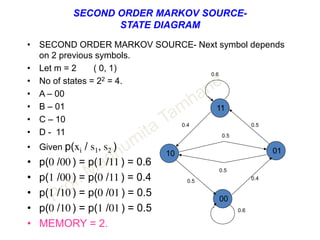
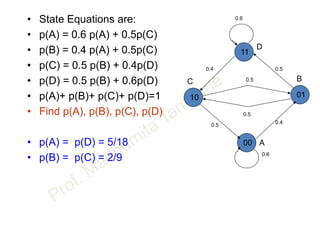
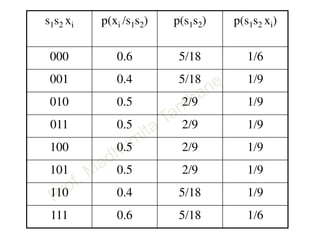
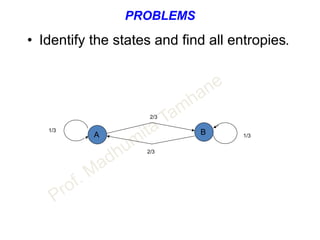
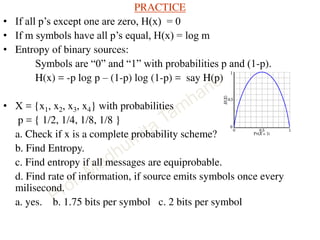
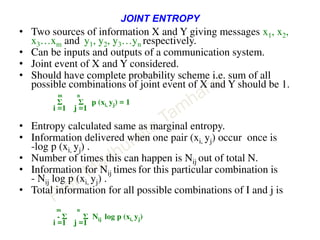
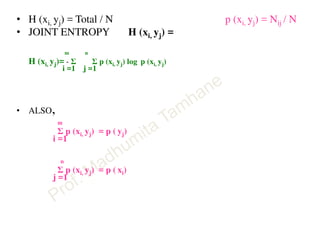
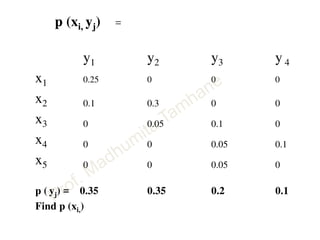
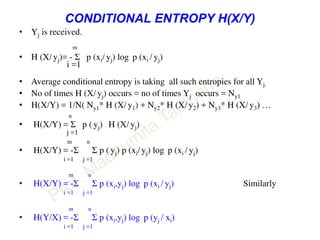
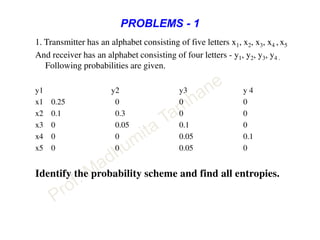
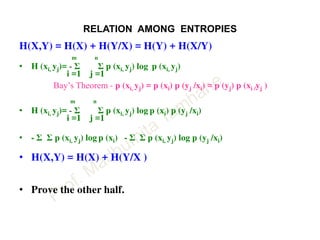
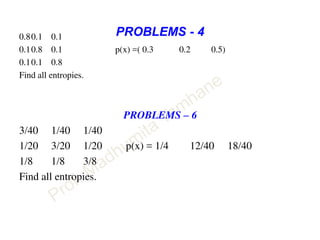
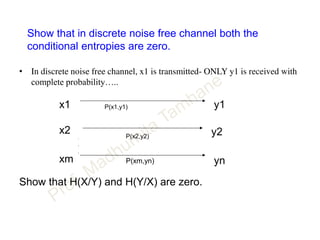
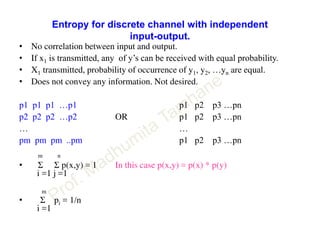
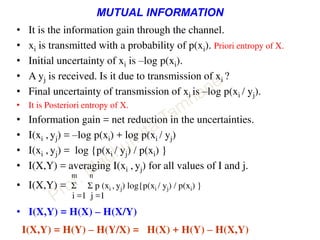
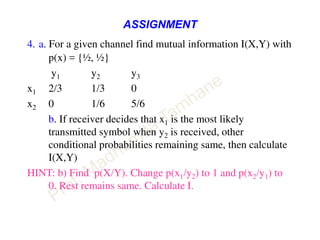
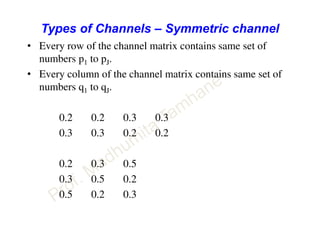
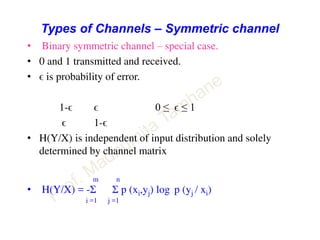
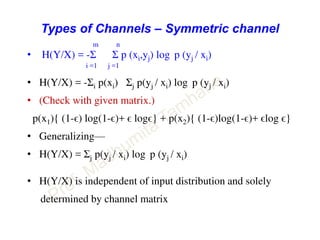
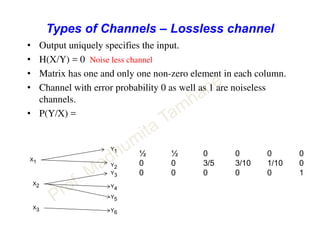
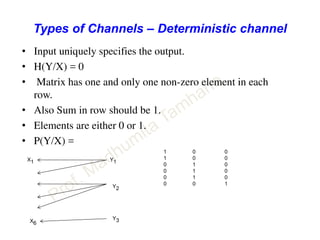
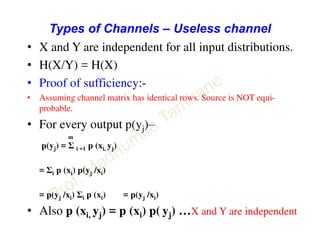
