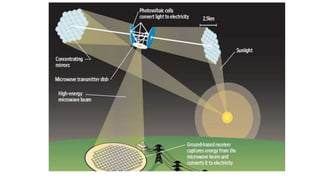
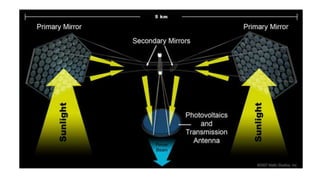
Space-based solar power (SBSP) involves collecting solar energy in space using satellites and transmitting it to receivers on Earth. SBSP has higher solar collection rates than ground-based systems due to lack of an atmosphere in space. SBSP satellites would convert sunlight to microwaves or lasers and transmit the energy to large rectenna receivers on Earth, avoiding transmission losses. Significant challenges to developing operational SBSP systems include reducing launch costs, demonstrating efficient space-to-Earth power transmission, and developing large in-space structures. If technical challenges can be overcome, SBSP could potentially supply all of Earth's electrical needs using the vast solar resources in space.