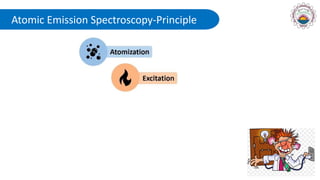
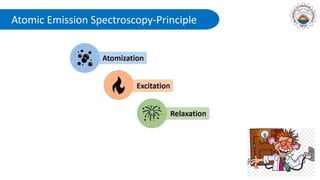
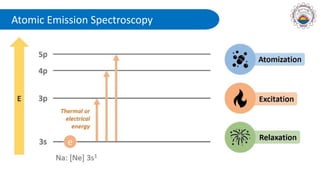
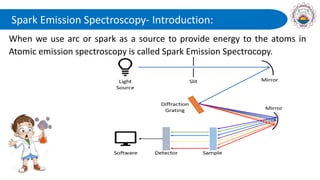
Spectroscopy is defined as the study of the interaction between radiation and matter as a function of wavelength. It involves splitting light into its constituent wavelengths to study how matter absorbs and emits electromagnetic radiation. There are several types of spectroscopy that are used for various applications like determining atomic structure, monitoring dissolved oxygen, and characterizing proteins. Atomic emission spectroscopy uses high temperatures to excite the atoms in a sample, causing them to emit light at characteristic wavelengths. This emitted light is analyzed to determine the elemental composition of the sample.