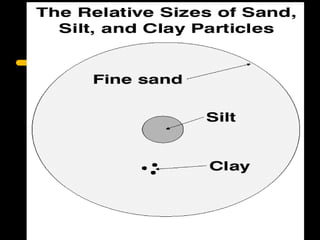
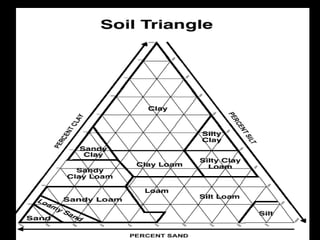
Soil texture is determined by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in a soil. It affects properties like water holding capacity, permeability, workability, and plant growth. Texture can be determined through lab testing or the ribbon test. Soil structure refers to how the soil particles clump together, forming peds, and is important for tilth, permeability, and resisting compaction. Structure forms through processes like freezing/thawing and is strengthened by clay and organic matter. There are eight primary soil structures that vary in appearance.