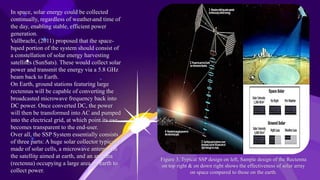
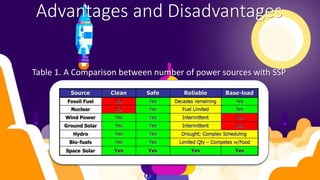
Space-based solar power (SBSP) involves collecting solar energy in space using satellites and transmitting it to Earth as microwaves or laser beams, with the potential for continuous power generation. While SBSP offers advantages such as independence from weather and day/night cycles, it faces challenges including high launch costs and the need for large-scale infrastructure. Successful implementation requires governmental support, lower launch costs, and private sector involvement.