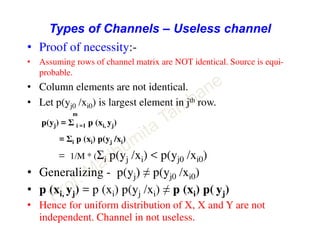
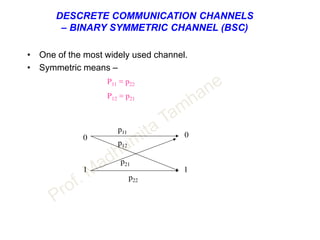
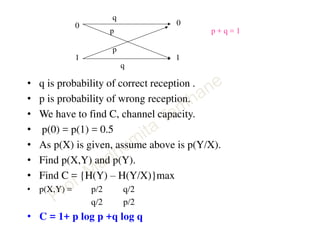
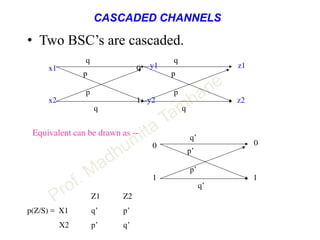
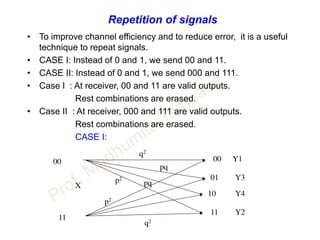
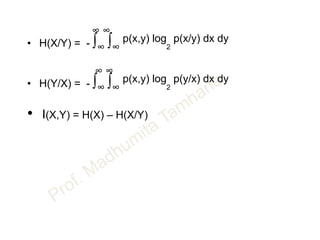This document discusses information theory concepts including information, entropy, joint entropy, conditional entropy, and mutual information. It provides definitions and formulas for quantifying information based on probability. Key points include: information is inversely proportional to probability; entropy H(X) quantifies average information of a source; joint entropy H(X,Y) quantifies information of two related sources; and conditional entropy H(X|Y) measures remaining uncertainty about a source given knowledge of the other. Several examples are provided to illustrate calculating these information theory metrics.





