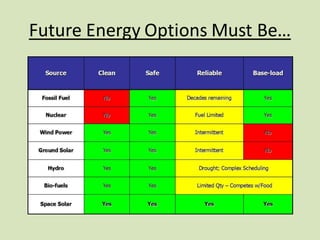
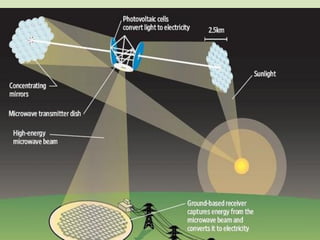
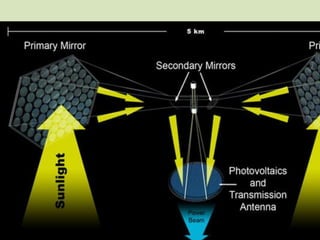
Space-based solar power (SBSP) collects solar power in space using solar satellites and beams it to large rectennas on Earth. SBSP has been researched since the 1970s as a potential future energy option that could provide abundant, continuous solar power without atmospheric or weather effects. While extremely expensive currently, SBSP could solve global energy needs long-term by tapping into the vast solar resources available in space.