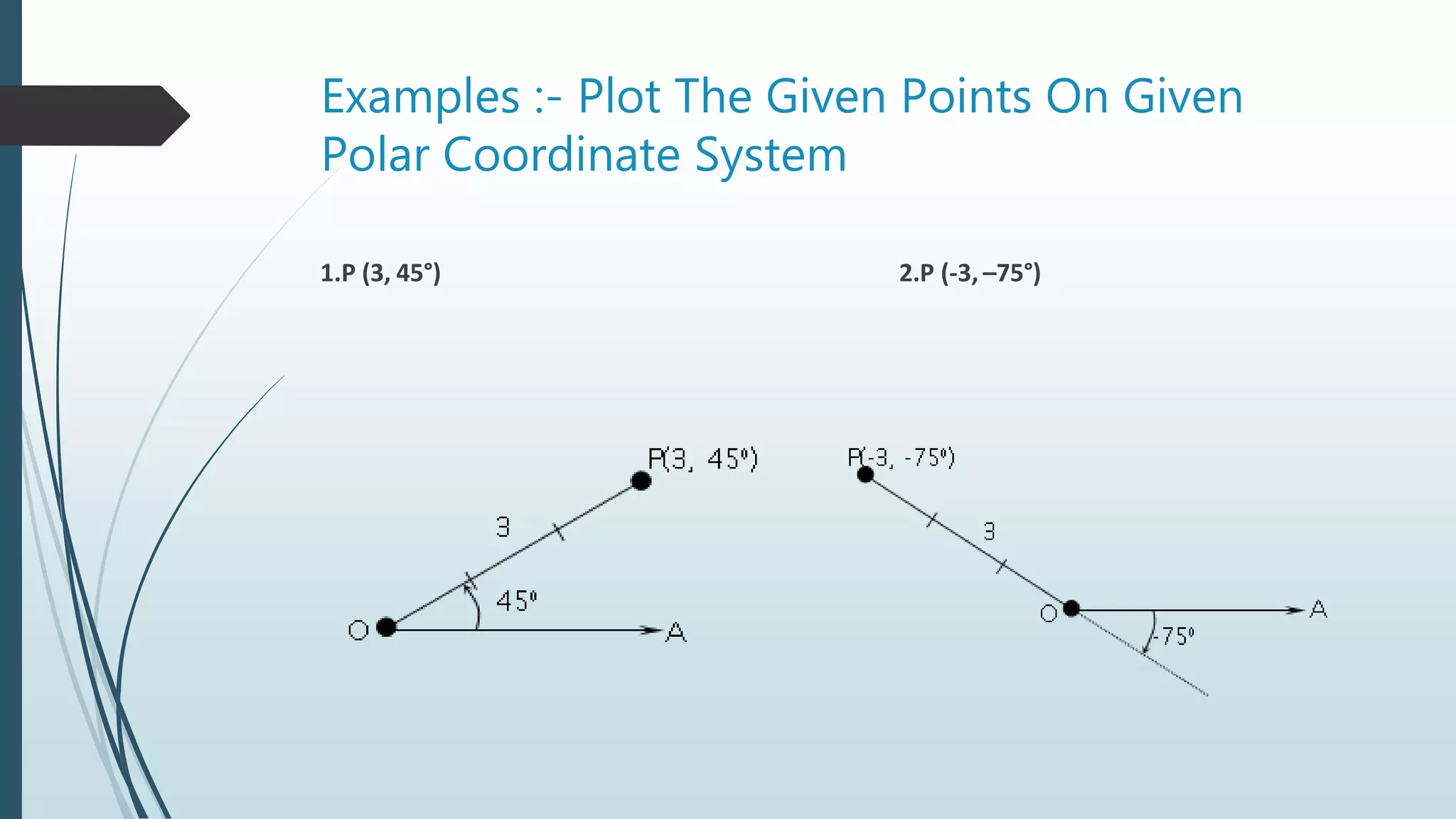
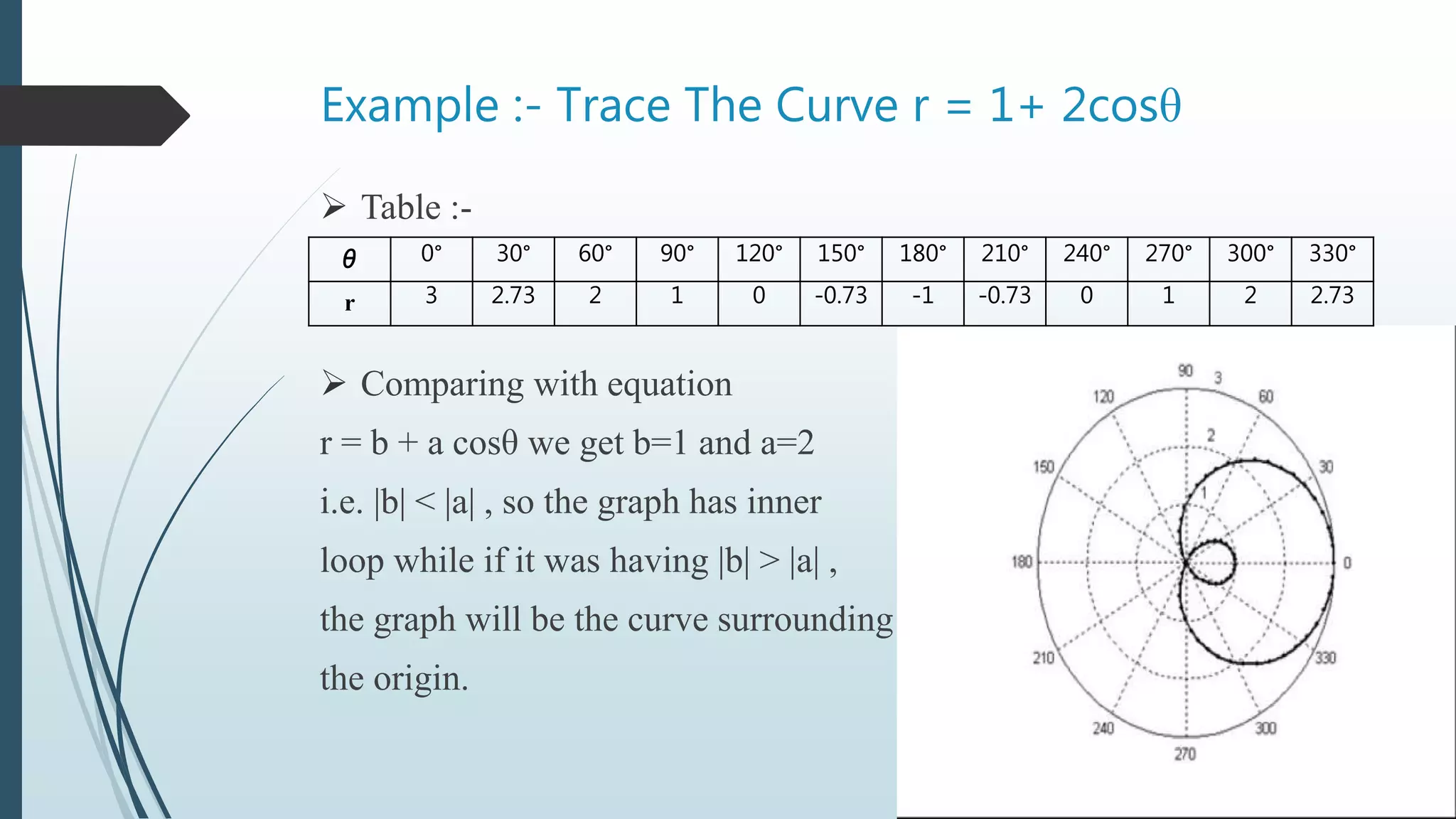
The document discusses polar coordinates, defining them as a system based on distances from a fixed point and directions from a fixed line. It covers the relationship between polar and rectangular coordinates, examples of plotting points, and the graphs of polar equations including special types like rose curves and limacons. The submission is for a group project at Sarvajanik College of Engineering and Technology, guided by Prof. Dixa P. Kevadiya.