![Show that entropy of source with equi-probable symbols
in always maximum.
• H(X) – log m = Σpi log1/ pi – log m
• = Σpi log1/ pi – Σpi log m
• = Σpi log 1/ (pi * m)
• we have ln a ≤ (a-1) ~ property of log
• H(X) – log m ≤ Σpi [(1/ (pi * m)) – 1] log2e
• ≤ [Σpi (1/ (pi * m)) – Σpi ] log2e
• ≤ [Σ 1/m) – Σpi ] log2e
• ≤ 0
• H(X) – log m ≤ 0
• H(X) ≤ log m
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-7-320.jpg)



![H(X) ≥H(X/Y) H(Y) ≥ H(Y/X)
• H(X/Y) -H(X) = - Σ Σ p (xi, yj) log p (xi / yj) + Σ p (xi) log p (xi)
n
as Σ p (xi, yj) = p ( xi)
J =1
• = -Σ Σ p (xi, yj) log p (xi / yj) +Σ Σ p (xi, yj) log p (xi)
• H(X/Y) -H(X) = Σ Σ p (xi, yj) log {p (xi)/ p (xi /yj)}
we have ln a ≤ (a-1) ~ property of log
• H(X/Y) -H(X) ≤ Σ Σ p (xi, yj) { {p (xi)/ p (xi /yj)} – 1 } log2e
• ≤ [ Σ Σ p (xi, yj) p (xi)/ p (xi /yj) - Σ Σ p (xi, yj) ] log2e
• ≤[ Σ Σ p ( yj) p (xi) - Σ Σ p (xi, yj) ] log2e
• ≤[1 – 1] log2e
• H(X/Y) -H(X) ≤ 0
• Prove H(X,Y) ≤ H(X) + H(Y) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-17-320.jpg)
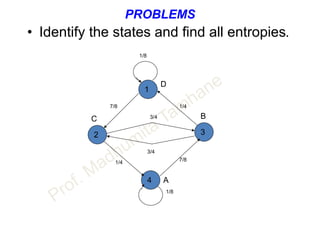
![PROBLEMS - 2
• Identify the following probability scheme and find all
entropies.
• Given P(x) = [ 0.3 0.4 0.3]
y1
y2
y3x1
x1
x1 3/5
1/5
1/5
1/5
1/5
1/5
1/5
3/5
3/5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-18-320.jpg)
![PROBLEMS - 3
• Given p(x) = [ 0.6 0.3 0.1] . Find all entropies.
y1
y2
y3x3
x2
x1
1-p
1-p
p
p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-19-320.jpg)






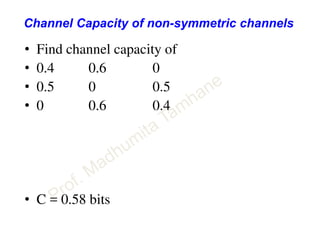
![• y1 y2 y3 y4
p(Y/X) = X1 q2 p2 pq pq
X2 p2 q2 pq pq
• Find C.
• C = (p2 + q2) * [ 1 + q2 / (p2 + q2) log { q2 / (p2 + q2) } +
p2 / (p2 + q2) log { p2 / (p2 + q2) } ]
• C = (p2 + q2) * [ 1 –H(p2 / (p2 + q2))]
• All above CAN NOT be used for non symmetric
channels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-42-320.jpg)

![Channel Capacity of non-symmetric channels
• [ P] [ Q] = - [ H] auxiliary variables Q1 and Q2
P11 P12
P21 P22
PY/X =
P11 P12
P21 P22
Q1
Q2
= P11 logP11 + P12 logP12
P21 logP21 + P22 LogP22
Matrix
Operation
Then
C = log ( 2Q1 + 2Q2 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-44-320.jpg)





