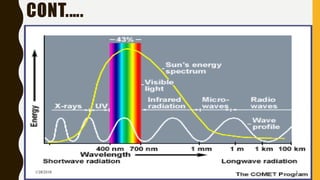
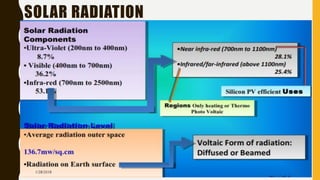
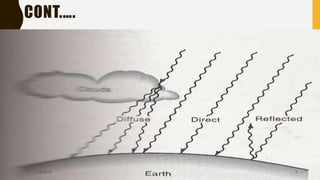
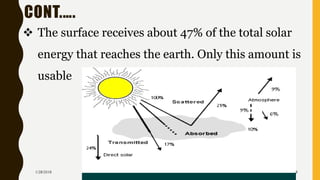
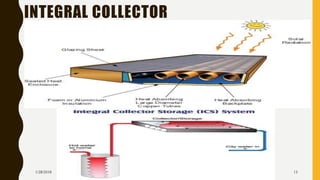
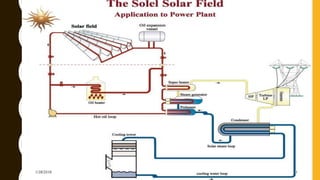
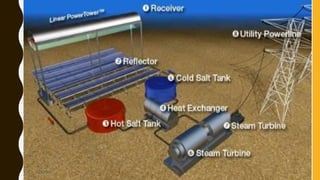
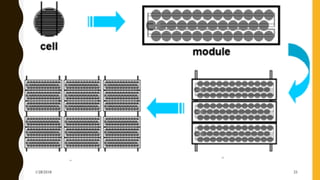
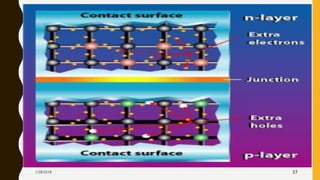
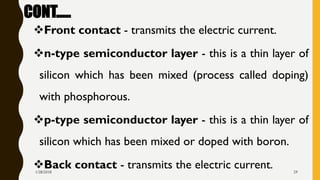
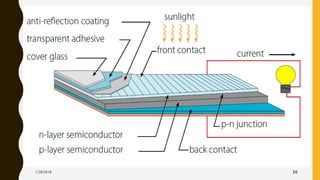
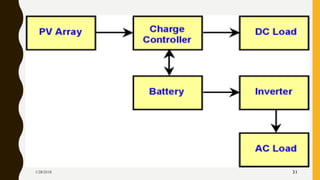
The document provides an overview of solar energy, explaining its origin from the sun and how it can be converted into electricity through technologies like photovoltaics and concentrated solar power. It details various methods of harnessing solar energy, including solar thermal technologies and the components of solar cells that facilitate the conversion process. Additionally, it discusses the structure and functioning of photovoltaic cells, highlighting their role in generating electricity from sunlight.