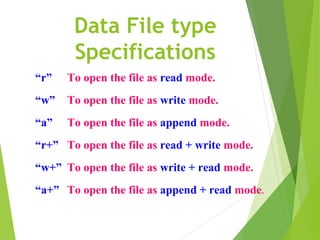
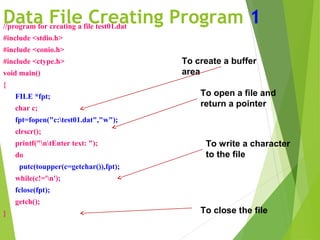
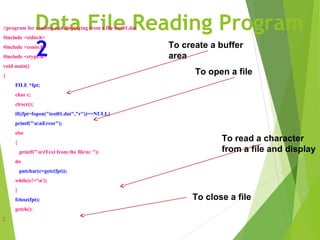
This document discusses data files in C programming. It defines a data file as a computer file that stores data for use by an application or system. It describes two types of data files: stream-oriented (text files and unformatted files) and system-oriented (low-level files). It explains how to open, read from, write to, and close data files using functions like fopen(), fclose(), getc(), putc(), fprintf(), and fscanf(). It provides examples of programs to create a data file by writing user input to a file and to read from an existing data file and display the contents.