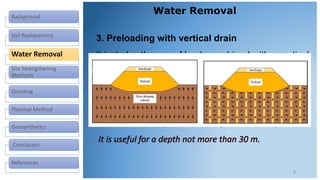
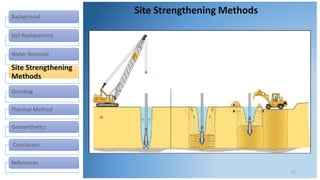
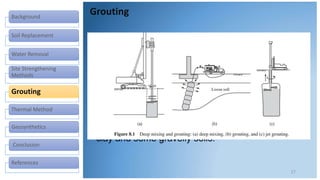
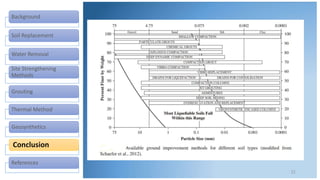
This document discusses various methods for improving different types of soil. It describes soil replacement, water removal through trenching, preloading, and vertical drains. Site strengthening techniques include dynamic compaction, vibro-compaction, vibro-replacement, and vibro-displacement. Grouting methods are injection of grout and deep mixing. Thermal methods involve heating and freezing soil. Geosynthetics provide erosion control, filtering, drainage, barriers, and soil reinforcement. The selection of a soil improvement method depends on factors like soil type, equipment, cost, time, skills, and experience.