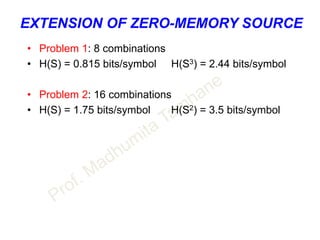
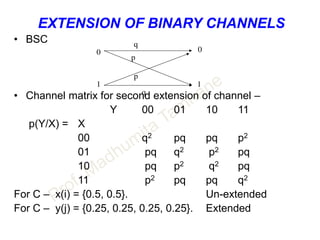
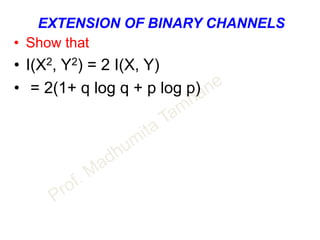



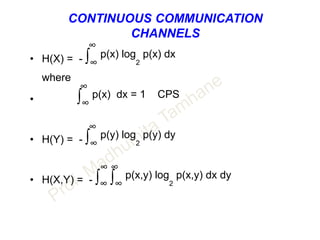
![CAPACITY OF GAUSSIAN CHANNEL
DESCRETE SIGNAL CONTINEOUS CHANNEL
• Channel capacity of white band limited Gaussian channel is
C = B log2[ 1 + S/N ] bits/s
• B – Channel bandwidth
• S – Signal power
• N – Noise power within channel bandwidth
• ALSO N = η B where
η / 2 is two sided noise power spectral density.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-57-320.jpg)

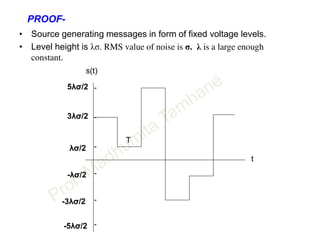
![• M possible types of messages.
• M levels.
• Assuming all messages are equally likely.
• Average signal power is
S = 2/M { (λσ/2 )2 + (3λσ/2 )2 + (5λσ/2 )2 + … ( [M-1] λσ/2 )2 }
• S = 2/M * (λσ/2 )2 { 1+ 3 2 + 52 + … [M-1]2 }
• S = 2/M * (λσ/2 )2 {M (M2 - 1)} / 6
Hint: Σ N2 = 1/6*N*(N+1)*(2N+1)
• S = (M2-1)/12 * (λσ )2
• M =[ ( 1+ 12 S / (λσ )2 ]1/2 N = σ 2
• M =[ ( 1+ 12 S / λ2 N ]1/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-60-320.jpg)
![• M equally likely messages.
• H = log2 M
• H = log2 [ 1+ 12 S / λ2 N ]1/2 Let λ2 =12
• H = ½ * log2 [ 1+ S / N ]
• Square signals have rise time and fall time through channel.
• Rise time tr = 0.5/B = 1/(2B)
• Signal will be detected correctly if T is at least equal to tr .
• T = 1/(2B)
• Message rate r = 1/T = 2B messages/s
• C = Rmax = 2B * H
• C = Rmax = 2B * ½ * log2 [ 1+ S / N ]
• C = B log2 [1+ S / N ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-61-320.jpg)

![SHANNON’s LIMIT
• Gaussian channel has noise spectral density - η/2
• N = η/2 * 2B = ηB
• C = B log2 [ 1+ S / ηB]
• C = (S / η ) (η / S) B log2 [ 1+ S / ηB]
• C = (S / η ) log2 [ 1+ S / ηB] (ηB / S)
Lim x → 0 ( 1+X ) 1/X = e
X = S / ηB
• At Shannon’s limit, B → ∞, S / ηB → 0
• C ∞ = (S / η ) log2 e
• C ∞ = 1.44 (S / η )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtheory-160202054047/85/Information-theory-63-320.jpg)