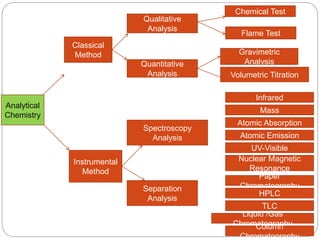
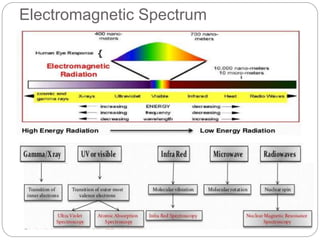
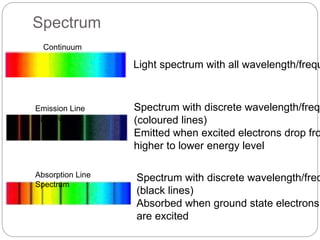
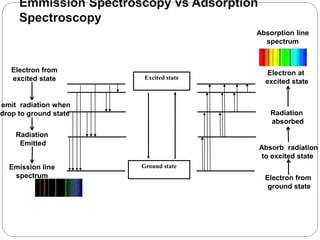
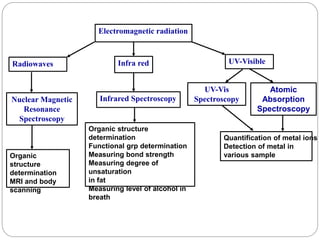
This document discusses various analytical techniques used in spectroscopy. It describes spectroscopy as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. There are different types of spectroscopy including absorption, emission, and scattering spectroscopy. Specific techniques are used to identify unknown substances, predict behavior of new materials, and qualitatively or quantitatively analyze chemical composition. The document provides examples of spectroscopy techniques and their applications in areas like determining organic structures and quantifying metal ions.