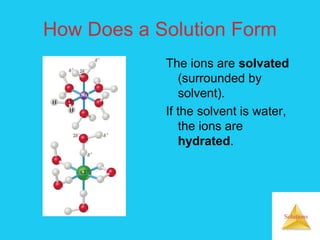
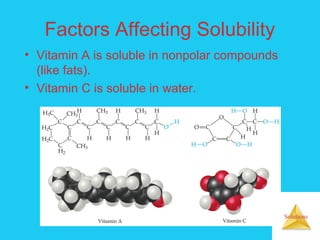
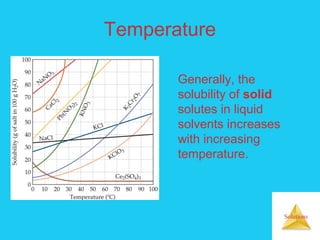
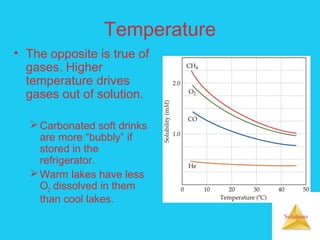
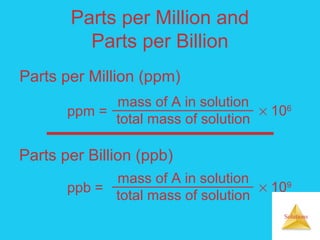
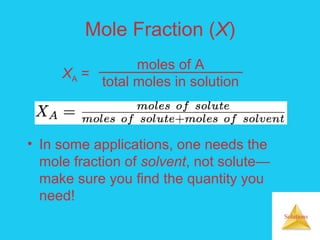
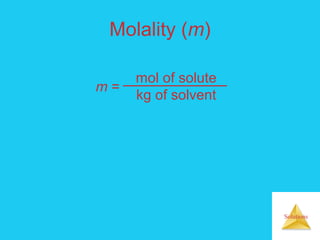
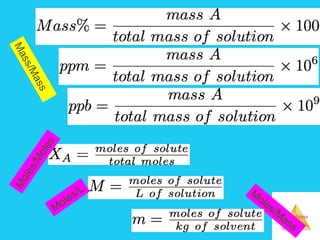
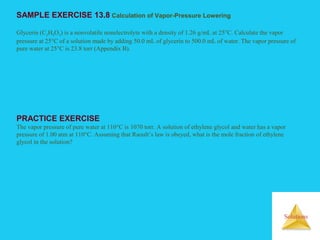
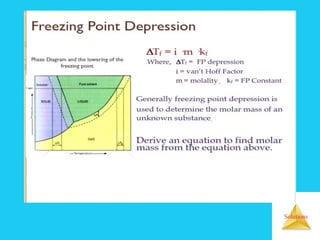
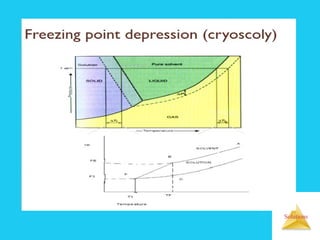
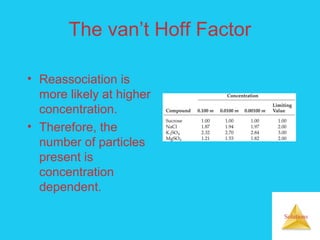
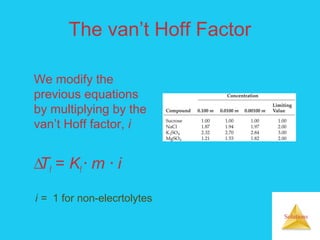
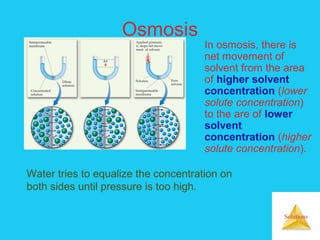
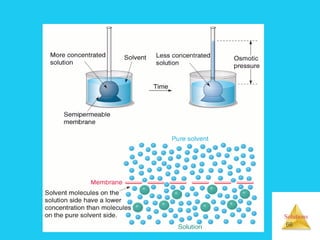
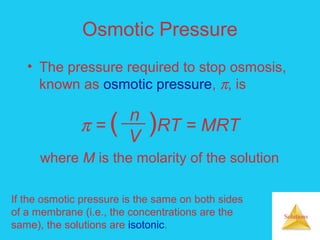
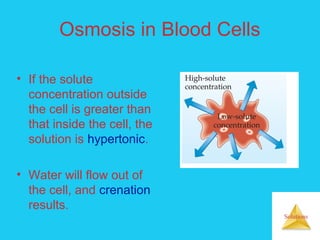
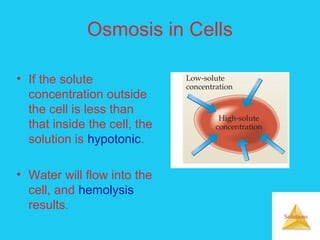
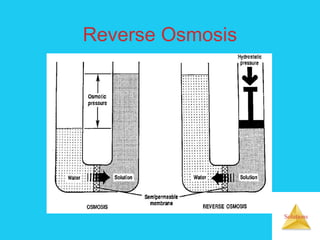
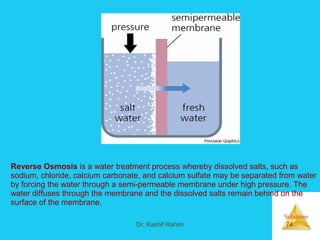
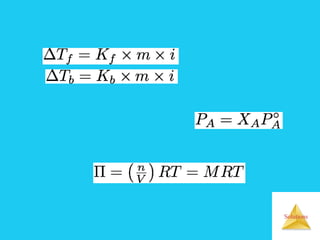Solutions are homogeneous mixtures formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent. For a solution to form, the solute and solvent molecules must interact favorably through intermolecular forces like ion-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, or dispersion forces. The solubility of a substance is affected by temperature, pressure, and how well the solute and solvent "like" each other. Solutions exhibit colligative properties like lowering of vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression that depend only on the number of solute particles and not their identity. Osmosis occurs when a semipermeable membrane separates solutions of different solute concentrations, causing net water movement from the lower to higher concentration side.