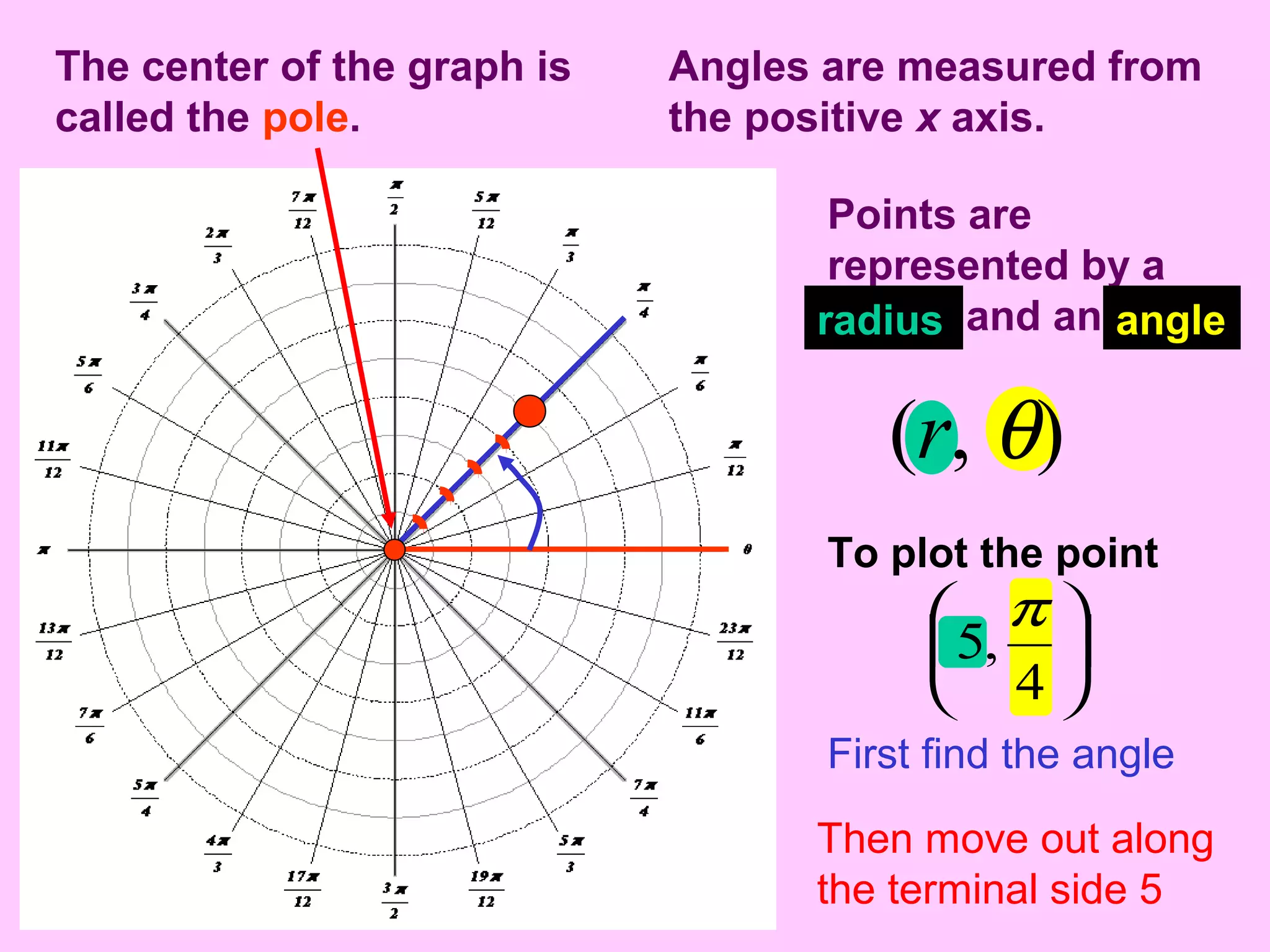
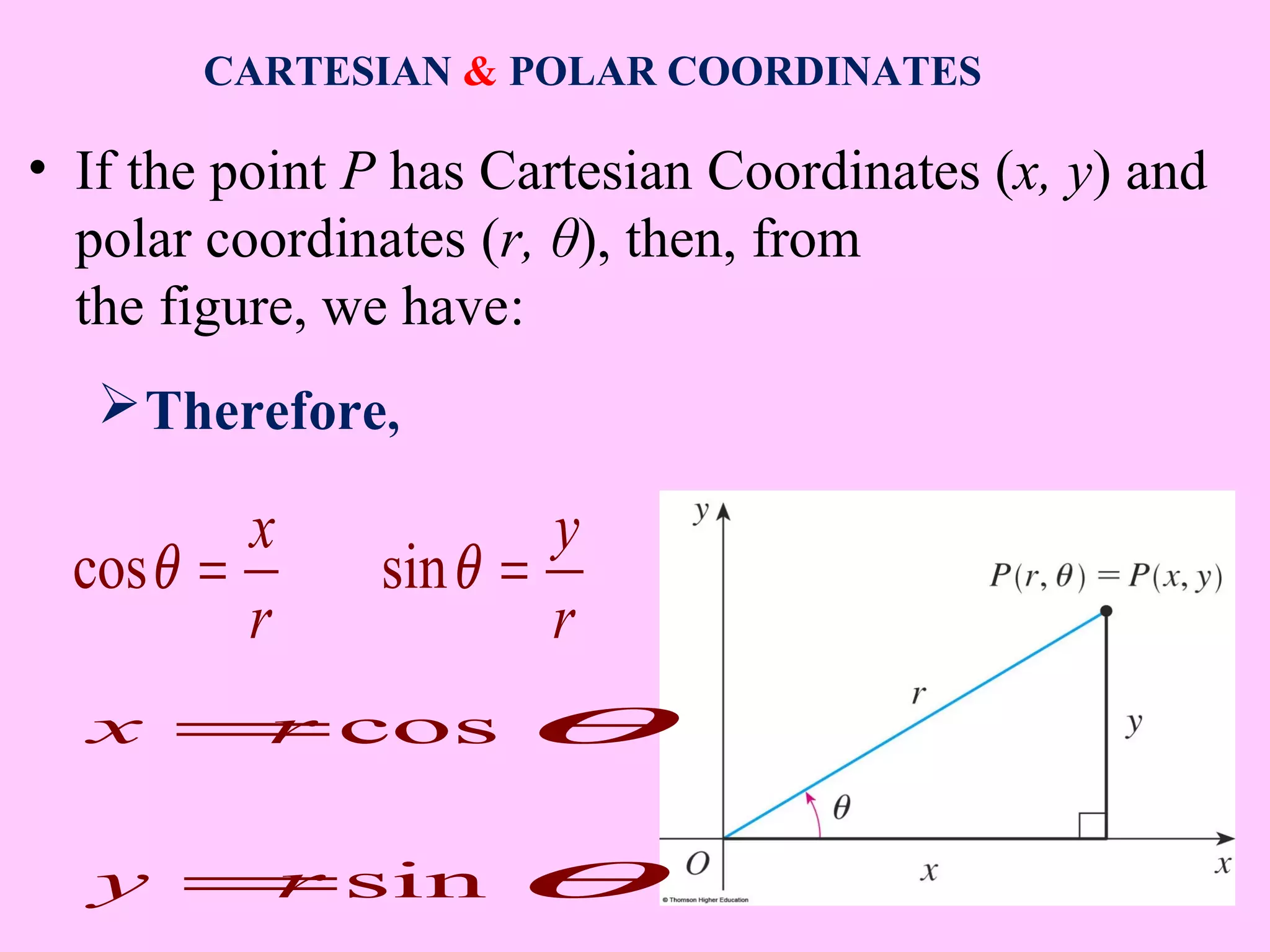
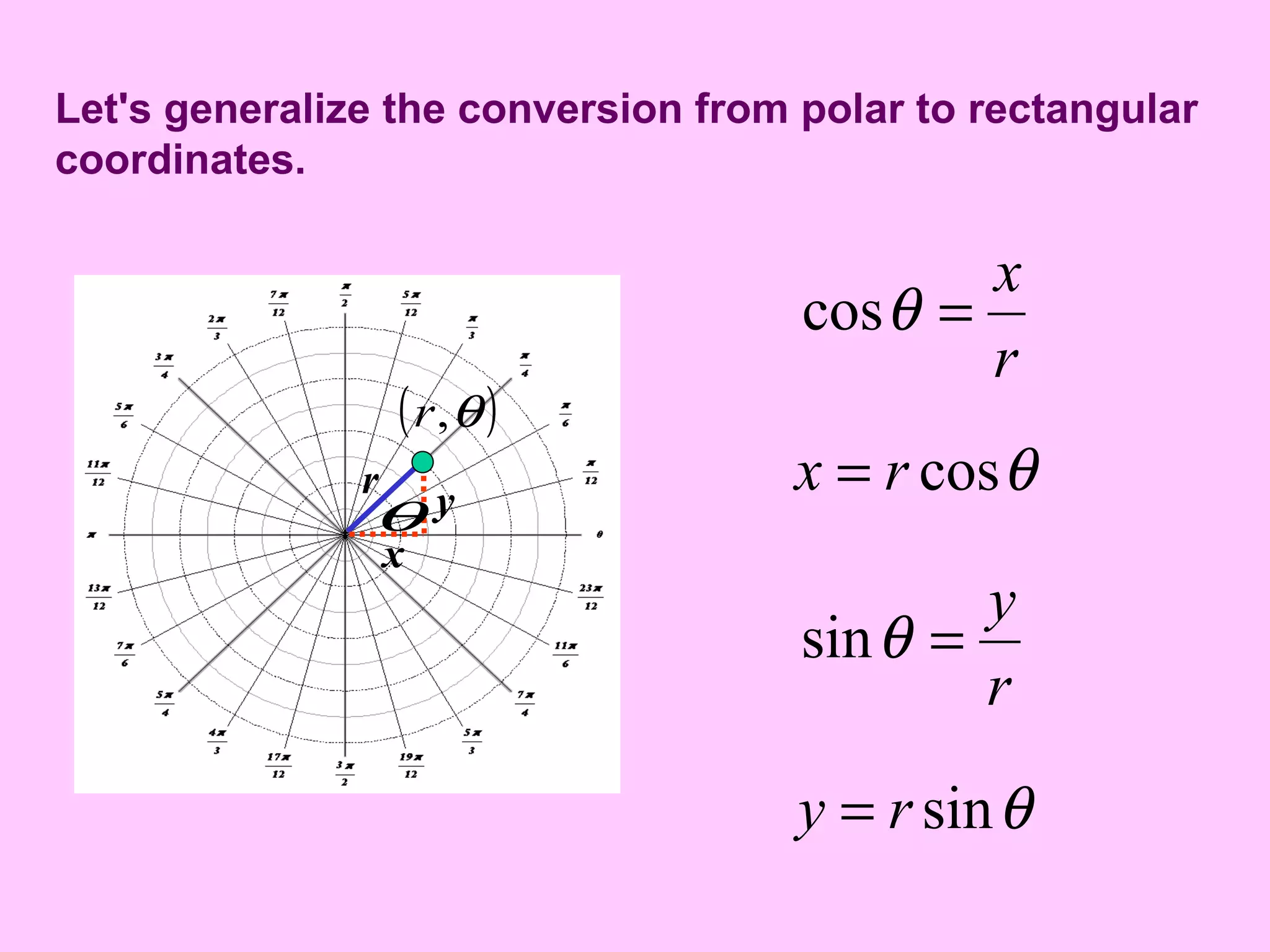
- In polar coordinates, a point P is represented by an ordered pair (r, θ) where r is the distance from a fixed point called the pole (or origin) to P, and θ is the angle between the polar axis and the line from the pole to P.
