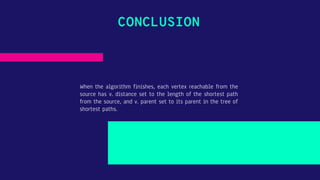
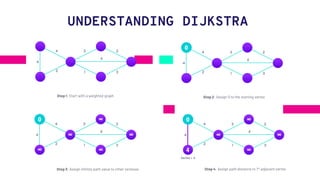
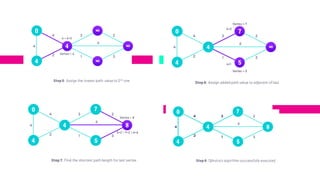
Dijkstra's algorithm allows finding the shortest path between any two vertices in a graph. It works by overestimating the distance of each vertex from the starting point and then visiting neighbors to find shorter paths. The algorithm uses a greedy approach, finding the next best solution at each step. It maintains path distances in an array and maps each vertex to its predecessor in the shortest path. A priority queue is used to efficiently retrieve the closest vertex. The time complexity is O(E Log V) and space is O(V). Applications include social networks, maps, and telephone networks.




![1 function Dijkstra(Graph, source):
2
3 create vertex set Q
4
5 for each vertex v in Graph:
6 dist[v] ← INFINITY
7 prev[v] ← UNDEFINED
8 add v to Q
9 dist[source] ← 0
10
11 while Q is not empty:
12 u ← vertex in Q with min dist[u]
13
14 remove u from Q
15
16 for each neighbor v of u still in Q:
17 alt ← dist[u] + length(u, v)
18 if alt < dist[v]:
19 dist[v] ← alt
20 prev[v] ← u
21
22 return dist[], prev[]
PSEUDOCODE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organized4-211211134112/85/Dijkstra-s-Algorithm-8-320.jpg)