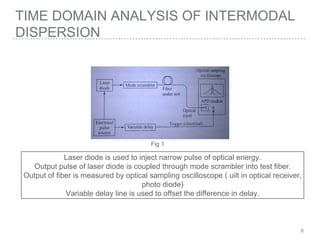
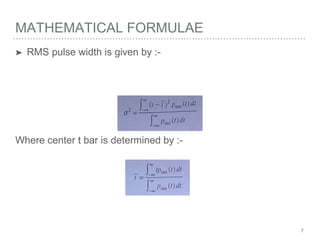
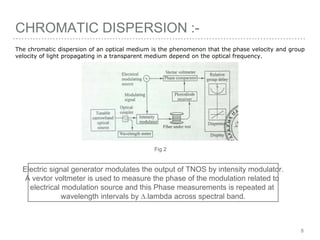
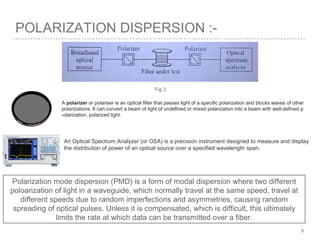
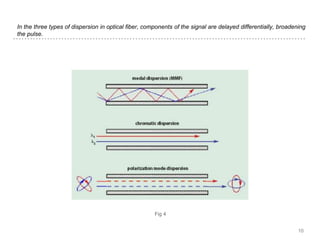
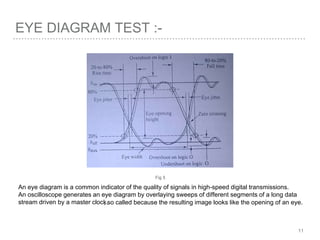
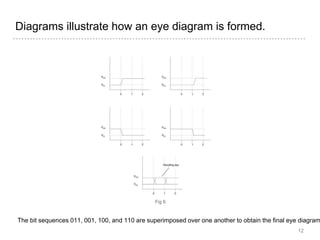
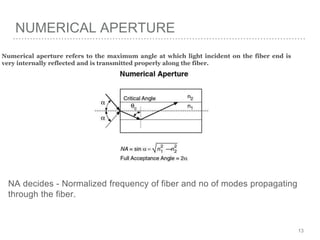
This document discusses measurement of dispersion, numerical aperture (NA), and eye diagrams in optical fiber communication. It defines dispersion as pulse broadening of light wave signals, and describes three types: intermodal, chromatic, and polarization mode dispersion. Formulas are provided for calculating root mean square pulse width and chromatic dispersion. Measurement techniques are outlined for each dispersion type using devices like optical sampling oscilloscopes and vector voltmeters. Numerical aperture is defined as the maximum angle of light acceptance, and impacts the number of propagating modes. Eye diagrams provide a way to assess signal quality by overlaying segments of a data stream on an oscilloscope. Diagrams illustrate how an eye diagram is formed from a bit sequence.