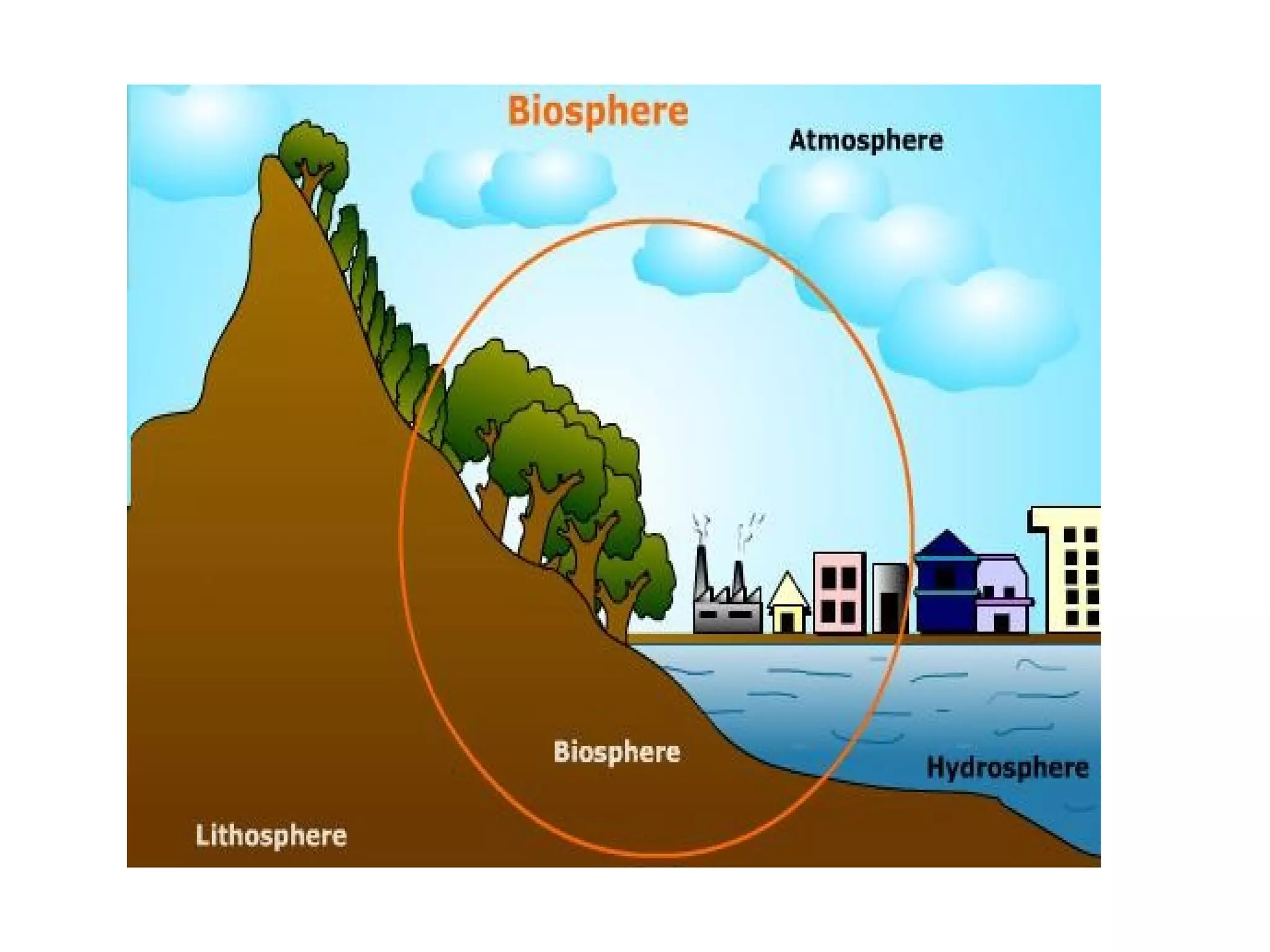
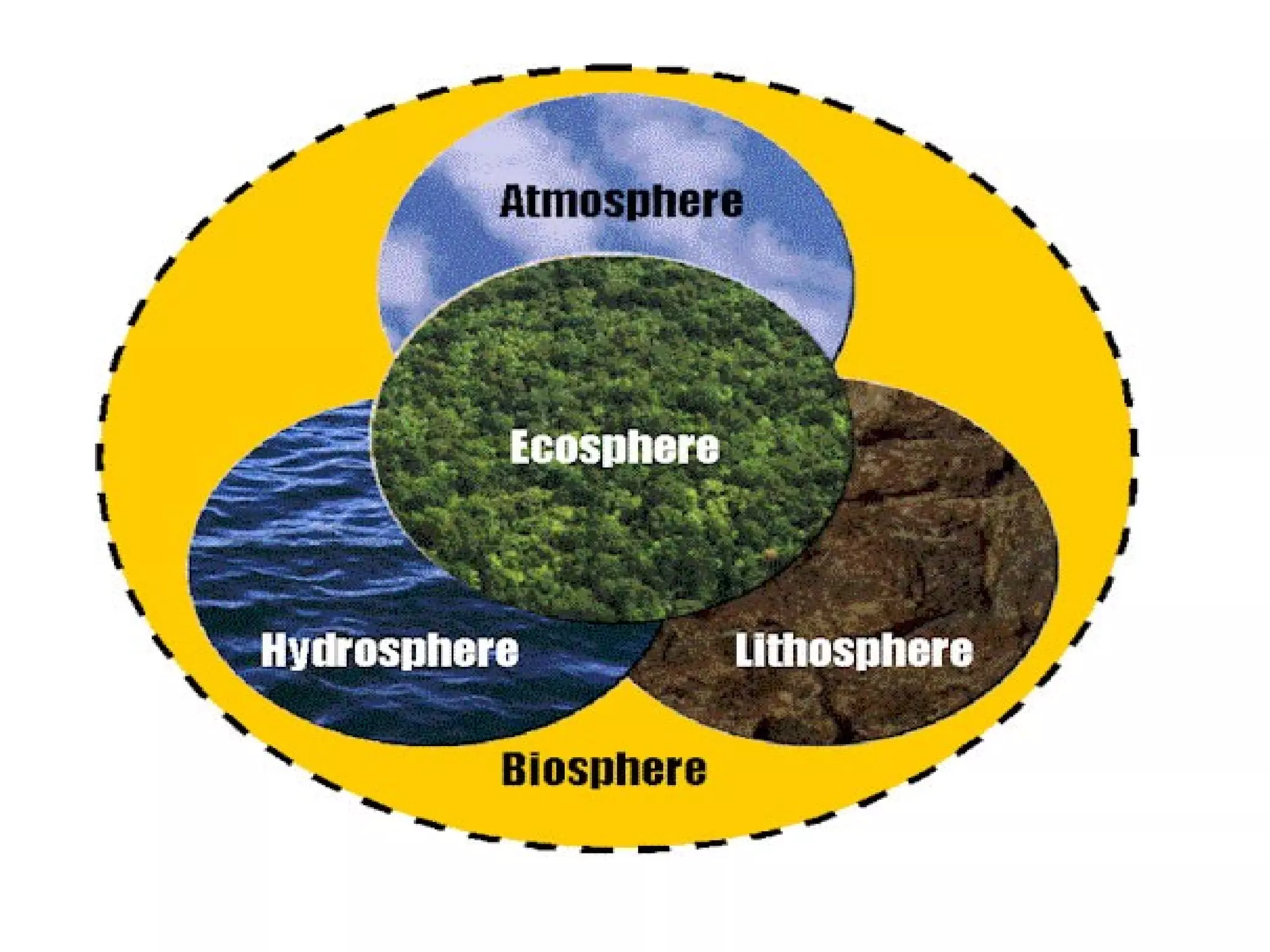
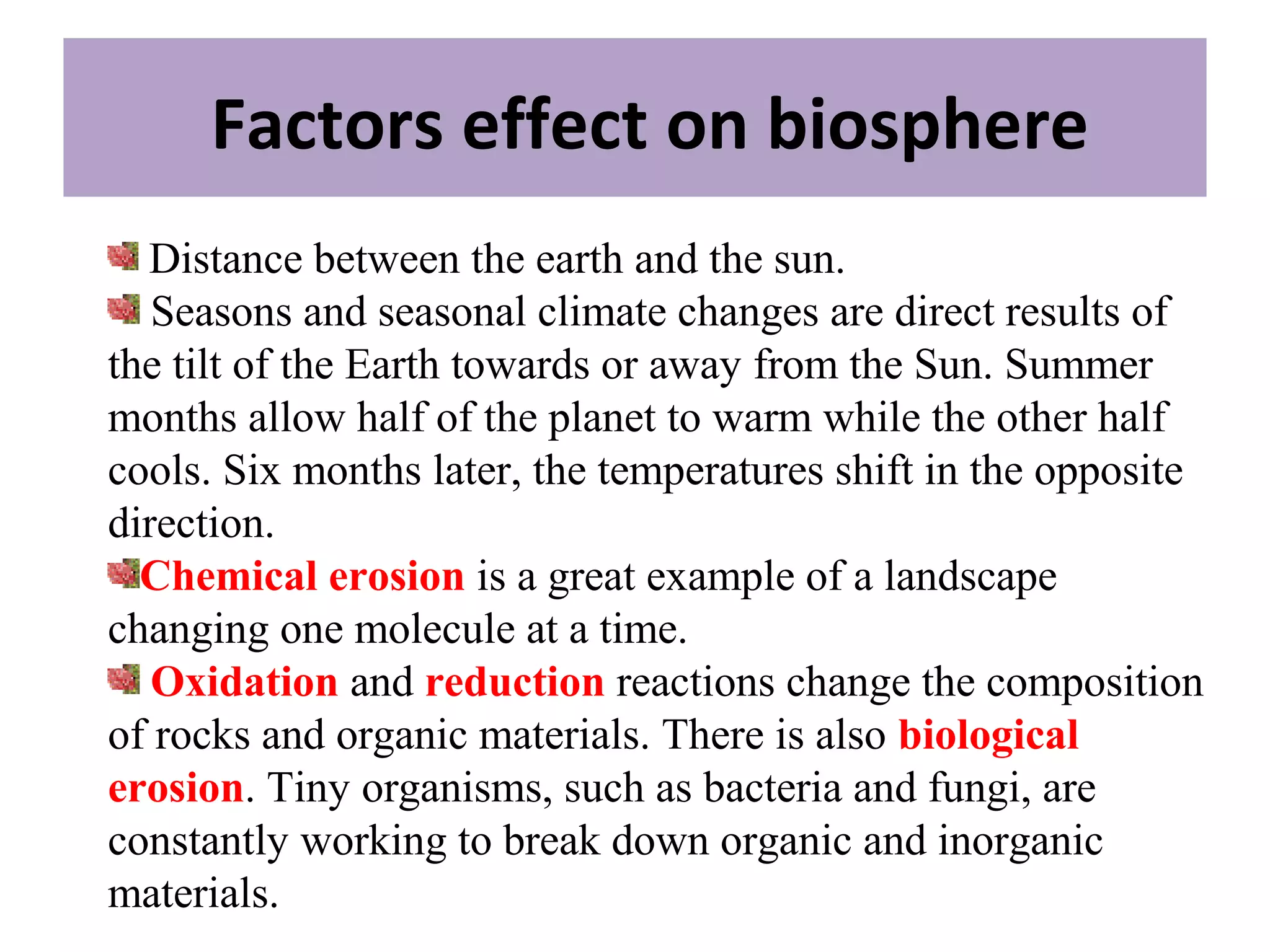
The document discusses the biosphere, which is defined as the global sum of all ecosystems and the zone of life on Earth. It originated from the work of Charles Darwin and Matthew Maury in the 1920s. The term "biosphere" was coined by geologist Eduard Suess in 1875 to refer to the place on Earth where life dwells. The biosphere concept is relevant to many scientific disciplines and examines the physical properties, levels of organization, and factors that affect the biosphere such as the distance between Earth and the sun and chemical and biological erosion.