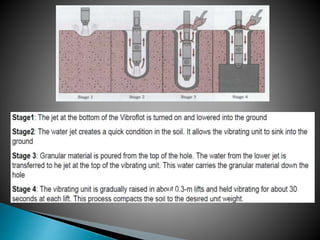
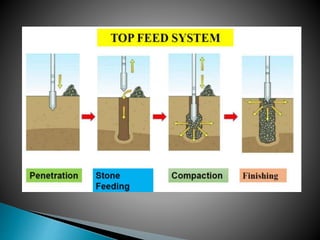
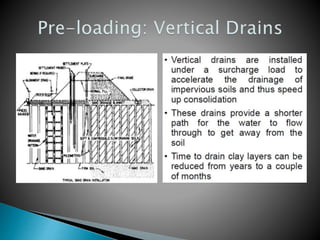
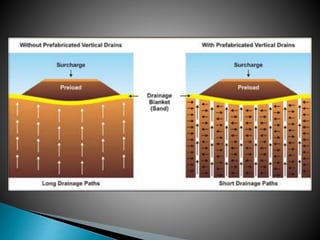
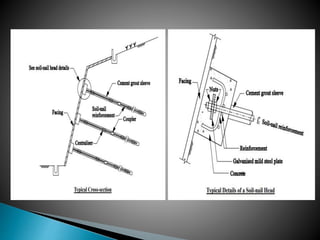
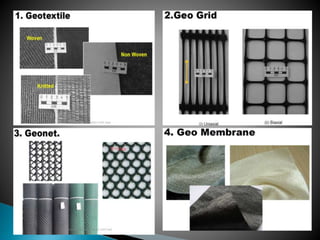
The document discusses various ground improvement techniques used to modify the engineering properties of soils, including densification, consolidation, reinforcement, and chemical treatment. It provides details on specific techniques like vibroflotation, ground freezing, and soil nailing. Geosynthetics are also introduced as natural or artificial products used in geotechnical constructions to improve properties of soils.