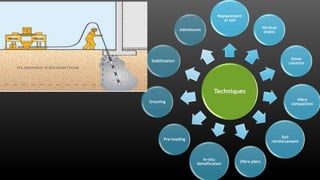
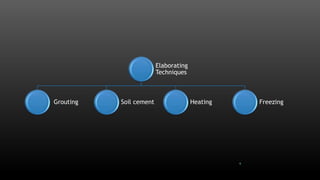
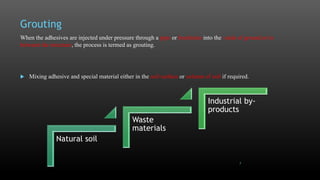
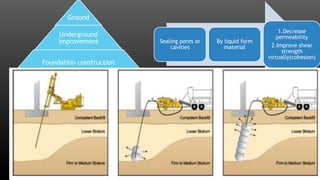
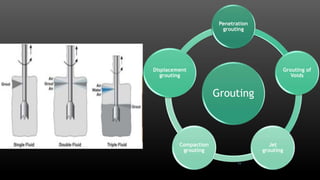
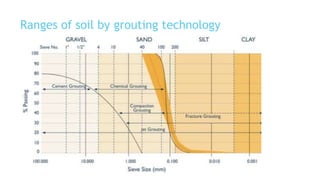
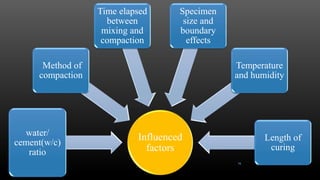
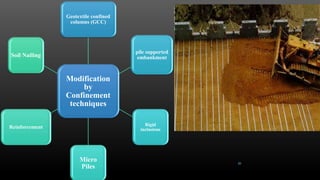
This document summarizes various physical soil improvement techniques including grouting, soil cement, heating, and freezing. Grouting involves injecting adhesives into soil to fill voids and increase strength. Types of grouting include penetration, compaction, and jet grouting. Soil cement mixes cement with soil to increase strength, stiffness, and durability. Heating soil to 300-1000°C changes its properties, making it harder. Freezing soil by refrigeration causes water to expand and bond particles, temporarily increasing strength for excavation support. The document provides details on each technique's process and applications.