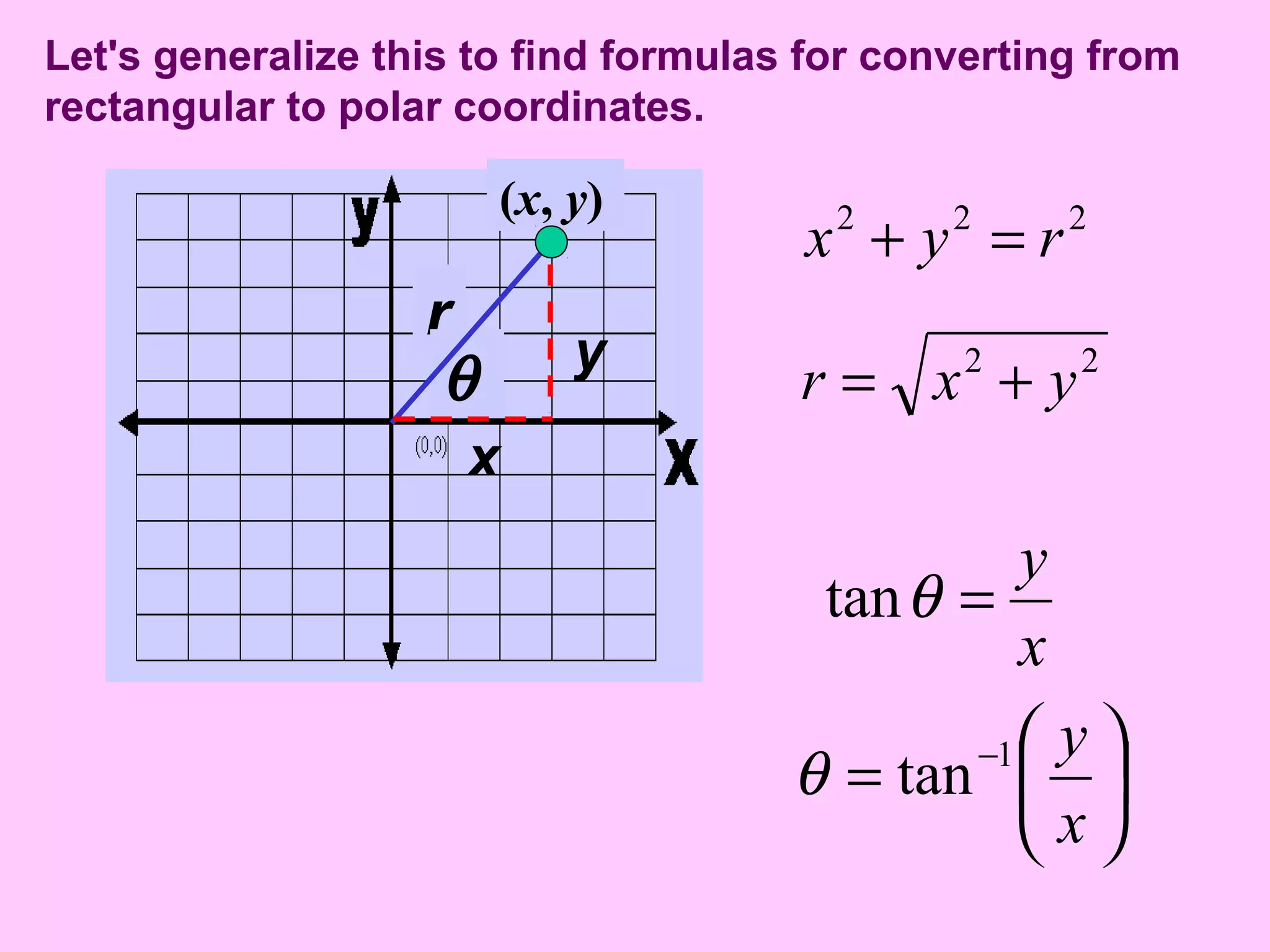
- Formulas are provided to convert between Cartesian (x, y) coordinates and polar (r, θ) coordinates. Specifically, r2 = x2 + y2 and θ = tan-1(y/x).
