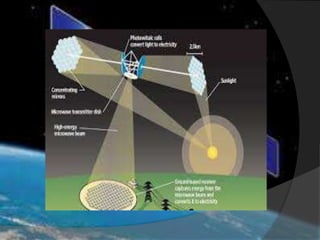
This document summarizes a seminar on space-based solar power systems. It discusses how solar power could be collected in space via solar panels on satellites, transmitted to Earth via microwave beams, and received on Earth using large rectenna arrays that convert the microwaves to electricity. The concept was first described in 1968 and offers advantages like constant power generation and lack of transmission losses. However, the major disadvantage is the high cost of launching infrastructure to space.