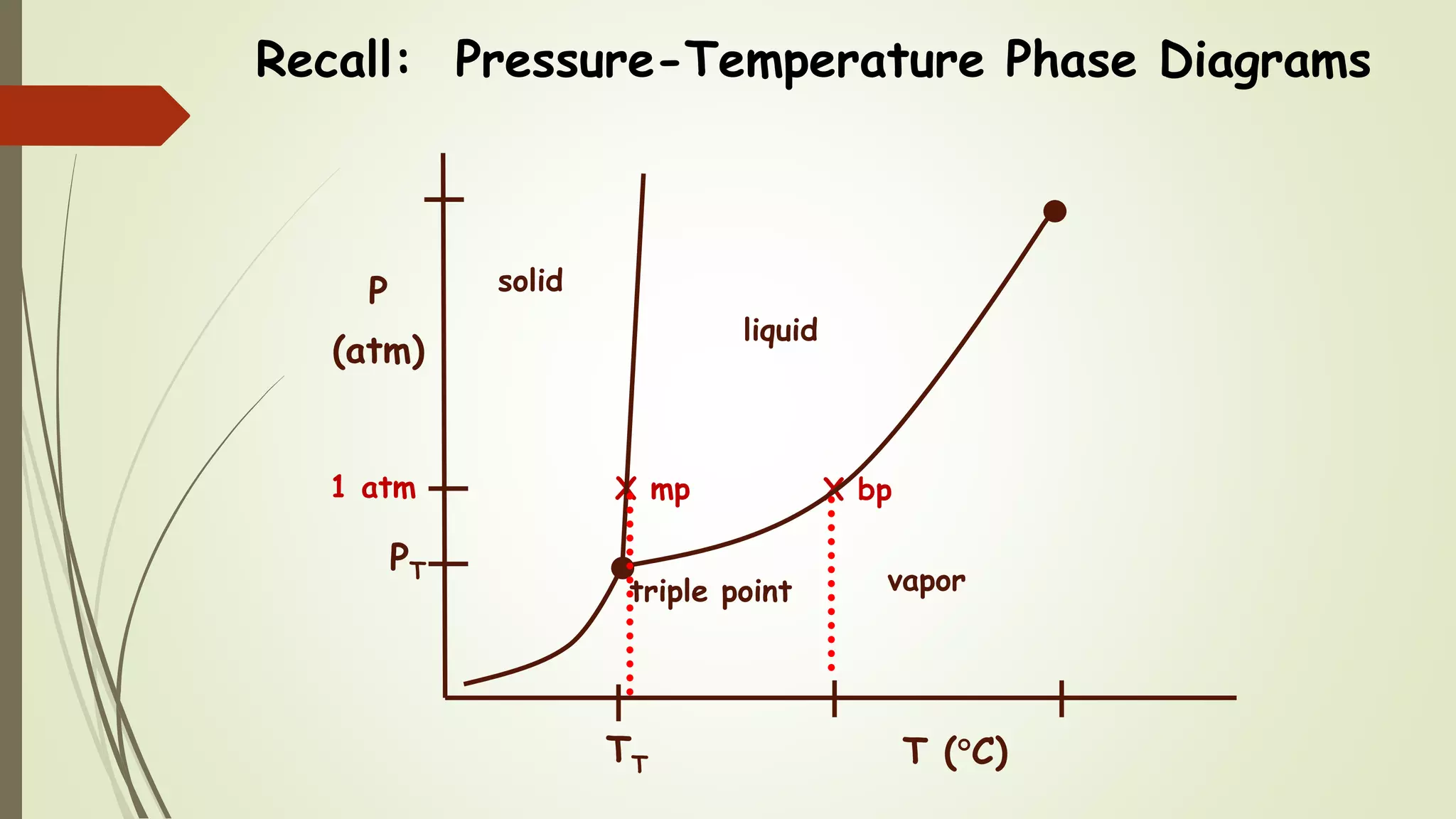
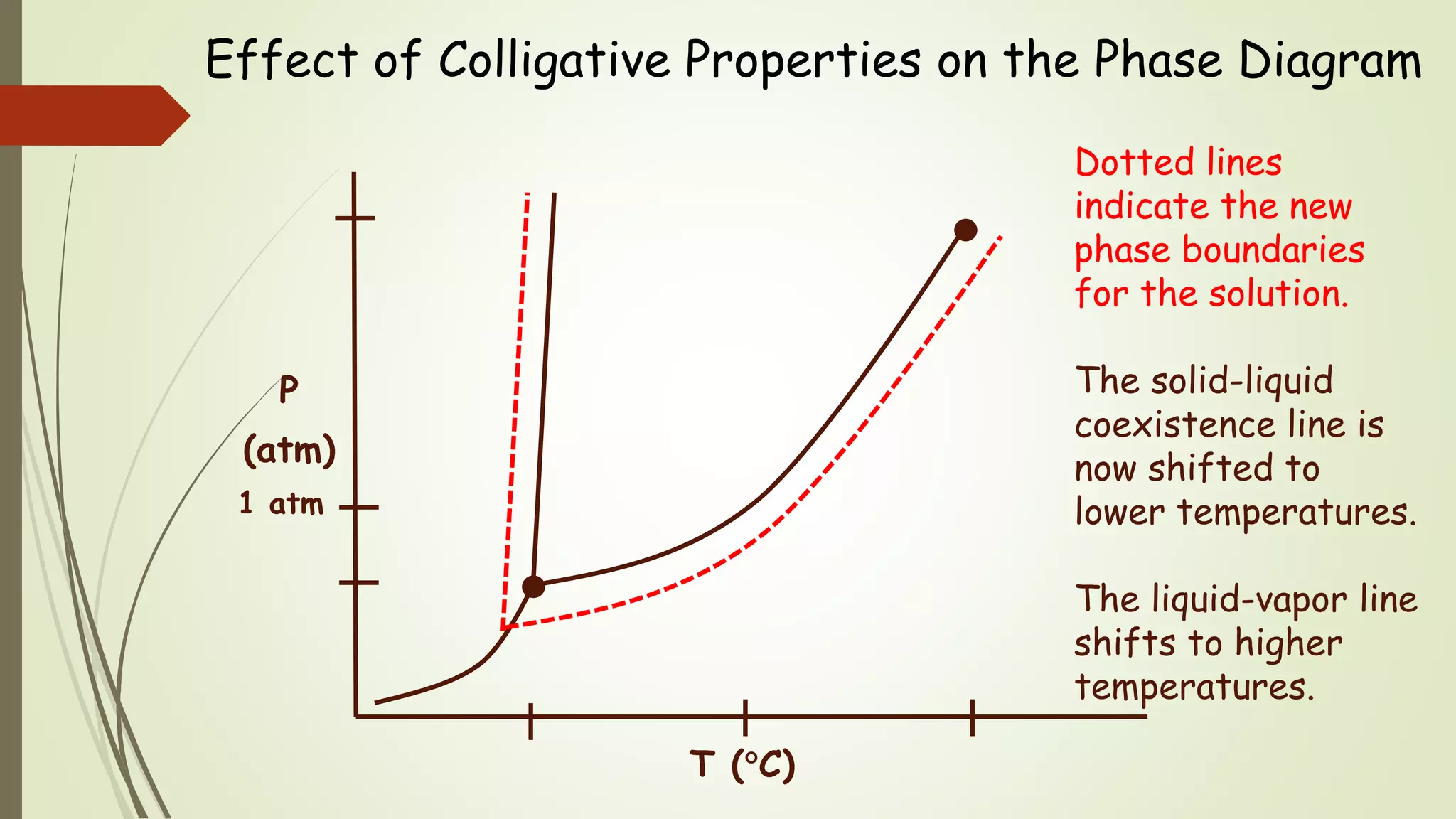
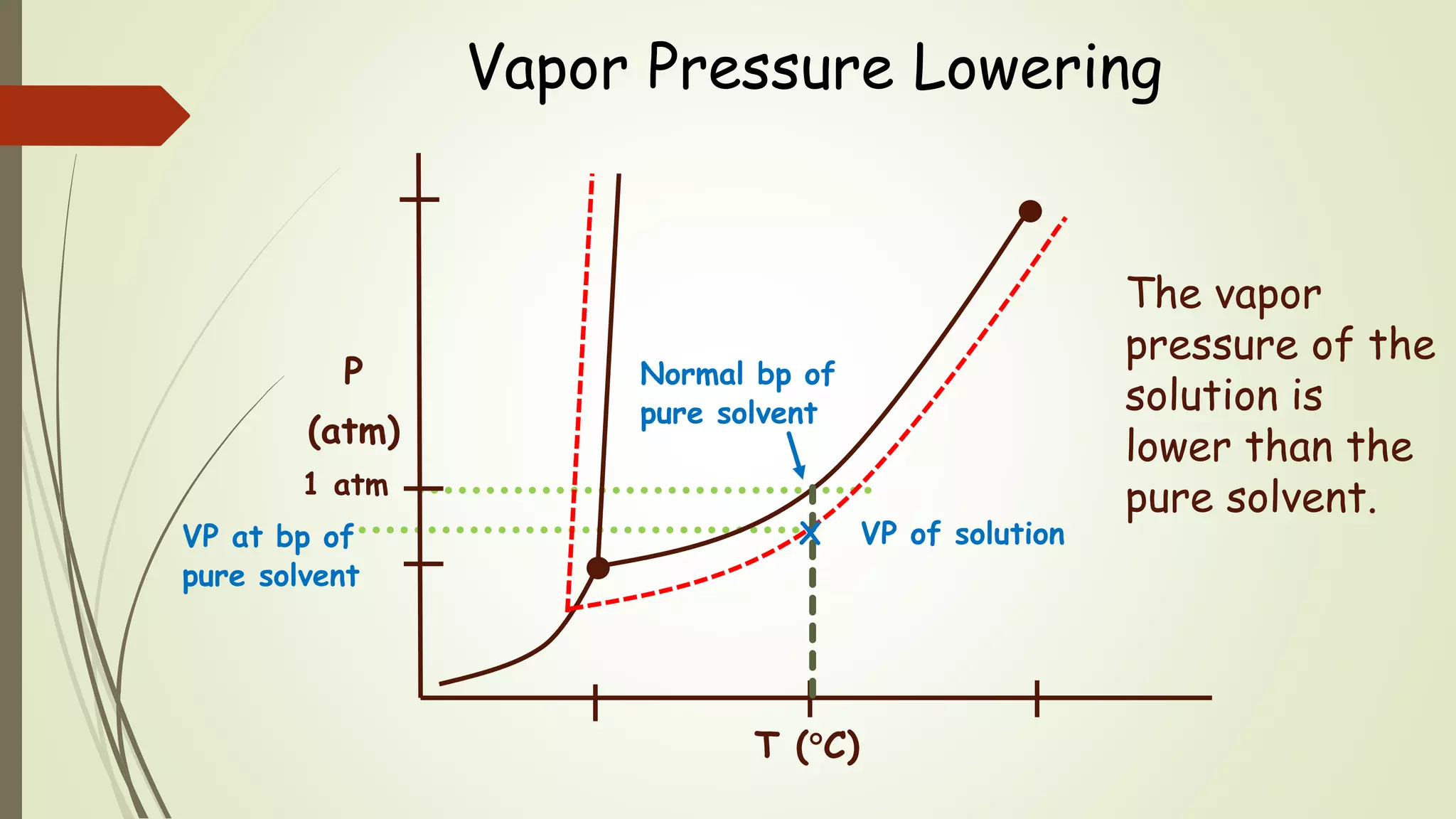
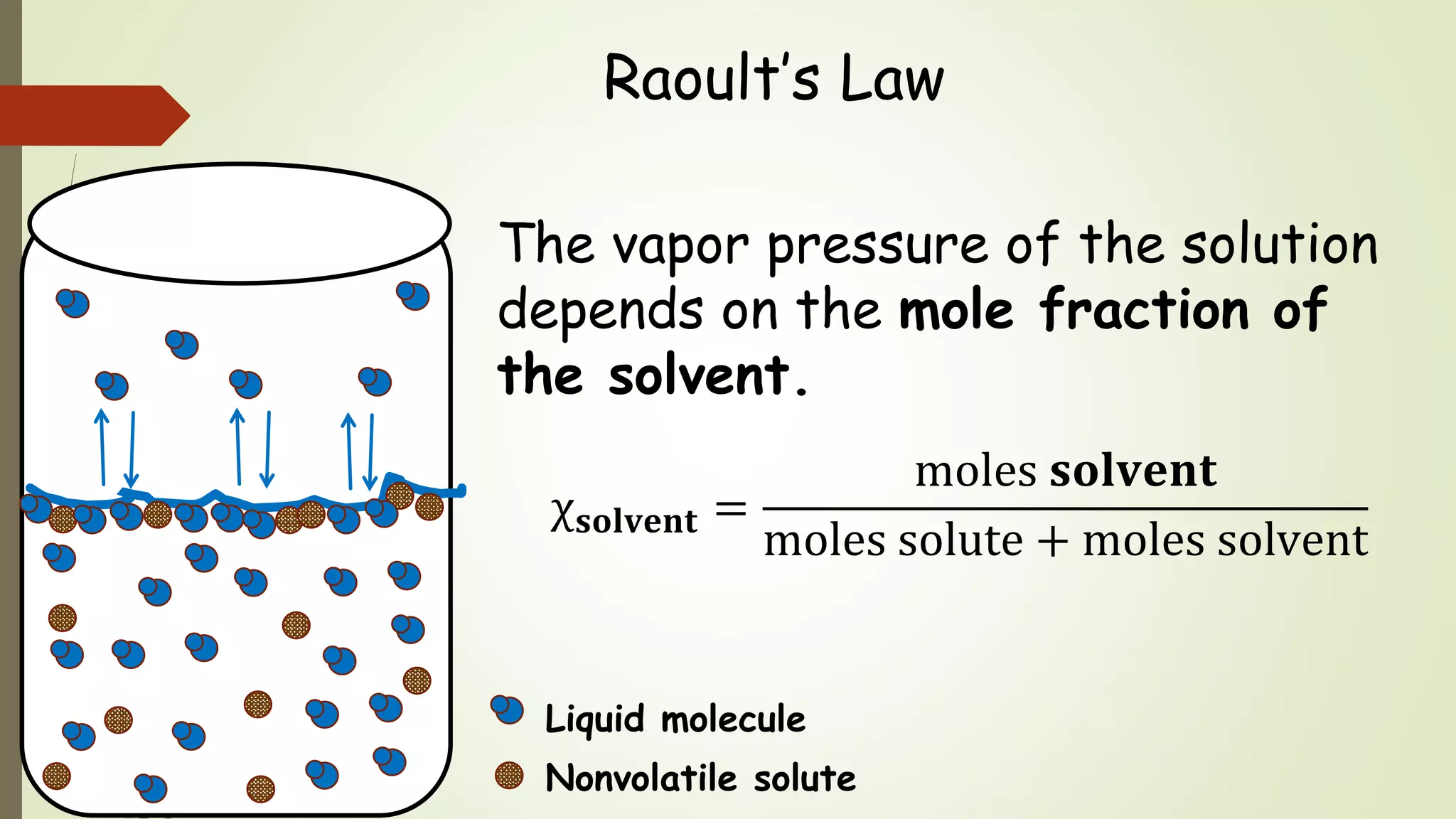
This document discusses colligative properties, which are physical properties of solutions that depend only on the ratio of solute to solvent particles and not the identity of the solute. It describes four colligative properties: boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure. It explains how adding a nonvolatile solute affects the phase diagram by shifting the freezing point downward and boiling point upward. Formulas are provided to calculate changes in boiling point and freezing point based on molality. Raoult's Law is introduced to explain how vapor pressure of a solution depends on the mole fraction of the solvent. Osmotic pressure is defined as the pressure required to prevent solvent flow across a semiperme









![Osmosis
The two regions are
separated by a
semipermeable membrane
that allows solvent to pass,
but not solute particles.
Osmosis By OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
The net movement of solvent molecules from a
region of lower solute concentration to one with a
higher concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solutionscolligpropsp15pt3final-160601155712/75/Colligative-Properties-III-14-2048.jpg)


