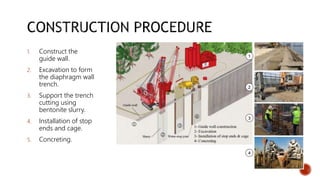
Diaphragm walls are underground retaining walls constructed using trench excavation supported by bentonite slurry. The process involves constructing guide walls, excavating a trench, installing reinforcement cages, and concreting. Diaphragm walls provide lateral support during deep excavations, serve as basement walls, and provide a water cutoff. They are suitable for use in congested areas and unstable soil below the water table.