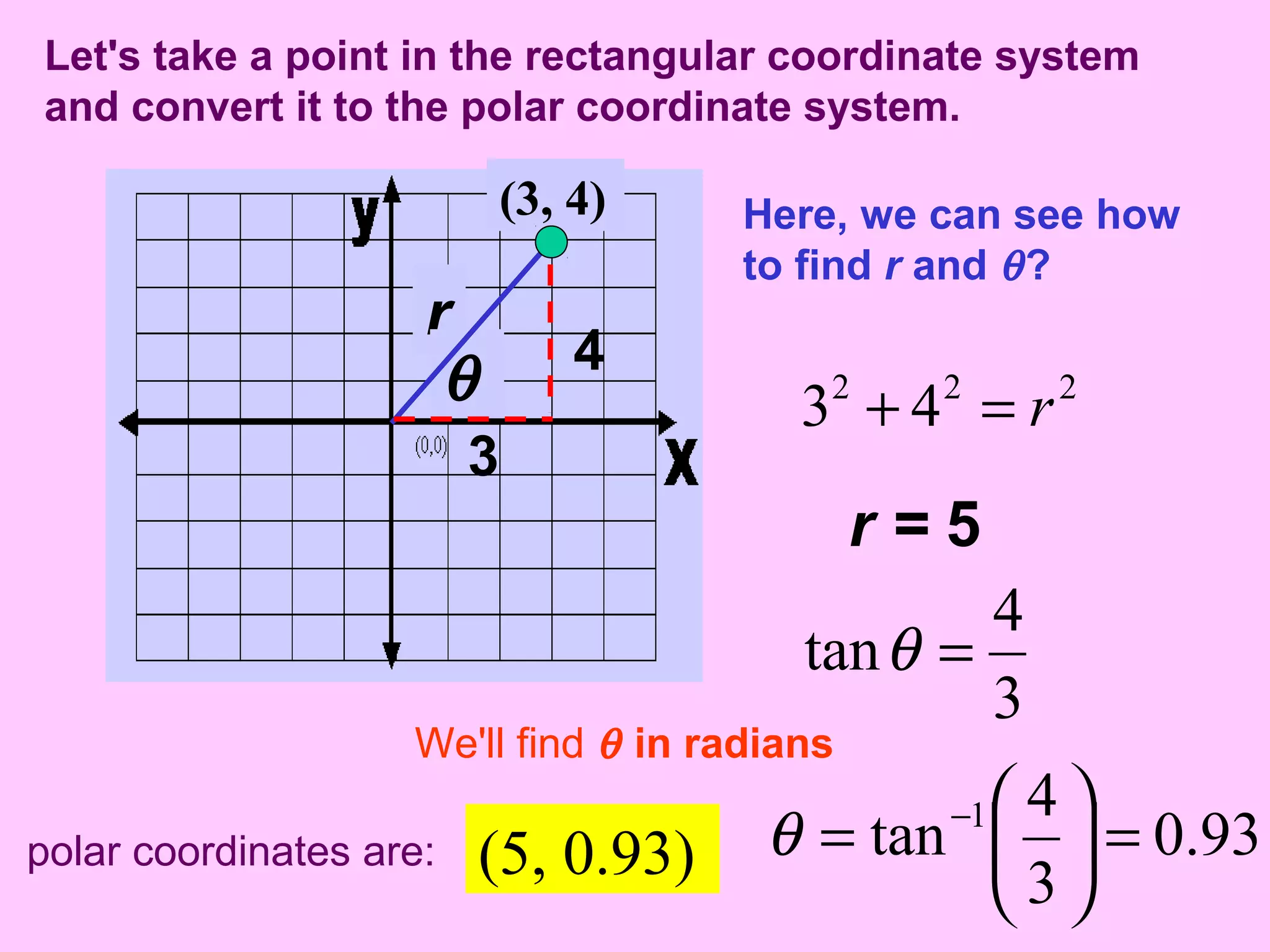
- An example shows calculating the polar coordinates (5, 0.93) for the Cartesian point (3, 4).