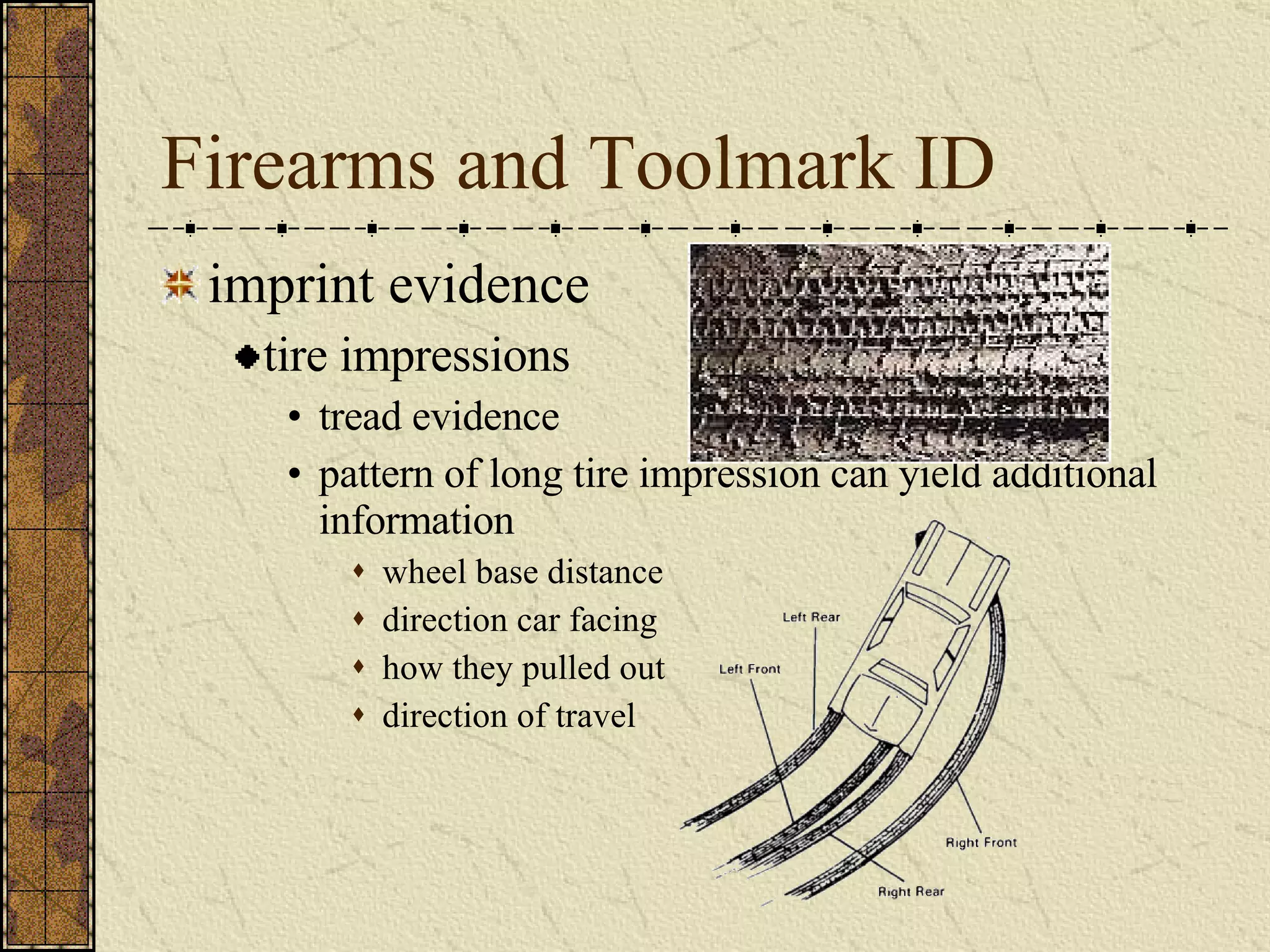
This document provides an overview of several topics in forensic science, criminal law, and careers in law enforcement. It discusses elements of forensic science like firearms identification, toolmark analysis, impression evidence analysis, and questioned document examination. It also covers forensic psychiatry and profiling, criminal law topics such as homicide, assault, rape, and burglary. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of careers in law enforcement and typical steps in the application process.