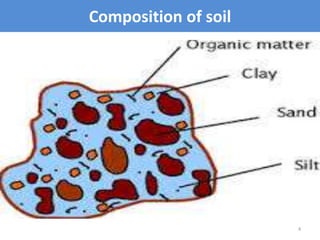
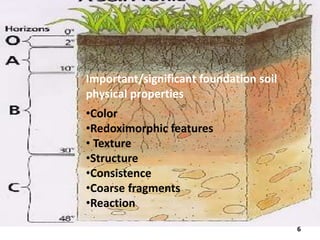
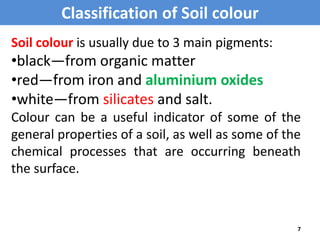
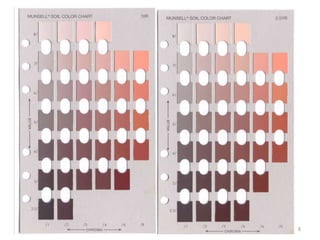
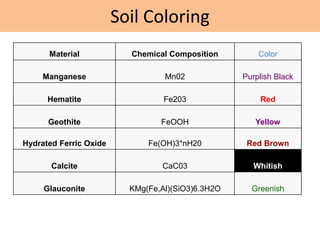
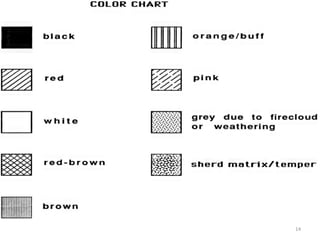
This document discusses soil color from the University of Salahaddin's College of Education Environmental Science department. It defines soil color, discusses the causes and classification of soil color. Soil color is influenced by organic matter, iron, aluminum, and silicate content and indicates environmental conditions during soil formation. Color can identify general properties and chemical processes in soil, ranging from gray to black, white, reds, browns, and yellows. Wet soil appears darker than dry soil and water affects oxidation rates influencing color.